In today's rapidly changing semiconductor industry, glass substrates, as a high-performance packaging material, are gradually becoming the new favorite of the industry. Its unique physical properties and advanced packaging potential make it play an increasingly important role in the manufacture of microelectronics and MEMS devices.
1. Characteristics and advantages of glass substrates
Glass substrates, also known as glass through-hole substrates, are a technology that realizes three-dimensional interconnection of electronic components by implementing a series of precision processes on high-quality borosilicate or quartz glass, such as drilling, seed layer sputtering, electroplating filling, chemical mechanical planarization (CMP), redistribution (RDL) and bump extraction. This technology not only improves the performance of the device, but also shows excellent performance in terms of flatness, packaging density, electrical properties and thermal properties.
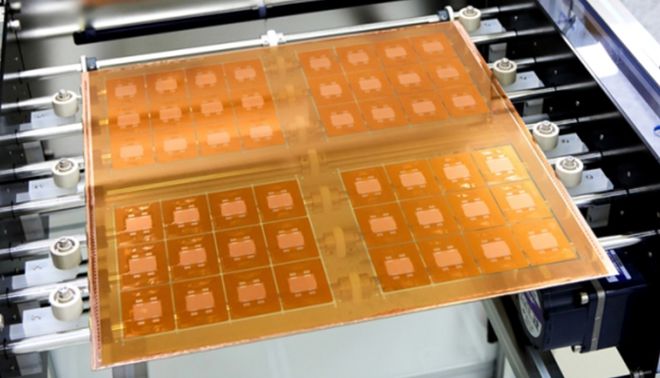
High flatness and low roughness: Glass substrates have extreme flatness and low roughness, which optimizes the focus depth of lithography and thus improves the interconnection density between chips.
Excellent thermal stability: Glass substrates can maintain stable performance in high temperature environments, and their thermal expansion coefficient is close to that of silicon, which reduces stress problems caused by thermal mismatch and helps solve the problem of 3D-IC stacking distortion.
Low dielectric loss: Glass is an insulator material with a dielectric constant of only about 1/3 of that of silicon, and a loss factor 2 to 3 orders of magnitude lower than that of silicon, which ensures the integrity of the transmitted signal.
2. Application fields of glass substrates
Glass substrates are widely used in the field of semiconductor packaging, mainly including the following aspects:
1) Replacement of FC-BGA substrates and silicon interposers: Compared with FC-BGA substrates, glass substrates can increase the placement of bare chips by about 50%, and their thickness can be reduced by nearly half. At the same time, as a new type of interposer material, glass substrates can not only carry a variety of chips such as processors, memory, sensors, etc., but their low dielectric loss characteristics also help to reduce the size of passive components.
2) High I/O density 2.5D interposer: Glass can achieve high I/O density interposers, thereby optimizing connectivity in complex devices.
3) RF and millimeter wave substrates: The dimensional stability, flatness and low loss characteristics of glass make it an ideal core material for RF applications.
4) Photonic substrates: Glass helps to achieve efficient optical functions and signal transmission, and is the foundation of photonic technology.
5) MEMS and sensor packaging substrates: Glass provides a precise and reliable platform for MEMS and sensor packaging.
3. Glass substrate industry chain structure
The glass substrate industry chain covers multiple links in the upstream, midstream and downstream:
Upstream: Mainly focused on the production of semiconductor-grade materials, such as the preparation of special glass raw materials, and the production of special plating solutions, etching solutions and other chemicals. In addition, it also includes the research and development of layered film materials and the manufacture of various processing equipment, among which semiconductor processing equipment is particularly critical.
Midstream: It is the production of glass substrates, which involves multiple complex process flows and has extremely high technical requirements. This includes key links such as hole forming, hole filling, and wiring. Among them, hole forming technology pursues high efficiency, low cost and large-scale mass production; the key to hole filling technology lies in breakthroughs in electroplating solutions and electroplating processes; wiring technology ensures the stability and accuracy of circuit connections.
Downstream: Pay attention to the performance of glass substrates in various applications. At present, HPC and AI chips, integrated passive components (IPD), scenarios with strict requirements for temperature tolerance (such as edge computing and industrial Internet of Things), and RF devices are all regarded as potential important application areas for glass substrates.
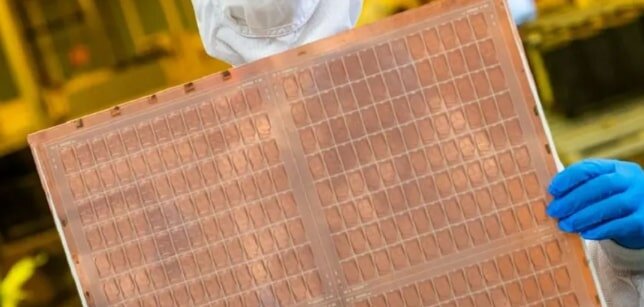
4. Development prospects of glass substrates
With the rapid development of fields such as artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC), the requirements for chip performance are increasing. Glass substrate technology is ushering in unprecedented development opportunities with its excellent physical properties and advanced packaging potential. Major semiconductor companies around the world, such as Intel and Samsung, are actively deploying glass substrate technology. Intel announced that it will mass-produce glass substrates in 2030 and has invested US$1 billion in the Arizona plant to establish a glass substrate R&D line and supply chain. Samsung has formed a united front of Samsung Electronics, Samsung Display, and Samsung Electro-Mechanics to enter the research and development of glass substrates. In addition, more and more leading companies including BOE and TSMC have also begun to actively explore glass substrate technology.
However, the development of the glass substrate industry also faces some challenges, such as high technical barriers and manufacturing costs. However, with the continuous advancement of technology and the gradual reduction of costs, glass substrates are expected to be used in a wider range of fields, injecting new vitality into the development of the semiconductor industry.
As a rising star in semiconductor packaging, glass substrates have become the focus of industry attention due to their unique characteristics and wide application prospects. With the continuous advancement of technology and the continuous expansion of the market, glass substrates are expected to play an increasingly important role in the semiconductor industry.