With the increasing importance of RF PCB technology and products, RF PCB circuit boards have also experienced rapid development. One important aspect is selecting data with low dielectric constant and low dielectric loss factor, which is an important performance engineering for achieving high-speed RF PCB circuit boards. We discussed the loss of substrate data and explained their relationship with the external environment, in order to reasonably and correctly evaluate and use various substrate data in PCB manufacturing.
There are currently three main types of commercialized high-frequency boards: polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) sheets; Thermosetting PPO (polyphenylene oxide) cross-linked polybutadiene substrate and epoxy resin composite substrate. It remains constant and small with temperature and frequency changes, approaching the thermal expansion coefficient of copper foil, and has therefore been widely used. The substrates made of polytetrafluoroethylene, glass fiber, and ceramics, such as the RO3200, RO3210, RO4350B and RO4003C series, meet the requirements of dielectric constant of 2.2-10.8 and operating frequency range of 30 MHz~30 GHz. Despite the rapid development of PTFE microwave board manufacturing, the technology suitable for PTFE microwave board manufacturing has been improved based on the traditional FR-4 printed circuit board manufacturing process.
At present, the rapid development of electronic information products, especially microwave devices, the significant increase in integration, as well as the requirements for digitization, high frequency, multifunctionality, and special environmental applications, pose challenges to the universal PTFE high-frequency board and manufacturing processes In response to the high-speed and high-frequency characteristics of microwave PCB, two technological approaches are mainly adopted: on the one hand, the development of high-density wiring micro lines and spacing, micro hole diameter, thinness, high conductivity reliability, and insulation. This can further shorten the signal transmission distance and reduce its transmission loss.
On the other hand, substrate data with high-speed and high-frequency characteristics should be used. The implementation of the latter requires a deeper understanding of such substrate data by the industry, and research work to identify and master accurate control over substrate data. The process method aims to achieve a reasonable match between the selection of substrate data and the manufacturing process, performance, and cost requirements.
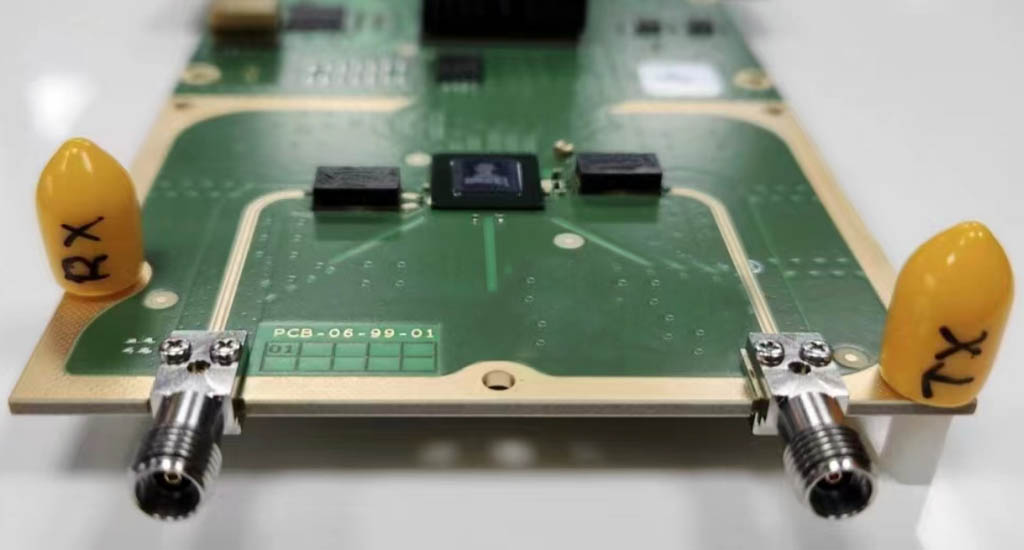
RF PCB circuit board application
Electroplated copper is the most widely used pre coating made to improve the adhesion of coatings. Copper coatings are an important component of the copper/nickel/chromium system for protective and decorative coatings. Flexible and low porosity copper coatings play an important role in improving the adhesion and corrosion resistance between coatings. Copper plating is also used for local anti-seepage carbon, metallization of printed circuit board holes, and as a surface layer for printing rollers. The colored copper layer after chemical treatment, coated with organic film, can also be used for decoration. In this article, we will introduce common problems and solutions of copper plating technology in RF PCB circuit board process.
