The demand for high-performance electronic devices has steadily increased in recent years. This has led to the miniaturization of circuit boards and a surge in the heat generated by these compact devices. Effective heat management is critical to ensuring the reliability and longevity of electronic components. One key solution that has become indispensable in managing heat dissipation is the circuit board heatsink.
1. The Role of PCB Heatsink
A heat sink is a thermal management component designed to dissipate heat generated by electronic components like integrated circuits (ICs), power transistors, or other heat-sensitive components. Without proper heat dissipation, components can overheat, leading to thermal stress, performance degradation, or even failure.
In circuit boards, heat sinks help maintain temperature within safe operating limits by conducting, convecting, or radiating heat away from the components into the surrounding environment. The ultimate goal is to reduce the risk of overheating while allowing the system to operate efficiently.
Key Functions of Heat Sinks:
Thermal Dissipation: Heat sinks absorb heat from high-temperature components and release it to cooler surroundings.
Preventing Thermal Damage: By maintaining safe operating temperatures, heat sinks prevent thermal-induced damage to circuit board components.
Maintaining Performance: Components like CPUs, GPUs, and power transistors can operate more efficiently under optimal temperatures. Heat sinks help stabilize the performance of the device.
2.Importance of Heat Sinks in Modern Electronics
Modern electronic devices are more compact, power-dense, and feature-rich than ever before. From smartphones to computers, these devices consist of densely packed electronic components, which leads to significant heat generation.
The role of heat sinks becomes more pronounced as electronics evolve, for several key reasons:
a.Component Protection
Excess heat can negatively impact a component's electrical properties, leading to malfunction or even permanent failure. Circuit Board Heat sinks reduce the risk of these issues, extending the lifespan of the components.
b.Performance Optimization
Electronic components tend to operate more efficiently when kept at a stable temperature. This is particularly important in high-performance systems such as servers, gaming consoles, and data centers, where thermal stability is key to maintaining performance levels.
c.Power Efficiency
Devices with proper heat management tend to use energy more efficiently. Reduced energy losses due to heat dissipation contribute to a device's overall energy efficiency, which is particularly important in modern applications where power consumption is a key concern.
d.Reliability and Durability
Devices that manage heat effectively tend to have fewer breakdowns and reduced wear and tear. This leads to increased reliability and a lower chance of premature failure.
3.Types of Circuit Board Heat Sinks
There are various types of heat sinks used in circuit boards, each designed for specific applications and heat dissipation requirements. The main types include:
a.Passive Heat Sinks
These heat sinks rely on natural convection to dissipate heat. They are made from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper, which allow heat to flow away from the heat source. Passive heat sinks have no moving parts, which makes them reliable and low-maintenance, but they may not be sufficient for high-power applications.
b.Active Heat Sinks
Active heat sinks use fans or other mechanisms to improve heat dissipation. The addition of airflow increases the rate of heat transfer, making active heat sinks more effective at managing higher power levels. However, they are more complex and may introduce issues like noise or the need for periodic maintenance.
c.Thermal Interface Materials (TIM)
TIMs are used in conjunction with heat sinks to improve thermal contact between the component and the heat sink surface. Materials like thermal paste, pads, or adhesives fill in microscopic gaps that may reduce heat transfer efficiency. This ensures that the heat sink can function optimally.
d.Liquid Cooling Heat Sinks
In more demanding applications where high heat loads are generated, liquid cooling systems are used. These systems circulate coolant through a heat exchanger, allowing for efficient heat dissipation. While more expensive and complex, liquid cooling is often necessary for gaming PCs, supercomputers, or high-power industrial applications.
