With the development and construction of 5G communication, there is an increasing demand for high frequency and high speed circuit boards in the electronic equipment industry. Due to the different environments, high-frequency circuit boards and high-speed circuit boards have a lot of common features and some differences. Combined with the use environment of high-frequency and high-speed circuit boards and the resin system of the boards, this paper describes the respective characteristics of high-frequency circuit boards and high-speed circuit boards, and also looks forward to the future development of high-frequency circuit boards and high-speed circuit boards.
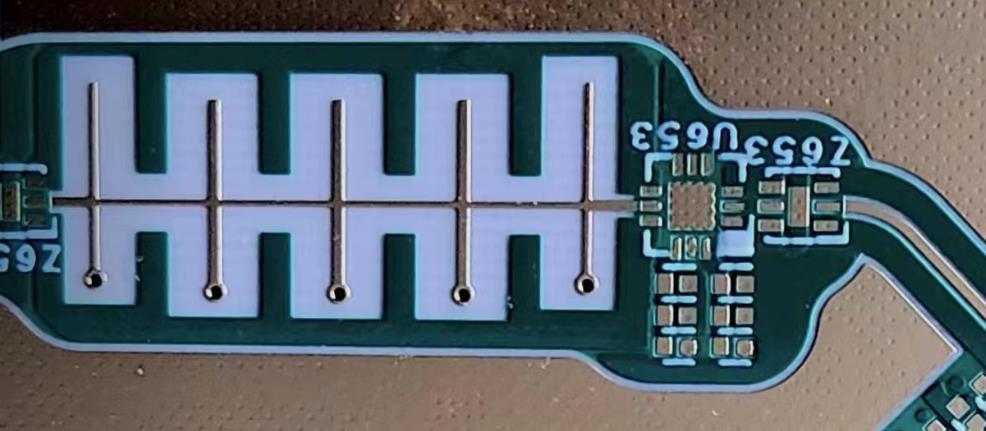
High Frequency Circuit Board
Demand for high-frequency and high speed circuit boards in 5G networks
5G,the fifth generation of mobile communications. Cellular mobile communication has undergone four upgrades from analogue communication (1G) to the now popular LTE (4G). Since 2012, research and testing of 5G networks has progressed rapidly. In the past, from 1G to 4G, the main scenario was person-to-person network communication, while 5G network will meet the interconnection of everything and open up a new revolution of information network. The 5G communication industry chain mainly includes the following five important links:
(1) Network planning and design (preliminary scientific research and network construction planning).
(2) Wireless main equipment (core network, base station antennas, RF devices, optical devices/optical modules, small base stations, etc., and the deployment of wireless support, network coverage and optimisation).
(3) Transmission equipment (wireless equipment followed by wired transmission links, followed by fibre optic cables, system integration, IT support, value-added services, etc.).
(4) Terminal equipment (matching chips to terminals).
(5) Operator.
In addition to the above five important links, the next two links are also very important:
(6) PCB/CCL industrial chain (for base station RF, baseband processing unit, IDC and core network router, etc.).
(7) Dielectric waveguide filters (for BTS RF).
In the process of 5G construction, different industries use different frequency bands for their products, which in turn leads to different requirements for high-frequency and high-speed circuit boards for different products in different industries. It can be seen that 5G network is a comprehensive application of multi-band microwave. Therefore, the choice of high-speed circuit boards and high-frequency circuit boards for products in different industries will be different.
2. Characteristics of high-frequency and high speed circuit boards
2.1 High-frequency and high-speed material dielectric constant and dielectric loss (Dk Df)
Speaking of high-frequency high-speed circuit boards, it is inevitable to talk about two concepts ‘dielectric constant - Dk’ and ‘dielectric loss - Df’. The PCB dielectric layer used for high-speed digital signal transmission not only plays the role of the insulation layer between the conductors, but more importantly, it plays the role of the ‘characteristic impedance’, which also affects the signal transmission rate, signal attenuation and heat generation.
The magnitude of the dielectric loss (Df) indicates the degree of attenuation of the signal transmission. This degradation of signal transmission is often consumed by heat generation. With high-frequency and high-speed digital signal transmission, the signal attenuation and heat dissipation are bound to increase rapidly with the high-frequency and high-speed digital signal transmission. For high-frequency and high-speed digital signal transmission, the smaller the dielectric loss (Df), the better.
In the development of high-speed products and high-frequency products, the dielectric constant (Dk) and dielectric loss (Df) of the sheet are required to develop in the direction of smaller. However, there are still some differences in the demand for plates between high-frequency products and high-speed products.
2.2 High-speed material properties
High-speed products pay more attention to the dielectric loss (Df) of the sheet. The grades of high-speed materials commonly used in the market are also classified according to the size of the dielectric loss (Df). Different substrate materials are classified according to the dielectric loss of the substrate into regular loss, medium loss, low loss, very low loss, and ultra-low loss). There are five corresponding levels of transmission signal loss.
2.3 High-frequency material properties
Compared with high-speed materials,high-frequency materials pay more attention to the size and change of the material's dielectric constant (Dk). High-frequency products are very sensitive to changes in the material dielectric constant (Dk). Therefore, the focus of high-frequency materials is on the stability of the dielectric constant (Dk), as well as the thickness of the dielectric,the temperature drift coefficient of the material, and the flicker efficiency of the material. There is no clear classification standard for high-frequency materials in the industry, but many PCB manufacturers roughly classify high frequency circuit boards according to the material's dielectric constant (Dk). Materials with the same dielectric constant (Dk) are considered similar and can be substituted for each other.