Common problems in acid copper electroplating
Copper sulfate electroplating plays an extremely important role in RF PCB circuit board electroplating. The quality of copper electroplating directly affects the quality and related mechanical properties of the electroplated copper layer, and has a certain impact on subsequent processing. Therefore, how to control the quality of copper electroplating is an important part of RF PCB circuit board electroplating, and it is also one of the difficult processes for many large factories to control.
The common problems with acid copper electroplating include the following:
1. Rough electroplating.
2. Electroplating pits.
3. Electroplating (RF PCB board surface) copper particles.
4. The RF PCB circuit board surface appears white or uneven in color.
A summary has been made regarding the above issues, along with a brief analysis of solutions and preventive measures.
1. Rough electroplating
Generally, the rough corners of the board are mostly caused by excessive electroplating current. You can lower the current and use a multimeter to check for any abnormalities in the current display; The whole board is rough and usually does not appear, but I have encountered it once at a customer's place. Later, it was found that the temperature was low in winter and the content of the light agent was insufficient; Sometimes, similar situations may occur when the surface of some reworked peeling film boards is not cleaned properly.
2. Copper particles on the electroplated surface
There are many factors that can cause the formation of copper particles on the surface of RF PCB circuit boards, including the entire process of copper deposition, pattern transfer, and electroplating copper itself. I have encountered copper particles on the surface of Rogers circuit boards caused by copper deposition in a state-owned large factory.
The copper particles on the surface caused by the copper deposition process may be caused by any one of the copper deposition processing steps. Alkaline degreasing, when the water hardness is high and there is a lot of drilling dust (especially for double-sided circuit boards without removing adhesive residue), not only causes surface roughness but also roughness inside the holes due to poor filtration. However, it usually only causes roughness inside the hole, and slight point like dirt and erosion on the surface can also be removed; There are several main situations of micro corrosion: the quality of the micro corrosion agent used is too poor, such as hydrogen peroxide or sulfuric acid, or the impurities in ammonium (sodium) persulfate are too high. It is generally recommended that it should be at least CP grade. In addition, industrial grade can also cause other quality failures. The slow precipitation of copper sulfate crystals is caused by high copper content in micro etching grooves or low temperature. The tank liquid is turbid and contaminated.
The activation solution is mostly caused by pollution or improper maintenance, such as leakage of the filter pump, low specific gravity of the tank solution, and high copper content (the activation cylinder has been used for too long, more than 3 years), which will produce granular suspended solids or impurity colloids in the tank solution, adsorbed on the plate surface or hole wall, accompanied by roughness in the hole. Gelling or acceleration: If the tank solution is used for too long, it may become cloudy because most of the current solution is prepared with fluoroboric acid, which will attack the glass fibers in FR-4, causing an increase in silicates and calcium salts in the tank solution. In addition, the addition of copper content and tin dissolution in the tank solution will cause the production of copper particles on the surface of the plate.
The main reasons for the copper plating tank itself are the high activity of the tank solution, dust generated by air agitation, and a large number of suspended small particles in the tank solution. This can be effectively solved by adjusting process parameters, adding or replacing air filter cartridges, and filtering the entire tank. After copper deposition, temporarily store the copper plate in a dilute acid tank, and keep the tank solution clean. If the tank solution becomes turbid, it should be replaced in a timely manner. The storage time of the copper plate should not be too long, otherwise the surface of the plate is prone to oxidation, even in acidic solutions, and the oxide film is more difficult to remove after oxidation, which will also produce copper particles on the surface. The copper particles on the RF PCB circuit board surface caused by the copper deposition process mentioned above are generally evenly distributed and have strong regularity on the RF PCB circuit board surface, except for those caused by surface oxidation. The pollution generated here, whether conductive or not, will cause the production of copper particles on the electroplated copper plate surface. When processing, some small test boards can be used to handle and compare them step by step. For on-site faulty boards, a soft brush can be used to gently brush them to solve the problem; Graphic transfer process: Developing excess adhesive (which can also be coated and wrapped during ultra-thin film electroplating), or cleaning after development is not clean, or the board is left for too long after graphic transfer, causing varying degrees of oxidation on the board surface, especially when the Rogers circuit board surface is poorly cleaned or stored in a workshop with heavy air pollution. The solution is to strengthen water washing, enhance planning and scheduling, and increase the intensity of acid oil removal.
The pre-treatment of the acid copper plating tank itself generally does not cause copper particles on the RF PCB circuit board surface, as non-conductive particles can cause leakage or dents on the Rogers circuit board surface at most. The reasons for copper particles on the surface of the plate caused by copper cylinders can be roughly summarized into several aspects: maintenance of tank liquid parameters, production operations, material and process maintenance. The maintenance of tank parameters includes high sulfuric acid content, low copper content, low or high tank temperature, especially in factories without temperature controlled cooling systems, which can cause a decrease in the current density range of the tank. According to normal production processes, copper powder may be generated in the tank and mixed into it.
