When we get a PCB board, the most intuitive thing that appears in front of us is its color. Common PCB board colors include green, black, blue, red, yellow, etc. What are the requirements for PCB boards of different colors?
Green PCB
Green PCB is the most common and cheapest on the market. Why? The main reasons are as follows:
Green is less irritating to the eyes. Since childhood, teachers have told us that green is good for the eyes, protects the eyes, and resists fatigue. Production and maintenance personnel are not prone to eye fatigue when staring at PCB boards for a long time, and the damage to the eyes is less.
2. Low cost. Since green is the mainstream in the production process, the purchase volume of green paint will naturally be larger, and the purchase cost of green paint will be lower than that of other colors. At the same time, using the same color paint in mass production can also reduce the cost of line change.
3. When the board is SMT soldered, it must go through tinning and patching and the final AOI verification. These processes all require optical positioning calibration. The green background color is better for the instrument's recognition effect.
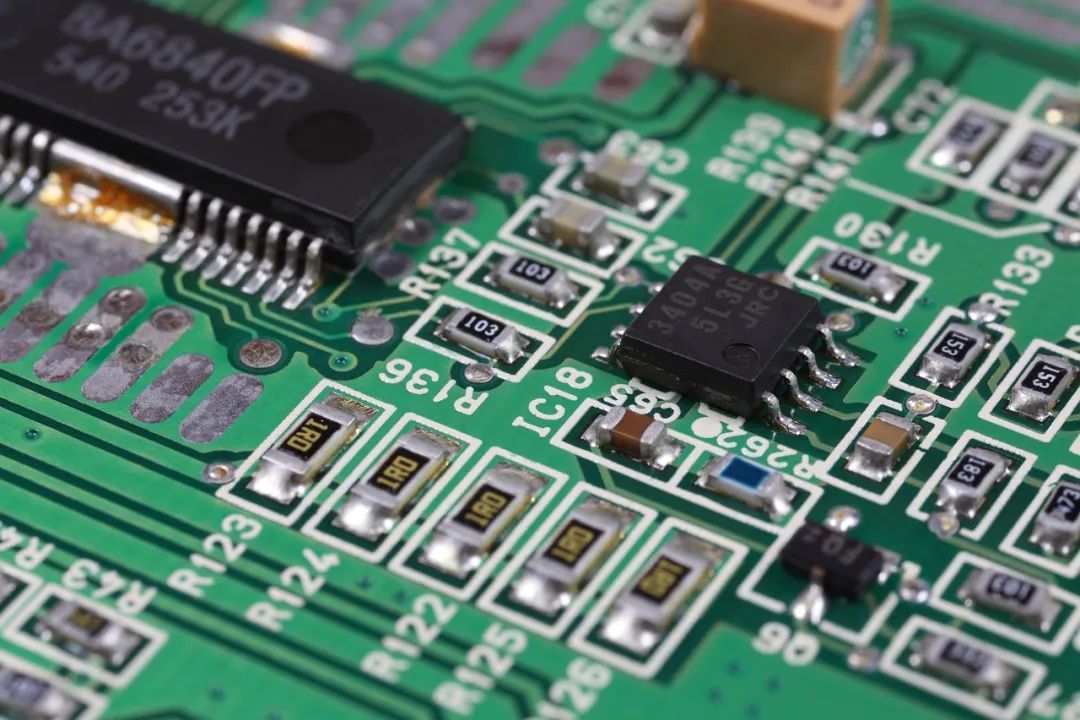
Green PCB
Black PCB
Some people think that black PCBs represent high-end, but in fact this perception is incorrect. The reason why "color represents high-end or low-end" is that manufacturers like to use black PCBs to manufacture high-end products and use red, blue, green, yellow, etc. to manufacture low-end products. In addition, black PCBs are not very convenient to manufacture and use because their surface traces are almost completely covered, which makes later repairs very difficult. Moreover, black PCBs have the highest difficulty in holes, so the yield rate is relatively lower than other color PCBs, so the price of black is relatively more expensive.
