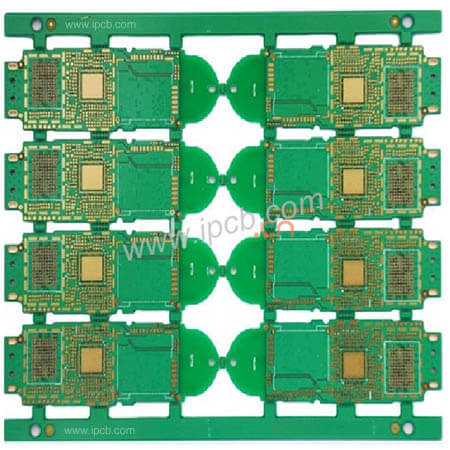
Name: 6-layer 1-stage HDI mobile phone motherboards
Base:FR-4
Layer:6L
Stacking structure:1+N+1 HDI
Finished board thickness: 1.0m
Copper Plating Thickness: 1oz (35 μ m)
Surface Finish: Chemical Gold
Minimum line width/spacing: 3/3 mil (75 / 75 μ m)
Hole Diameter: Laser Hole = 0.1mm, Mechanical Hole = 0.2mm
Application: Mobile phone motherboards
Definition of HDI board:
HDI (High Density Interconnection) means High Density Interconnection, which is usually characterised by high wire density and finer wiring than ordinary PCBs,and the presence of microvias (commonly known as blind vias, with apertures <125um) in multi-layer,high-precision printed circuit boards.The stacking structure of HDI is commonly known as the circuit board laminating and adding layers to the piping diagram,also known as the machine structure. Usually, for the same number of layers of PCBs, different stacks will go through different processes.
The number of times the HDI has been through the laser is usually referred to as the stage, with one stage being called PULLS I, and the second stage being called PULLS II, and so on.
Build-up method in HDI board:
The so-called build-up printed circuit board (build-up printed circuit board) is the use of overlapping piping layer by layer of circuit assembly to form a three-dimensional structure of the HDI circuit board. The circuit boards formed by the build-up method have a much higher density of holes between the upper and lower layers of circuits than conventional printed circuit boards, which effectively increases the circuit density of the boards.
In fact, the concept of layered circuits is not a new technology. As early as the 1970s, when the development of transistor process technology began, the concept of layering has been used to form multi-layer layered structures on silicon wafers, such as aluminium wires and polyimide insulating layers.
Nowadays,the concept of layering has been applied to the substrates used in current wafer packaging technology.Since the 1970s, the development of chip packaging modules for mainframe computers has been based on the use of layer-building circuit board technology,which involves the formation of copper wires and polyimide insulation layers on a ceramic substrate.The ceramic substrate has an additive insulating layer, and the wires above and below the insulating layer can be routed through peg holes and laminate tubes to encapsulate wafers on the substrate. In the area around the wafer, there are copper and polyimide additive circuits.The thermal conduction module is an example of a typical high-density layered HDI circuit board.
Positional Bit Accuracy of HDI board:
In addition to the dimensional accuracy of the wires, the biggest technical issue in the production of fine line HDI circuit boards is the accuracy of the positional bit matching. Because high-density HDI boards must be assembled with high-density components, these encrypted operations make it more difficult to align the boards' relative geometries. For example, the position of the drilled holes must be matched with the exposure of the wiring, while the image of the solder mask must be matched with the image of the wiring. These matching actions are all positional accuracy issues in circuit board manufacturing, and are also important technological issues typically faced in high-density HDI pcb board manufacturing.
The impact of HDI boards on accuracy:
Generally speaking, the substrate material used to make a circuit board is an important determinant of positional accuracy.This is because the PCB material itself is a mixture of various materials.Especially the main body of the resin material, it will be with the temperature,barbecue time,humidity and other factors and variations. In addition, in the process of processing,if it is necessary to make extended mechanical processing, the size of the antique will be more variations.However,the problem of positional matching has always existed in the production of substrates. After the vias are produced, they still have to go through various wet processes to achieve the energy-conducting function of the vias.The line etching process releases much of the stress accumulated in the previous process,and if a special process is used that requires the addition of a burn-in, then the overall variation is even greater.
The effect of the negative on accuracy:
Regarding the negative, regardless of the material and form of the negative used, and given that most circuit boards are still produced using flat-plate contact production piping,the negative is another factor that has to be discussed in terms of dimensional accuracy of the alignment. Most adhesive film backing sheets are almost impossible to use for higher precision boards because of their poor dimensional stability. However, for small quantities of substrates where high efficiency is not a concern, there are some manufacturers who use smaller substrate feed sizes to overcome the alignment problem. For the majority of mass producers, how to utilise the large size of the alignment mode of production is still an important technical issue in the production of fine line substrates.
Influence of tools and materials on accuracy:
For the stability of accuracy of production tools and materials,controlling the source of the material is an important control issue. This includes the supplier's stability of material production, quality control capability, type of material used, grade of production machinery,cleanliness,stability of polymerisation, etc.Many factors will affect the subsequent dimensional change of the tool and material. In particular, in the selection of substrates, special attention must be paid to the stable quality of the fibre cloth supply, the stability of the substrate manufacturer's coating and operation control capabilities, and the dimensional stability of the pressed substrate boards. These problems often occur outside of the substrate manufacturer, and once the material enters the production line, the room for improvement is very limited.
Basically, a simple analysis of the alignment itself is based on only two important materials, one of which is that the stability of the production tools and product dimensions must be high; otherwise, large variations will cause random changes in the variability, and there is no possibility of matching the dimensions at all.The second is the alignment programme during the alignment process,which generally represents the control capability of the exposure machine.
In the part of the mechanical alignment, since the main alignment accuracy almost entirely depends on the control ability of the alignment system,the producer must have an in-depth understanding of the use of the exposure system alignment capabilities.At present, most exposure systems used for mounting boards use a four-target alignment system to improve the overall fit.
Currently, most automatic exposure systems use solid-state cameras to read the images of the alignment targets of the negative and the substrate,and then use the programme to calculate the difference as the basis for correcting the position.
However,the problem of positional matching has always existed in the production of substrates.After the vias are produced,they still have to go through various wet processes to achieve the energy-conducting function of the vias.The line etching process releases much of the stress accumulated in the previous process, and if a special process is used that requires the addition of a burn-in,then the overall variation is even greater.
iPCB ® is a professional high-precision PCB circuit board R & D and production of manufacturers, mass production of 4-46 layer pcb boards, circuit boards, high-frequency boards, high-speed boards, high-frequency boards, IC packaging boards, transistor test boards, multi-layer circuit boards, hdi boards, mixed voltage boards, high-frequency circuit boards, rigid-flexible boards, and so on.
Name: 6-layer 1-stage HDI mobile phone motherboards
Base:FR-4
Layer:6L
Stacking structure:1+N+1 HDI
Finished board thickness: 1.0m
Copper Plating Thickness: 1oz (35 μ m)
Surface Finish: Chemical Gold
Minimum line width/spacing: 3/3 mil (75 / 75 μ m)
Hole Diameter: Laser Hole = 0.1mm, Mechanical Hole = 0.2mm
Application: Mobile phone motherboards
iPCB Circuit provides support for PCB design, PCB technology, and PCBA assembly. You can request technical consultation or quotation for PCB and PCBA here, please contact email: sales@ipcb.com
We will respond very quickly.