1. PCB (Printed Circuit Board)
A PCB is a board made from insulating materials (such as fiberglass) that is populated with conductive traces used to support and connect electronic components, enabling electrical functionality in electronic devices.
Material: Insulating material
Conductive tracks: Conductive traces
Circuit design: Circuit design

2. PCBA(Printed Circuit Board Assembly)
PCBA refers to the process of mounting electronic components (such as resistors, capacitors, chips, etc.) onto a PCB using SMT or other techniques to form a complete circuit board assembly.
Assembly: Assembly
Component placement: Component placement
Soldering: Soldering
Inspection: Inspection
Testing: Testing
3. SMT (Surface Mount Technology)
SMT is a technology where electronic components are directly mounted onto the surface of a PCB, and it is an essential technique in modern electronic manufacturing.
Surface mounting: Surface mounting
Pick-and-place machine: Pick-and-place machine
Solder paste: Solder paste
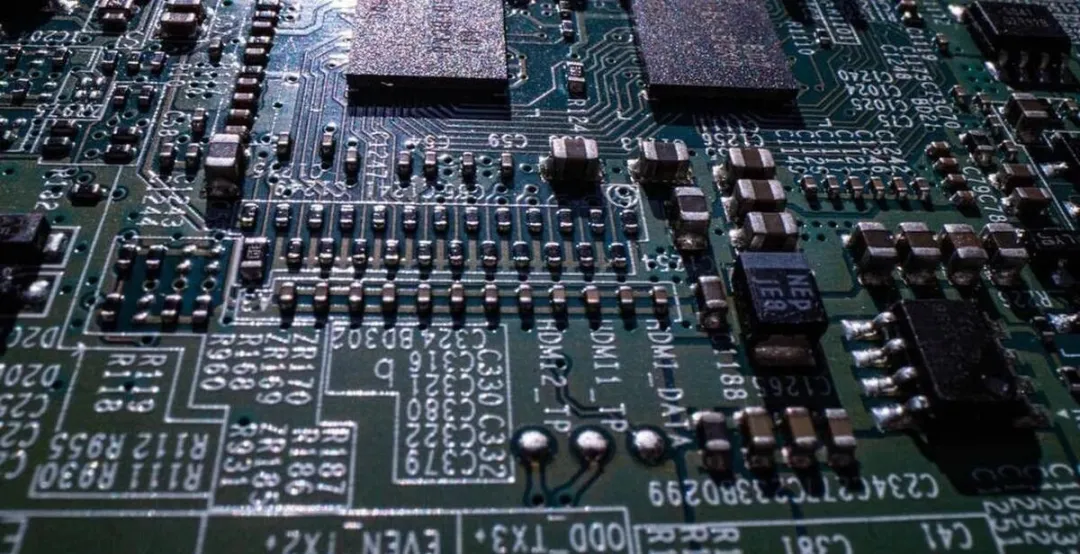
4. Soldering Process
Soldering is the process of ensuring a strong connection between the electronic components and the PCB. It typically involves the use of high temperatures to melt solder paste, forming electrical connections.
Wave soldering: Wave soldering
Reflow soldering: Reflow soldering
Solder joint: Solder joint
5. Inspection and Testing
After soldering, the completed PCBA undergoes rigorous quality checks to ensure the reliability of electrical connections and the correctness of functionality.
Visual inspection: Visual inspection
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
Functional testing: Functional testing
SMT (Surface Mount Technology) is an indispensable technology in modern electronic manufacturing, and PCB and PCBA are the two core elements of this technology.
So, what are PCB and PCBA? What role do they play in SMT? This article will take you to explore it from a professional perspective in a concise and detailed language. (Insert picture)
Let's learn about PCB.
PCB, the full name of which is Printed Circuit Board, is translated into Chinese as printed circuit board.
It is a board made of insulating materials (such as fiberglass) and covered with conductive lines.
These lines connect electronic components together through precise design and processing to achieve the transmission of electrical functions.
In short, PCB is a "motherboard" used to carry electronic components and make electrical connections.
In SMT, PCB is the basis of the entire production process.

First, engineers will design appropriate circuit diagrams according to product requirements, and then convert these drawings into PCB design files.
Next, the factory will make actual PCB boards according to these files.
After these boards have undergone rigorous quality inspection, they will be sent to the SMT production line to prepare for the next step of assembly.
