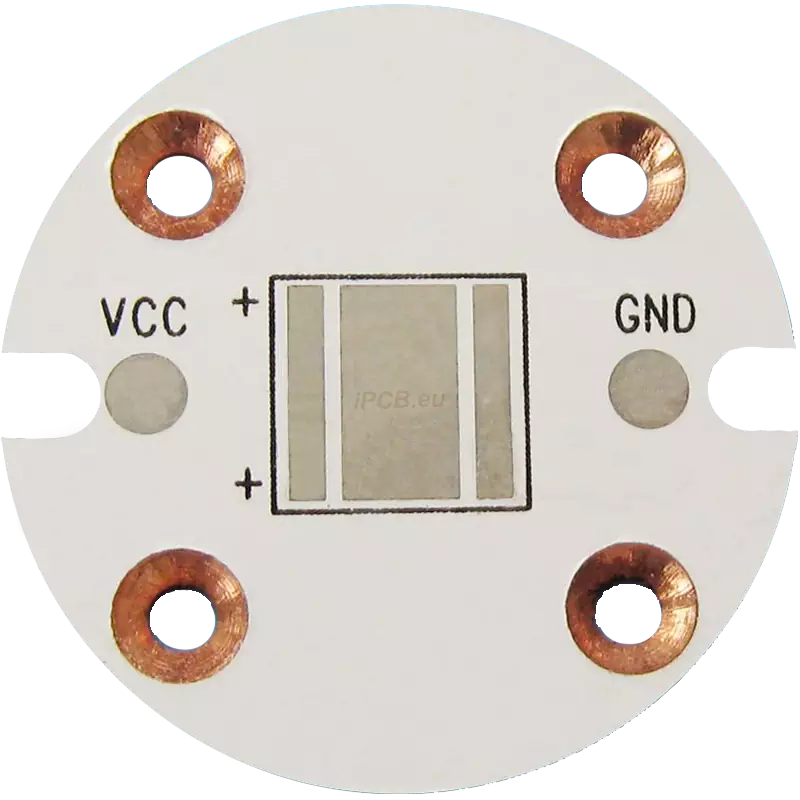
Product: Countersink Hole Copper PCB
Material: Copper substrate
Layer: 1
Color: White/Black
Finished thickness: 1.6mm
Copper thickness: 2oz
Surface treatment: HASL
Minimum line width: 10mil
Minimum spacing: 10mil
Thermal conductivity: 3W/mK
Application: High power LED lighting
What is Countersink Hole? Countersink Hole, also known as Counterbore Hole, is a stepped hole, funnel hole, or horn hole. Usually used when the head of a flat head screw is required to be located below the surface of the part. There is a horn shaped opening on one or both sides of the circuit board. The hole is conical and moves away from the center of the plate as the diameter increases. When fixed on the PCB, this horn shaped opening provides clearance for fastener heads such as screws or bolts. Countersink Hole solves the problem of how to sink the fixed screw holes on the PCB.
The Countersink Hole provides a conical opening for fasteners, which has significant advantages. The functions of the Countersink Hole are as follows:
1. Consistent fastener head gap: Ensure that the fastener head maintains a consistent gap with the solder pads or traces on the PCB surface.
2. Flatten fastener head: When using flat head screws, the depth of the countersunk hole should make the fastener head flush with the surface of the PCB.
3. Smooth surface finish: Provides a continuous surface suitable for EMI shielding, gaskets, and enclosures.
4. No component interference: Provide sufficient clearance between components and fastener heads for easy placement of components.
5. Consistent board level support: The countersunk edges provide consistent edge support for the PCB surface around the fasteners.
6. Improve manufacturability: Simplify the assembly process and allow for certain positioning tolerances.
There are mainly two types of Countersink Holes used in PCB, and the characteristic of Countersink Hole is where the chamfer appears on which side.
The front countersunk hole (sometimes referred to as a "countersunk") has a conical opening on the top layer or component side of the PCB. This allows the fastener head (such as a flat head screw) to be flush with the top surface of the installation component.
The front countersunk hole is the most common and is used in conjunction with any fastener that installs components or hardware onto the top surface of a circuit board. The depth of the sinkhole ensures that the fastener is flush with the outer layer.
The back countersunk hole (sometimes referred to as a "countersunk hole") has a tapered hole opening at the bottom of the PCB. The straight hole wall passes through the plate thickness, and the chamfer is located on the lower side.
The back countersunk allows the fastener head to be flush with the bottom surface. This is very useful when the bottom requires unobstructed fastener contours, such as fixing the PCB on a flat surface. The heat sink also benefits from a flat bottom.
Countersink Hole PCB Design Considerations
1. Depth of countersunk hole: It should match the thickness of the fastener head and leave appropriate clearance.
2. Aperture: It should match the shaft diameter of the fastener and leave appropriate clearance to ensure fixation.
3. Surface diameter: Sufficient clearance must be provided for the fastener head and any washers.
4. Chamfering: The angle between the hole wall and the plate surface affects the head clearance and edge support.
5. Hole pattern: Follow the hole spacing pattern recommended by the fastener manufacturer to avoid circuit board splitting or bending.
6. Electroplating and Non Electroplating: Countersink Holes are usually non electroplated unless used as through holes.
7. Copper clearance: Ensure that all copper on the chamfered surface is removed from the tapered holes to avoid uneven fastener interfaces.
8. Circular ring: Avoid placing pads or marks near Countersink Hole to avoid limiting welding and masking openings.
Product: Countersink Hole Copper PCB
Material: Copper substrate
Layer: 1
Color: White/Black
Finished thickness: 1.6mm
Copper thickness: 2oz
Surface treatment: HASL
Minimum line width: 10mil
Minimum spacing: 10mil
Thermal conductivity: 3W/mK
Application: High power LED lighting
iPCB Circuit provides support for PCB design, PCB technology, and PCBA assembly. You can request technical consultation or quotation for PCB and PCBA here, please contact email: sales@ipcb.com
We will respond very quickly.