Teflon PCB, alternatively known as PTFE PCB, denotes a printed circuit board that utilizes polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) as its substrate material. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), often nicknamed the "king of plastics," is a high-molecular-weight compound resulting from the polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene, with the chemical formula (C₂F₄)ₙ.
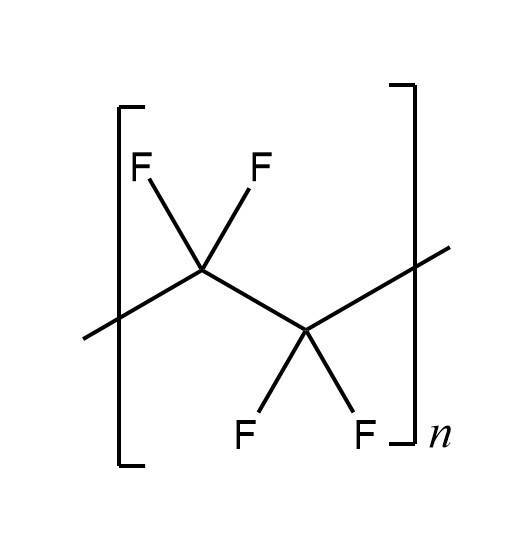
Figure1:Chemical molecule diagram
Teflon exhibits excellent comprehensive performance, encompassing high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, non-stick properties, self-lubrication, superior dielectric properties, and an extremely low friction coefficient. When applied to printed circuit boards (PCB), Teflon PCB stands out as a high-performance, high-frequency material, making it highly suitable for applications in radar systems, high-frequency communication equipment, radio equipment, and other related fields.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Figure 2: Teflon PCB diagram
Teflon PCB products are widely used in situations with high signal transmission requirements or harsh environmental conditions, including communication equipment such as satellite communications and mobile phone base stations, RFID tags, readers and other radio frequency identification systems, automotive electronics such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), aerospace flight control systems and industrial high-temperature equipment control circuits in high-temperature environments, as well as medical devices such as electrocardiographs and ultrasound equipment.
Communication Field
5G base stations: RF front-end modules and antenna arrays utilize Teflon PCBs to minimize signal loss, improving coverage and communication capacity.
Satellite communications: Applied to core components such as communication repeaters, they ensure high-speed data transmission and precise positioning.
Microwave communications: They facilitate efficient signal transmission in radar transceiver modules, thereby improving detection accuracy.

Figure 3:Application examples of Teflon PCBs in 5G base stations
Aerospace Field
Aircraft avionics system: High temperature stability and lightweight characteristics support flight control, navigation, and communication systems, ensuring stable operation in extreme environments.
Missile guidance system: High-speed transmission and improved anti-interference performance enhance hit accuracy and combat effectiveness.

Figure 4:Teflon PCBs in aircraft avionics systems
Automotive electronics field
ADAS system: The ability to resist electromagnetic interference is applied to sensors such as millimeter-wave radar to ensure accurate signal processing.
Electric vehicle power system: The battery management system (BMS) and motor controller utilize high-power processing characteristics to optimize safety and driving range.

