High frequency circuit board Rogers RO4003C and Rogers RO4350B parameters do not know which one is better? Today iPCB introduced the parameters of Rogers RO4003C and Rogers RO4350B high-frequency PCB in detail.
For high-frequency PCB design engineers, there are more choices for high-frequency PCB materials than ever before. Each high-frequency PCB material has its own advantages and disadvantages. It is difficult to choose the most suitable PCB material without carefully comparing various parameters of high-frequency PCB materials. By comparing the main parameters of Rogers microwave boards RO4003C and RO4350B, ipcb can help circuit design engineers understand and choose the most suitable board.
The main parameters of Rogers RO4003C and Rogers RO4350B are shown in the figure below.
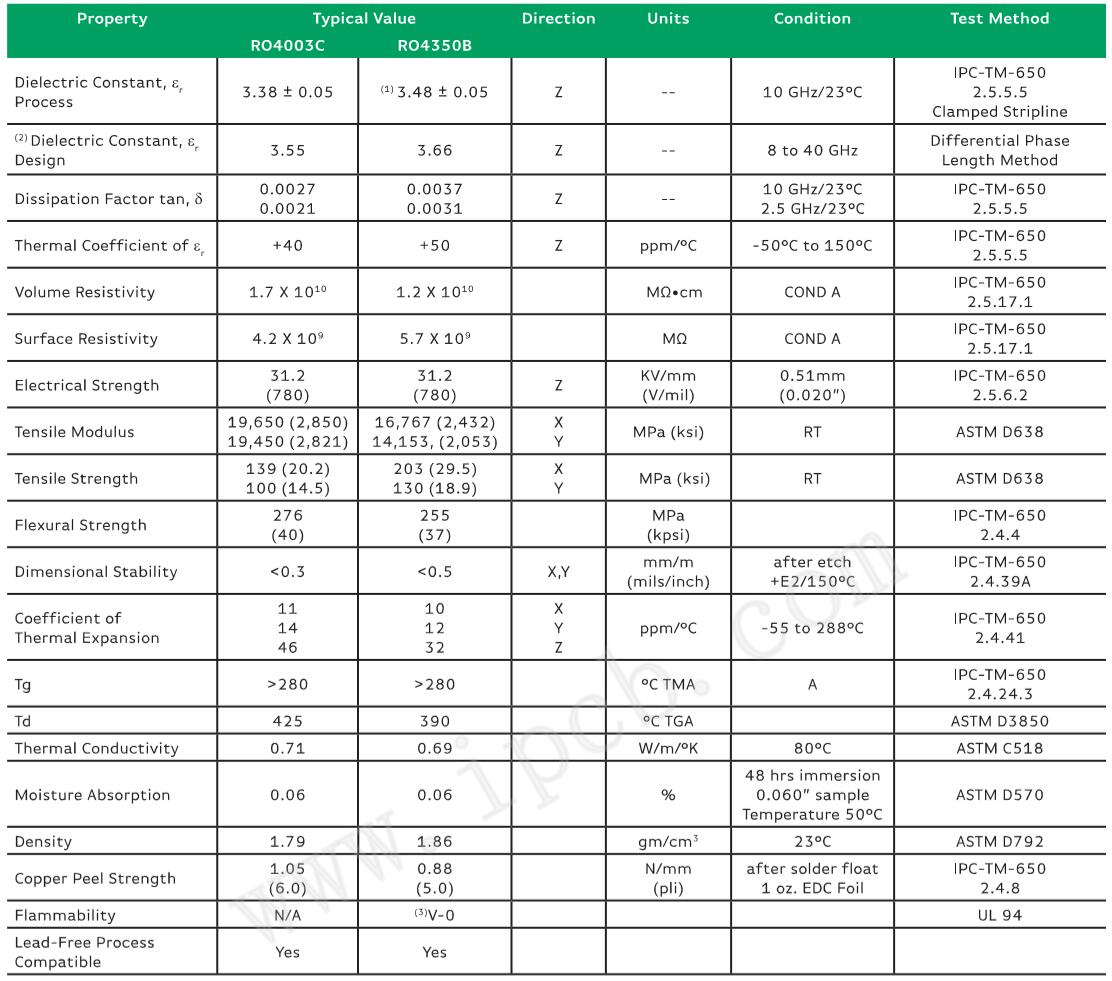
Rogers RO4003C and Rogers RO4350B Parameters
When PCB design engineers choose a PCB board, the first thing they care about is whether the operating frequency of the board meets the requirements. In addition, the dielectric constant also affects the line width of the transmission line or matching line. The smaller the DK, the wider the transmission line. Line widths for materials with different dielectric constants need to be recalculated or simulated.
Dissipation factor DF
Without considering the influence of other factors, the smaller the loss factor, the smaller the signal loss during transmission. The loss factors of RO4003C and RO4350B are both very low, and the transmission line loss of RO4350 is larger than that of RO4003C. When the system gain design margin is tight, choosing RO4003 with a smaller dissipation factor can reduce the transmission loss of the dielectric board.
Ɛr Thermal stability factor
Changes in temperature will cause changes in the dielectric constant. Through the thermal stability coefficients of Rogers RO4003C and Rogers RO4350B, the dielectric constants of the two plates at a certain temperature can be estimated to determine whether they are within an acceptable range. The lower the absolute value of the Ɛr thermal stability coefficient, the more stable the dielectric constant is within the operating temperature range.
Thermal expansion coefficient
Changes in temperature will inevitably lead to changes in the physical dimensions of the board. For PCBs, the copper layers (including vias) and dielectric materials are pressed together at room temperature. As the temperature changes, copper and the medium will produce different thermal expansion coefficients, which will inevitably produce temperature stress. When the temperature stress exceeds the carrying capacity of the copper layer, the dielectric, or the bond between the copper layer and the dielectric, the PCB will be damaged. Z-axis temperature stress can cause metallized vias to break; repeated stress in the X/Y axis can cause the copper layer to tear or the bond between the copper layer and the dielectric to loosen. During the sheet processing process, due to etching shrinkage (baking after etching), the thermal expansion coefficient is different,
The thermal expansion coefficient of copper is about 19ppm/℃, and the thermal expansion coefficient of RO4003C and RO4350B is similar to that of copper. The values of the X/Y/Z axis are 11/14/46 (PPM/℃) and 10/12/32 (PPM/℃) respectively. In comparison, RO4003C is closer to the thermal expansion coefficient of copper on the X/Y axis and has better dimensional stability in sheet metal processing; r04350b is closer to the thermal expansion coefficient of copper on the Z axis and can better protect the metal vias。
Water absorption rate
Water absorption indicates the ability of an object to absorb water under normal atmospheric pressure. The higher the water absorption rate, the higher the proportion of water in the medium, and the greater the impact on the medium properties. In high-humidity environments, it is more suitable to choose RO4003C sheets with low water absorption.
Of course, when selecting a board, in addition to the above main indicators, other performance indicators of the board should also be considered according to the actual application environment, such as copper foil peeling strength, thermal conductivity, flame retardant grade, lead-free process, cost, etc., to fully understand the actual application environment and the meaning of various parameters of the board, so as to choose the most suitable board.
The above is a parameter comparison between RO4003C and RO4350B. If you have any other questions, please consult iPCB. iPCB specializes in the development and production of various high-frequency PCBs, high-frequency hybrid PCBs and Rogers PCBs.