Underfill process is a commonly used process in the manufacture of electronic equipment, its main role is to fill the gap at the bottom of the electronic product to improve the stability and safety of the product.
The reason why the underfill is needed after the flip chip welding is completed is mainly because there are the following problems in the flip chip assembly:
① There are differences in thermal expansion coefficients between different materials, resulting in thermal stress;
② Bending deformation may occur, which may lead to component failure;
③ Susceptibility to failure due to drop, impact or mechanical vibration;
④ Under the action of static loads, such as the heat generated when the heat sink is working, it may lead to the degradation of component performance or failure;
⑤ In order to improve the service life of the component under thermal cycling conditions, bottom filling is required to enhance its reliability.
Chip underfill process steps
Pre-preparation
Selection of glue: Choose a suitable underfill glue, usually epoxy resin-based, with good fluidity, toughness and strength. According to the characteristics of the glue, it may need to be preheated or thawed to ensure that the use of the best condition.
Equipment check: Prepare the dispenser, heating equipment and other necessary tools to ensure that the equipment operates normally. The dispenser should have thermal management function to keep the glue temperature stable.
Motherboard/chip pre-treatment stage
Baking treatment: Bake the motherboard or chip to ensure that the surface is dry to prevent bubbles when filling. Baking temperature and time depend on the material and requirements.
Preheating operation: preheat the motherboard or chip to improve the fluidity of the bottom filler adhesive for easy filling. The preheating temperature is controlled at 40~60℃ to avoid high temperature damage to the motherboard or chip.
Dispensing and filling process
Dispensing operation: Use the dispenser to dispense the underfill adhesive at the designated position on the chip or motherboard according to the predetermined path and amount. When dispensing, the amount of glue, path, waiting time and angle and other parameters should be strictly controlled to ensure the filling effect.
Filling operation: using the capillary effect and other methods, the bottom of the filler adhesive naturally diffuse and fill the gap between the chip and the substrate. Avoid air bubbles during the filling process to ensure that the filling is uniform and without leakage.
Curing
Heating curing: put the filled chip or motherboard into the heating equipment, high temperature baking to accelerate the epoxy resin curing. The curing temperature and time depends on the characteristics of the bottom filling adhesive.
Quality Inspection: After curing is completed, the filling effect is inspected to ensure that the glue is filled evenly and without defects, such as bubbles, overflow or incomplete curing. Inspection methods include destructive tests (e.g. cutting and grinding) and non-destructive tests (e.g. X-ray inspection) to ensure that the filling effect meets the design requirements and quality standards.
Subsequent Treatment Stage
If other subsequent processing is required (e.g. welding, testing, etc.), this should be carried out after ensuring that the underfilled adhesive is fully cured.
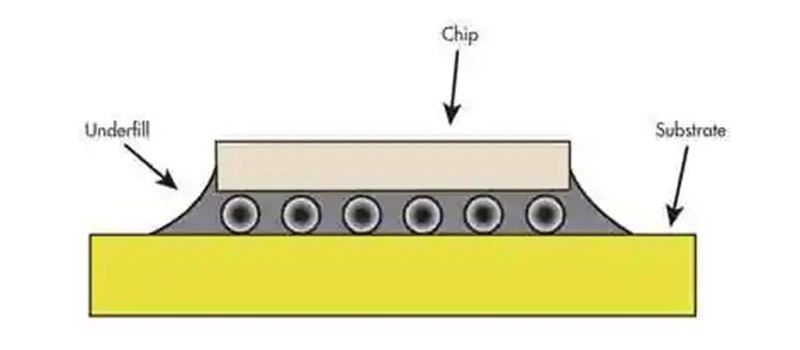
Advantages of the underfill process:
(1) Enhances the robustness of the solder joints and thus extends the life of the product;
(2) Provide environmental protection for the solder joints and enhance the corrosion resistance of the product;
(3) Reduce the thermal stress between the chip and the substrate, and enhance the product's thermal cycle resistance;
(4) Strengthen the bonding force between the chip and the substrate, and improve the impact and vibration resistance of the product.
Disadvantages of the underfill process:
(1) Increases the cost and complexity of the package, requiring the investment of additional equipment and material resources;
(2) Underfill materials and parameters must be carefully selected to ensure that they match the characteristics of the chip and the substrate, preventing failures such as residual stress, cracks, corrosion, and voids;
(3) Once the package is complete, it is difficult to repair or rework, and the underfill must be removed before the solder joints can be inspected or replaced;
(4) It is possible to adversely affect the electrical properties of the chip, such as causing signal delay, crosstalk, noise and other problems.
Underfill process has an important role in the manufacture of electronic equipment, although it brings certain challenges, but its advantages are obvious. In practical application, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the advantages and disadvantages of the process, and reasonably choose to use it to ensure product stability and reliability.