Now, let's focus on PCBA.
PCBA is the abbreviation of Printed Circuit Board Assembly, which means printed circuit board assembly.
As the name suggests, PCBA is a complete assembly that installs various electronic components on the basis of PCB through SMT and other technologies.
This process includes multiple steps such as component placement, welding, and inspection, and finally forms a complete electronic product module. (Insert picture)
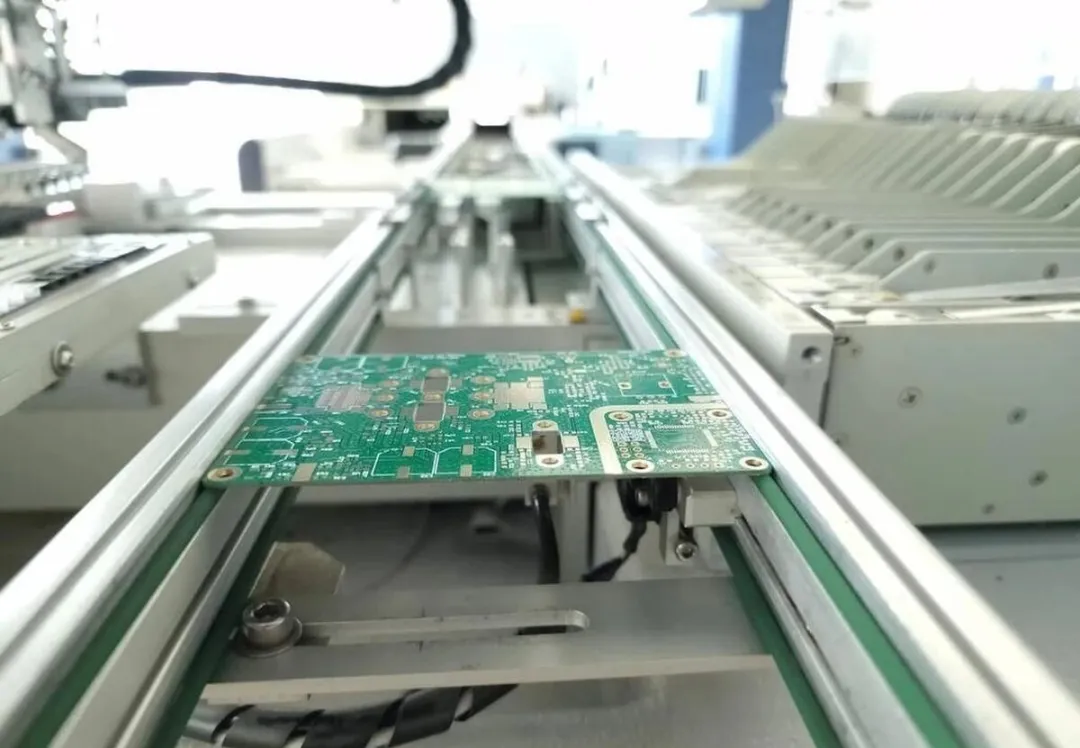
In SMT, PCBA is a key part of the entire production process.
When the PCB board is completed and delivered to the production line, workers will use advanced automation equipment to mount the pre-prepared electronic components one by one on the PCB.
These components can be various types of electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, chips, etc. They are firmly fixed on the PCB through the precise operation of SMT equipment and form a good electrical connection with the conductive lines on the circuit board. (Insert picture)
After the mounting is completed, PCBA will enter the next link-welding.
The purpose of this step is to ensure that the connection between the electronic components and the PCB is stable and reliable.
Through high-temperature hot air or infrared lamps, the solder paste will be melted and filled into the gap between the electronic components and the PCB to form a strong weld.
In this way, the electronic components truly become part of the PCB, and together they constitute a complete electronic device module.
After rigorous testing and inspection to ensure that each PCBA meets quality standards, it can be used for the assembly of the final product.
In this process, PCB, as a basic carrier, provides stable support for electronic components; while PCBA integrates various electronic components to achieve the functions required by the product.
The two complement each other and jointly promote the development and application of SMT technology.
PCB and PCBA play a vital role in SMT.
They are the cornerstone and soul of the field of electronic manufacturing, and are also an important force in promoting the continuous advancement of modern technology.
I hope that through the introduction of iPCB, I can help you better understand these two concepts and their important roles in SMT.