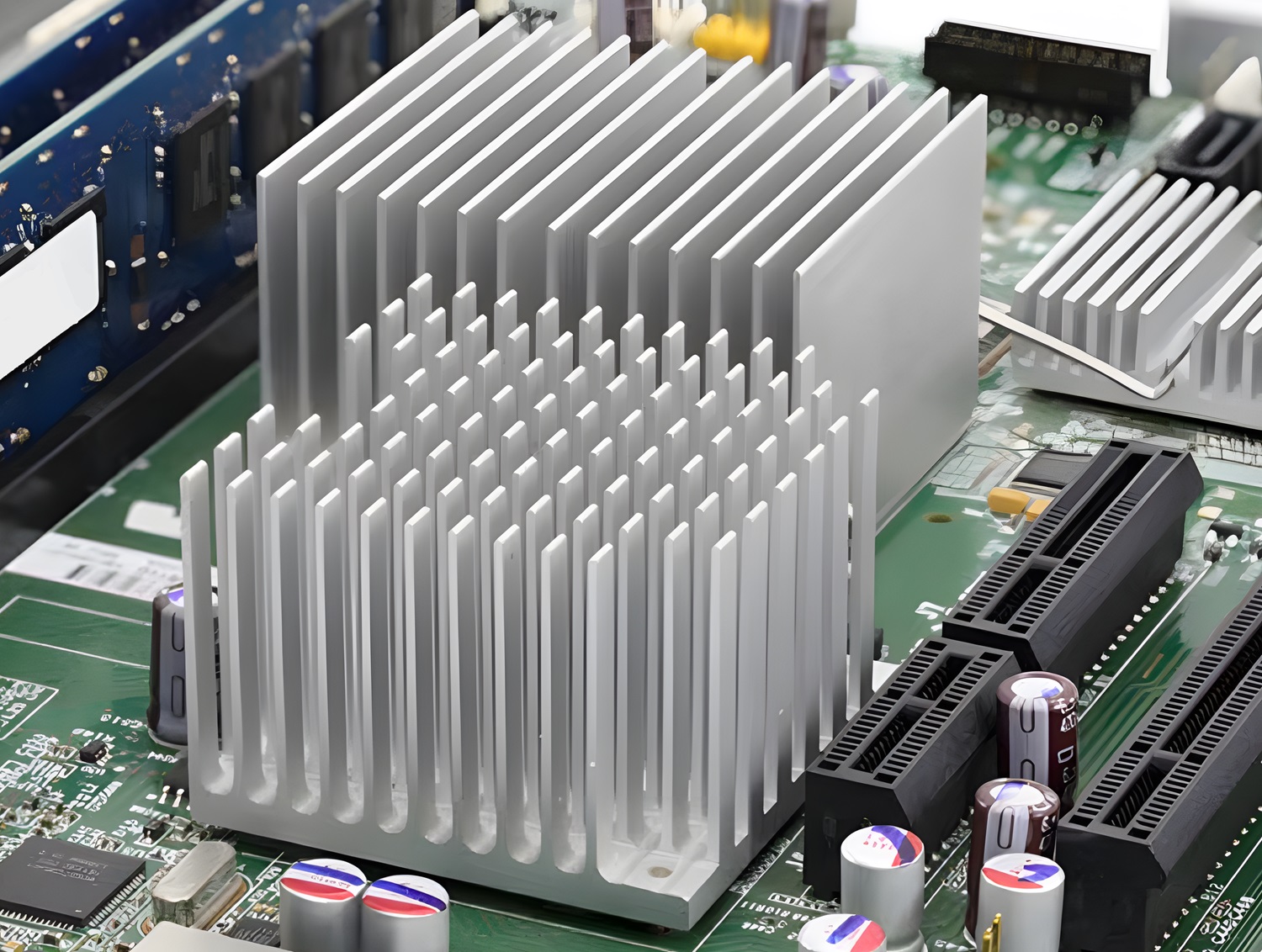
4. Materials Used in Heat Sinks
The performance of a pcb heatsink depends heavily on the materials used in its construction. The most commonly used materials for heatsinks are:
a.Aluminum
Aluminum is a widely used material for heat sinks due to its excellent thermal conductivity, lightweight nature, and affordability. Its relatively lower cost makes it ideal for mass production, and it is easy to fabricate into various shapes and sizes.
b.Copper
Copper offers superior thermal conductivity compared to aluminum. It is more efficient in transferring heat, making it a preferred material for high-performance applications. However, copper is more expensive and heavier, which can be limiting factors in some designs.
c.Graphite
Graphite-based heat sinks are becoming more common due to their excellent thermal conductivity and lightweight properties. They are often used in applications where weight savings and space constraints are critical.
d.Ceramics
Some specialized applications may require ceramic heatsinks, which offer good thermal conductivity while being electrically insulating. These heat sinks are used in situations where electrical isolation is required.
5.Design Considerations for Heat Sinks
Designing an effective heat sink for a circuit board involves balancing multiple factors. These include:
a.Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance is the measure of how well a heat sink can transfer heat. The lower the thermal resistance, the more efficient the pcb heatsink.Designers must carefully calculate the thermal resistance based on the heat load and required dissipation.
b.Surface Area
A larger surface area allows for greater heat dissipation.Fins,pins,or other structures are often added to increase the surface area without making the heatsink too bulky.
c.Airflow
For both passive and active heat sinks,ensuring adequate airflow is critical for optimal performance. Designers need to consider the airflow paths on the circuit board and the surrounding components to ensure the heat sink works efficiently.
d.Form Factor
The physical size and shape of the pcb heatsink must be compatible with the circuit board design. Compact electronics may have limited space for heat sinks,requiring custom designs or innovative solutions to fit within the available space.
6. Applications of Circuit Board Heat Sinks
PCB heatsinks are used in a wide range of electronic devices, each with unique heat dissipation requirements. Some common applications include:
a. Computers and Servers
In computers, heat sinks are essential for cooling processors (CPUs and GPUs) that generate large amounts of heat during operation. High-performance servers use advanced cooling systems with multiple heat sinks to manage thermal loads.
b. Telecommunications
In telecommunications equipment, heat sinks help dissipate heat from power amplifiers and other components in base stations or network infrastructure. Maintaining proper cooling is critical to avoid signal degradation or component failure.
c. Power Electronics
Power electronics, such as converters, inverters, and motor drives, rely on heat sinks to manage heat from power transistors, diodes, and other high-power components.
d. Automotive Electronics
Modern vehicles feature numerous electronic systems, from infotainment to engine control units (ECUs), which require effective heat dissipation to maintain reliability, particularly in harsh environments.
e. Consumer Electronics
Consumer products like smartphones, gaming consoles, and wearable devices use heat sinks to manage heat generated by processors and batteries. Miniaturization and efficient heat management are crucial for these devices’ performance.
7. Conclusion
Circuit board heat sinks play a vital role in ensuring the reliable operation of modern electronic devices. From protecting components from thermal damage to optimizing performance, their importance cannot be overstated. With advancements in material science and heat sink design, electronic systems are becoming more efficient in managing heat, ensuring they can meet the increasing demands of modern technology.
In conclusion, as devices become more power-dense and feature-rich, effective heat management solutions like circuit board heat sinks will continue to be a crucial factor in maintaining system stability and prolonging device lifetimes.