Figure 5: Teflon PCBs in automotive ADAS system
Medical equipment field
Medical imaging equipment: Signal loss characteristics improve image resolution and diagnostic accuracy in devices such as MRI and CT.
Implantable devices: Biocompatibility and chemical stability ensure the long-term safe operation of implants such as pacemakers.
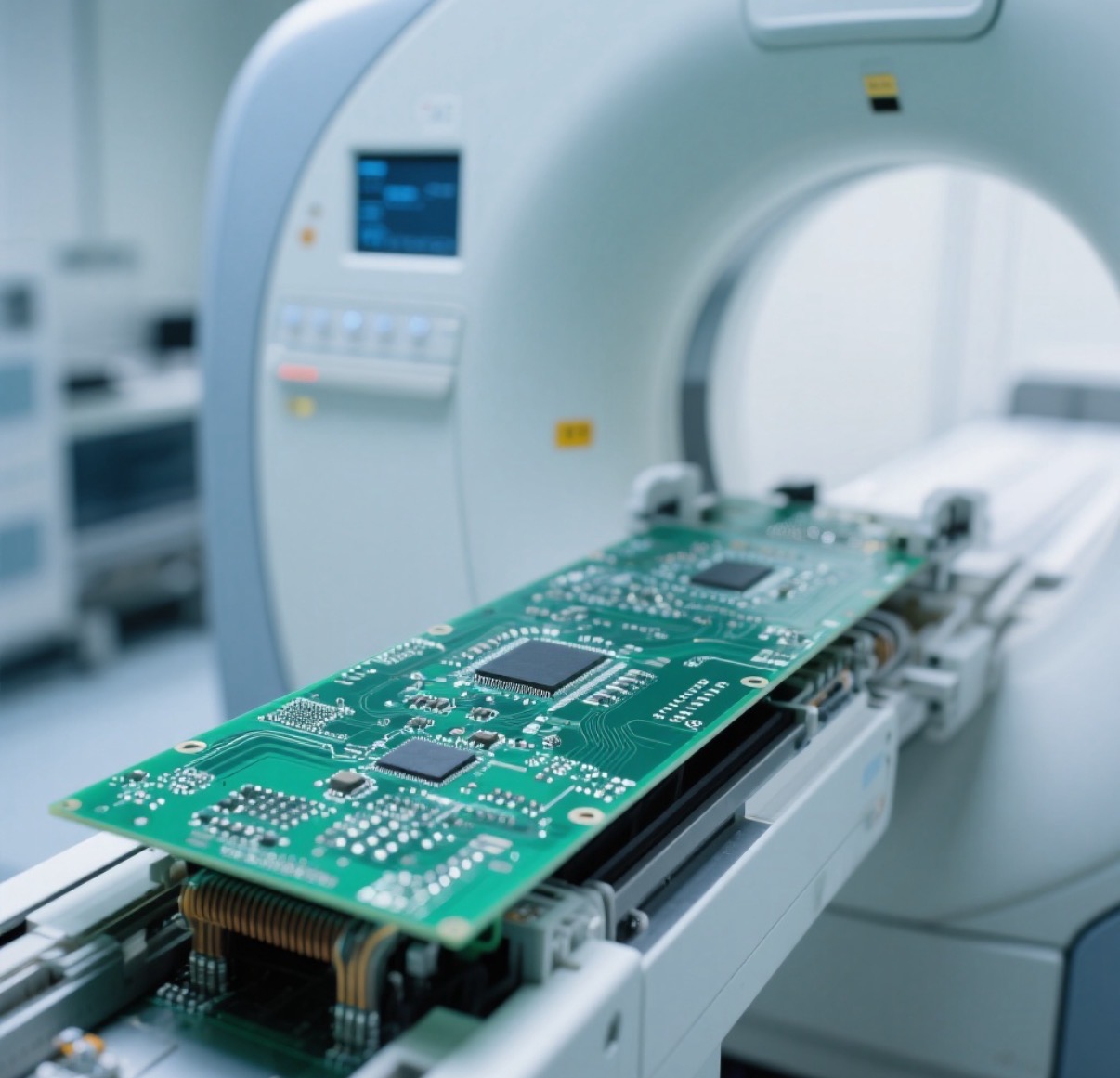
Figure 6: Application of Teflon PCBs in MRI equipment
Industrial control field
Automated production line: High-speed signal transmission capability supports robot control systems, enabling precise motion control.
High-temperature industrial environment: The high-temperature resistance characteristic is utilized for sensor connections in industries such as steel smelting, ensuring stable data collection under high temperatures.
Despite the numerous advantages of Teflon PCB, their manufacturing process poses certain challenges compared to traditional PCB materials.
1. Difficulty of material processing
The high lubricity and low surface energy of Teflon may lead to delamination and tearing during processing. Solutions include:
Use diamond-coated cutting tools; Optimize cutting parameters (reduce speed, increase feed rate) to reduce stress
2. Copper foil bonding issue
The chemical inertness of Teflon results in poor adhesion to copper foil. Common enhancement methods include:
Surface roughening treatment (such as sodium etching) to enhance mechanical engagement; Electroless plating to enhance surface activity
3. Welding process challenges
The non-stick property poses difficulties for welding, thus necessitating:
Special soldering flux; Optimize parameters (increase temperature, extend welding time); Use silver-containing solder to improve wettability
Generally speaking, manufacturers rarely use Teflon sheets. However, with the continuous advancement of technology, the demand for high-performance PCBs in electronic devices will continue to grow. Teflon PCBs, with their unique material properties and broad application prospects, will play a more important role in future electronic technology. The F4B series Teflon PCB laminates, in particular, meet the needs of multiple industries at a lower price, offering significant advantages and making them an excellent choice for Teflon PCBs. IPCB has many years of experience in processing Teflon PCB products and offers a variety of Teflon PCBs from well-known brands, such as Rogers Teflon PCBs and Taconic Teflon PCBs. We can process both Teflon PCBs and Teflon + FR4 multilayer hybrid PCBs. We also have an ample supply of Teflon PCBs to meet your needs quickly. IPCB's products are used in various industries and have earned an excellent reputation.