In the modern electronics manufacturing industry, electric assembly is a critical process, encompassing everything from a single PCB (Printed Circuit Board) to the final assembly of a complete product. This link connects design, production, and marketing, and is the ultimate guarantee of product quality and performance.

PCBA
What is electric assembly?
Electrical assembly generally refers to the process of combining electronic components, circuit boards, electromechanical components, and other accessories into a complete product according to design requirements.
From a technical perspective, electric assembly involves circuit layout design on the PCB, component mounting methods (such as surface mount (SMT) and through-hole (THT), packaging and protection, functional testing, and process control.
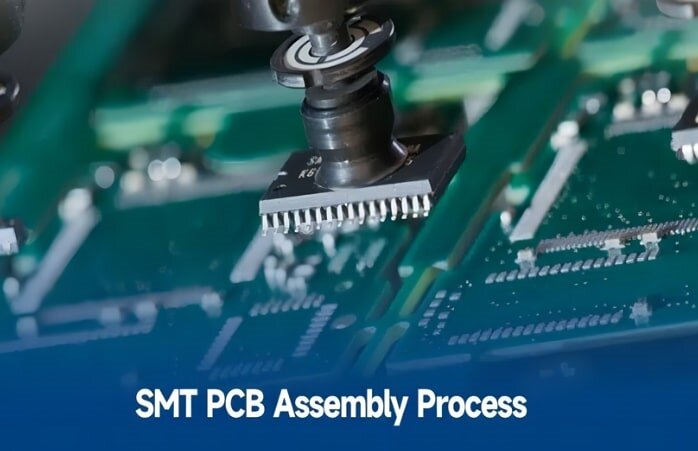
Key Steps in PCB Assembly
Board and Component Preparation: PCB Fabrication: PCB production according to Gerber files, including processes such as traces, vias, and gold deposition.
Component Procurement and Screening: Surface mount ICs, resistors, capacitors, and electromechanical components such as connectors and housings must meet specifications and quality requirements.
electric assembly
The entire PCB assembly production process can be divided into the following steps:
Pretreatment - Offset Printing - SMT - Insertion - Wave Soldering - Testing - Packaging
1. Pretreatment: This step primarily includes operations such as detinning, degumming, and deoxidation. Detinning involves treating pads and SMDs where glue is likely to stick. Degumming involves removing the solder mask and coverlay from the PCB surface to improve glue adhesion and conductivity. Deoxidation involves cleaning the oxide layer from the PCB surface.
2. Offset Printing: A layer of glue is applied to the PCB surface to secure the SMDs in place. This step requires high-precision equipment and techniques to prevent SMDs from shifting, which could affect the quality and stability of the PCB assembly.
3. Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
In the early stages of PCB assembly, the SMT process is used to attach surface mount components (SMDs) to the PCB surface. Typically, solder paste is applied by screen printing, components are positioned by a placement machine, and then soldered in place in a reflow oven. SMT offers the advantages of high speed, high density, and high reliability, making it a core step in the assembly of modern electronic products, particularly suitable for small, highly integrated PCBs.
4. Through-Hole Technology (THT)
Through-hole technology (THT) is typically performed after SMT and is used to mount components requiring stronger mechanical support or high current flow, such as connectors, inductors, and transformers. Component pins are inserted into through-holes on the PCB and then secured using wave soldering or hand soldering. Although more traditional, THT remains indispensable in fields such as industrial control and automotive electronics.
5. Wave Soldering
A soldering method that uses heat, flux, and pressure to connect electronic components. It is used to solder wire leads to the body of an electronic component.
The wire is connected to a wave soldering machine, which moves across the component in a wave-like motion. The heat generated by the machine melts the solder, causing it to flow around the wire and into all corners of the component before cooling again.
6. There are three types of PCBA testing. Every PCBA undergoes these types of inspections to ensure quality:
Manual Inspection
The manual inspection step in the PCB assembly process, as the name suggests, involves a person inspecting the printed circuit board and comparing it to the original design. Inspectors look for any problems that may have occurred during the production process.
Optical Inspection:
After components are soldered to the PCB, they are inspected to ensure they are properly aligned and all solder joints are secure and strong. Optical inspection equipment is used for this step. This is typically an LED microscope with high magnification and a bright light source.
The glass slide used to hold each circuit board must be clean and free of any contaminants. This is to ensure the microscope's image quality is not affected. The technician performing this task handles each circuit board using tweezers. They ensure they do not touch any surfaces with their hands and contaminate them.
X-ray Inspection
This inspection is performed after all components are soldered and before any other processes occur.
The X-ray machine emits rays into the PCB assembly. These rays bounce off the internal components and display their image on a monitor. The X-ray technician can then see any defects in the assembly, such as missing or misplaced parts.
If no defects are found during this step, it means all connections were completed correctly. This means all components are securely positioned on the circuit board. 7. Finished Product Assembly and Shipping
7. In the final stage of appliance assembly, the rigorously tested and qualified PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) is first assembled into the housing. This step not only integrates the electronics with the mechanical housing but also ensures the overall product structure and user experience. After housing assembly, the finished product enters the final testing phase, undergoing comprehensive functional and performance testing to ensure that the assembled appliance meets design specifications and quality standards. Only products that pass final testing are packaged and shipped, ensuring that every device received by customers has undergone a complete electrical assembly process and quality control, achieving high reliability and stability.

electric assembly
PCB assembly, a crucial step in appliance assembly, is crucial for achieving the functionality and performance of electric assembly products. With the increasing complexity and diversity of electronic products, PCB assembly technology is constantly advancing, evolving from traditional manual soldering to automated, high-precision surface-mount technology (SMT) and hybrid assembly. Furthermore, the integration of design optimization (such as Design for Manufacturing (DfMA)) with intelligent manufacturing technologies is further improving assembly efficiency and product quality.
In the future, with the widespread use of flexible circuit boards, HDI (High Density Interconnect) boards, and environmentally friendly materials, electric assembly will place even greater emphasis on refinement and sustainable development.