In terms of production operations, excessive current, poor clamping plates, empty clamping points, and the dissolution of boards in the slot against the anode can also cause some boards to have excessive current, resulting in copper powder falling into the slot solution and gradually leading to copper particle faults. In terms of materials, the main issues are the phosphorus copper corner phosphorus content and the uniformity of phosphorus distribution. In terms of production maintenance, it mainly involves major processing. When adding copper corners, they fall into the tank, mainly during major processing, such as anode cleaning and anode bag cleaning. Many factories cannot handle them well and there are some hidden dangers. The copper ball treatment should clean the surface thoroughly and use hydrogen peroxide to slightly etch the fresh copper surface. The anode bag should be soaked in sulfuric acid hydrogen peroxide and alkaline solution successively to clean thoroughly, especially the anode bag should use a 5-10 micron gap PP filter bag.
3. Electroplating pits
This defect also causes multiple processes, ranging from copper deposition, pattern transfer, to pre-treatment before electroplating, copper plating, and tin plating. The main cause of copper deposition is poor long-term cleaning of the copper deposition basket. During micro corrosion, contaminated liquid containing palladium copper will drip from the basket onto the surface of the plate, forming pollution. After electroplating the copper deposition plate, it will cause point like plating leakage or pits. The graphic transfer process is mainly caused by poor equipment maintenance and development cleaning, due to various reasons: contamination of adhesive stains by the brush roller suction stick of the brush plate machine, drying of the internal organs of the air knife and fan in the drying section, oil stains and dust, improper dust removal before film coating or printing on the board surface, unclean development of the developing machine, poor water washing after development, and contamination of the Rogers circuit board surface by silicon containing defoamers. Pre electroplating treatment, because both acidic degreasers, micro corrosives, pre immersion, and tank solutions mainly consist of sulfuric acid, when the water hardness is high, turbidity and surface pollution may occur; In addition, some companies have poor adhesive coating on their hanging equipment, and over time, it may be found that the coating dissolves and spreads in the tank at night, contaminating the tank solution; These non-conductive particles are adsorbed on the surface of the board, which may cause varying degrees of electroplating pits for subsequent electroplating.
4. The RF PCB circuit board appears white or uneven in color
The acid copper electroplating tank itself may have the following aspects: the drum tube deviates from its original position, and the air agitation is uneven; The filter pump leaks air or the inlet is close to the air duct to suck in air, producing fine air bubbles that are adsorbed on the surface or edges of the board, especially at the horizontal edges and corners of the line; In addition, there may be another point that the use of low-quality cotton core is not thoroughly treated, and the anti-static treatment agent used in the manufacturing process of cotton core pollutes the bath solution, resulting in leakage of plating. In this case, the air blowing can be increased, and the liquid level foam can be cleaned up in time. After the cotton core is soaked in acid and alkali, the Rogers PCB surface is white or uneven in color: mainly due to gloss or maintenance problems, sometimes it may also be cleaning problems after acid degreasing, and micro corrosion problems. Copper cylinder photocatalyst imbalance, severe organic pollution, and high tank liquid temperature may all cause it. Acidic degreasing generally does not have cleaning problems, but if the pH value of the water is acidic and there is a lot of organic matter, especially in recycled water washing, it may cause poor cleaning and uneven micro corrosion; Micro etching is mainly considered when the content of micro etching agent is too low, the copper content in the micro etching solution is too high, and the temperature of the groove solution is low, which can also cause uneven micro etching of the plate surface. In addition, the quality of the cleaning water is poor, the washing time is slightly long, or the pre immersed acid solution is contaminated. After treatment, the surface of the board may have slight oxidation. During copper plating, due to acidic oxidation and the charged board entering the tank, the oxide is difficult to remove, which can also cause uneven color of the board. In addition, RF PCB circuit boards that come into contact with anode bags, uneven anode conductivity, and anode passivation can also cause such defects.
High frequency circuit board
Here are some common issues in the acidic copper plating process summarized. At the same time, the acidic copper plating process is widely used due to its simple solution composition, stable solution, high current efficiency, and the addition of appropriate brighteners to obtain coatings with high brightness, leveling, and uniform plating ability. The quality of acidic copper plating layer also depends on the selection and application of acid copper brightener. Therefore, we hope that the staff can accumulate experience in their daily work, not only to discover and solve problems, but also to innovate and fundamentally improve the technological level of high-frequency circuit boards.