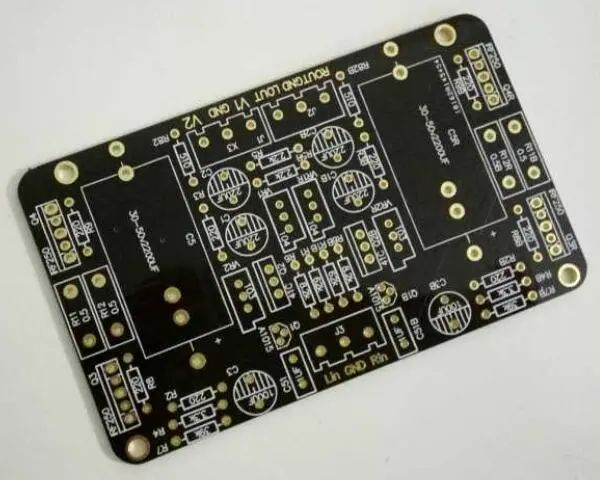

Black PCB
Blue PCB
Blue circuit boards perform outstandingly in precision manufacturing, high-frequency applications and brand differentiation scenarios. Their core value lies in balancing producibility, reliability and user experience. When choosing, you need to weigh the cost and specific needs. For example, consumer electronics may prefer blue to enhance the selling point, while large quantities of low-end products still tend to traditional green.
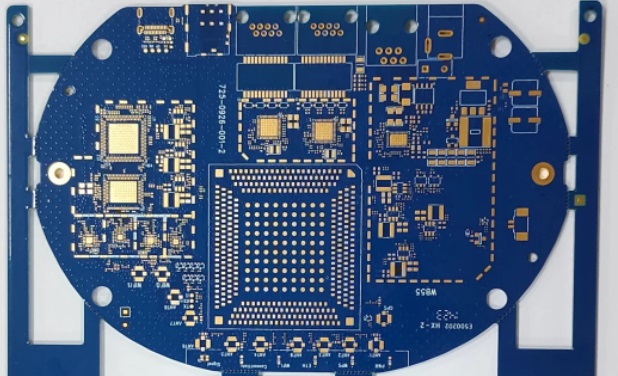
Blue PCB
1. Visual and production optimization
(1) High contrast detection: The contrast between the blue background and the white silk screen (about 70% or more) is better than that of green, which is convenient for manual visual inspection and AOI equipment to identify minor defects (such as cold solder joints).
(2) Reduce glare: Under long-term operation, blue can relieve visual fatigue better than bright green, and is suitable for debugging high-density wiring boards (such as industrial control motherboards).
2. Brand and user experience
(1) Blue symbolizes a sense of technology and is often used in high-end products (such as ASUS ROG motherboards and DJI drone control boards) to enhance brand recognition.
(2) In open mid-range devices (such as RGB computer hardware), blue PCBs can coordinate with lighting effects and enhance aesthetics.
3. Special application adaptability
(1) UV protection: Some blue inks contain anti-ultraviolet additives and are suitable for outdoor equipment (such as solar inverters).
(2) Customized needs: The military or aerospace fields may use specific blue solder mask layers to distinguish functional modules (such as RF and power supply areas).
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are usually composed of pads, vias, solder mask, silk screen, copper wires, and various components. Among them, the solder mask refers to the part of the printed circuit board that is to be painted green. As we have already learned from the previous introduction, solder mask ink is not only green, but also red, yellow, blue, purple, black, etc., but green is the most common. The role of the solder mask:
(1) Prevent physical disconnection of the conductor circuit;
(2) Prevent short circuits caused by bridges during the welding process;
(3) Only weld the parts that must be welded to avoid solder waste;
(4) Reduce copper contamination of the welding tank;
(5) Prevent insulation deterioration and corrosion caused by external environmental factors such as dust and moisture;
(6) It has high insulation, making it possible to increase the density of the circuit.
The difference between PCBs of different colors lies in the different colors of solder mask applied at the end. If the PCB design and manufacturing process are exactly the same, the color will not have any effect on performance or heat dissipation.