In the field of high frequency materials there is also a common division of materials into PTFE and non-PTFE materials.This is closely related to the application areas of high frequency products. The current RF field can be divided into two parts. One is the frequency below 6GHZ,commonly used frequencies are 3.5GHZ, 2.7GHZ, 1.8GHZ. The main products are power amplifiers,antenna calibrators,arrays and other products. The other part of the millimetre wave field is more than 20GHZ commonly used frequencies are 24GHZ,66GHZ, 77GHZ, the main products are radar products. This is mainly because with the new frequency,non-Polytetrafluoroethylene products flash effect, dielectric loss on the signal transmission of the impact of the sharp increase in the Polytetrafluoroethylene material has a better performance characteristics.
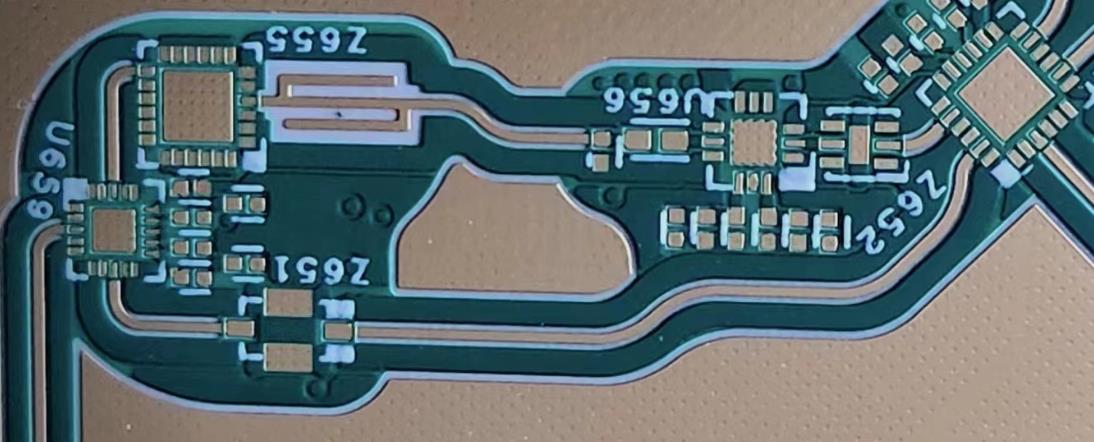
High Frequency Circuit Board
3.High-frequency and high speed circuit board development prospects
Traditional laminate material transmission loss is large, can not meet the requirements of high-frequency signal transmission quality. In this regard, the most important performance of PCB substrate materials used in 5G communications is to meet the requirements of high-frequency and high-speed, as well as integration, miniaturisation, lightweight, multi-functional and high reliability requirements. In particular, resin materials require low dielectric constant (Dk), low dielectric loss (Df), low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) and high thermal conductivity. Currently, rigid laminates represented by polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) thermoplastic materials and hydrocarbon resin (PCH) type thermoset materials occupy the majority of the market for high-frequency/high speed PCB substrates due to their unrivalled low dielectric performance. In recent years, new resin materials such as polyphenylene ether (PPO or PPE), bismaleimide (BMI), cyanoacrylate (CE), triazine resin (BT), benzoxazine (BOZ), and benzocyclobutene (BCB) and related modifications have been used for high-frequency/high-speed PCB substrates.
In addition, the processability of PPO material is much better than that of PTFE material, so nowadays, modified PPO resin is mostly used for Very Low Loss and Ultra Low Loss in high speed circuit boards, such as Panasonic M6, M7N, and IT968, IT988GSE of Lianmao. The resin system for high frequency circuit boards is mainly made of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) thermoplastic materials and hydrocarbon resins (PCH) are the mainstays. Although extremely low dielectric loss (Df) and stable dielectric constant (Dk) can be obtained, the poor processability of the material is not suitable for high-multilayer boards, and even less suitable for the processing of HDI board products. With the development of 5G communication, the PCB complexity of high-frequency products is also increasing (traditional high-frequency PCBs are mainly single- and double-sided, and the development of multi-layer boards even has HDI design requirements) In recent years, material developers have also adopted PPO resin to make high-frequency circuit boards. In recent years, material developers have also adopted PPO resin for high frequency circuit boards to ensure that the boards have extremely low dielectric loss (Df) and stable dielectric constant (Dk), and at the same time, to obtain good PCB processability. For example, the high-frequency circuit boards such as IT-88GMW, IT-8300GA, IT-8350G, IT-8338G, IT-8615G launched by Lianmao are made of a mixture of modified PPO resin and hydrocarbon resin. While meeting the requirements of high-frequency signal transmission, the processability of the material is greatly enhanced.
On the one hand, the development of 5G communications to higher speeds and higher frequencies will inevitably require the material dielectric constant and dielectric loss (Dk Df) to the direction of smaller development. On the other hand, 5G products require miniaturisation and more uniformity corresponding to the PCB will inevitably develop in the direction of high multilayer and even HDI, which requires materials with good processability. At present, whether from the high-frequency circuit boards or high-speed circuit boards, the use of polyphenylene ether (PPO or PPE) resin is a good development direction.