Embedded copper block circuit board, As electronic products become smaller and smaller in dimension, PCB also continue to shrink in dimension and become more and more dense in circuit design. As the power density of components to improve the PCB heat dissipation is too large, thus affecting the life of the components, aging and even component failure. Previously, a well-known mobile phone battery explosion so that designers and PCB manufacturers to raise the alarm, the mobile phone to reserve a certain amount of space inside, and in the mobile phone heat dissipation should also take into account the wireless charging coil charging heat dissipation problems. This incident proves once again the urgency of thermal management of electronic products. Based on the new generation of information technology, energy saving and new energy vehicles, power equipment and other areas of development, the solution to the problem of heat dissipation is imminent. Currently, there are many ways to solve the PCB heat dissipation problem, such as dense heat sink design, thick copper foil circuit, metal base (core) board structure, embedded copper block design, copper-based platform design, high thermal conductivity materials. Directly embedded in the embedded copper block circuit board, is one of the effective ways to solve the heat dissipation problem. However, the existing production process exists copper and substrate bonding force is insufficient, poor heat resistance, overflow of plastic is difficult to remove, product qualification rate is low and other issues, limiting the buried embedded copper PCB technology results of the application and promotion of the existing technology to be further researched and improved.
Embedded copper block circuits board has the features of high thermal conductivity, high heat dissipation and space saving, which can effectively solve the heat dissipation problem of high power electronic components. Embedded copper PCB heat dissipation technology, is embedded in the copper block to FR4 substrate or high-frequency mixed-pressure substrate, copper thermal conductivity coefficient is much greater than the PCB dielectric layer, the heat generated by the power device can be effectively conducted through the copper block to the PCB and through the heat sink dissipation. The PCB carrying the copper blocks can be designed as a multi-layer board, and the substrate material is FR4 (epoxy resin) or high-frequency composite material according to the product structure design needs. Embedded copper block design is mainly divided into two categories: the first is the copper block half-buried type, named "buried copper block"; the second is the copper block through the type, named "embedded copper block". The thickness of the embedded copper block is less than the total thickness of the plate, one side of the copper block is flush with the bottom layer, the other side is flush with one side of the inner layer, the thickness of the embedded copper block is close to or equal to the total thickness of the plate, and the copper block penetrates through the top layer, and there are embedded stepped blocks and embedded straight blocks in this type of designed copper block.
With the continuous improvement of the technology of the heat sink substrate and the rapid development of the market, the heat sink substrate in the substrate data and product structure, presenting technological change and innovation of the boom. Specific performance:
1. Adoption of high thermal conductivity substrate data, such as aluminium substrate data, copper substrate data, metal composite materials, ceramic substrate data, and so on;
2. Changes in product structure, such as thick copper foil substrate, metal-based (core) board, embedded copper circuit boards, ceramic substrates, copper-based tabs, copper conductor columns, as well as PCB and heat sinks, such as the new structure of the product.
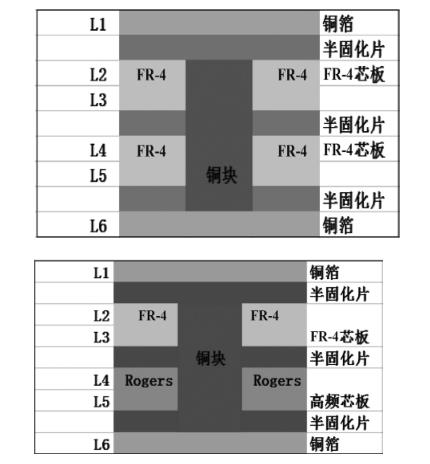
The embedded copper grooves are milled in the embedded copper areas of FR4 core boards and semi-cured sheets, and then the copper blocks are browned and pressed together so that the copper blocks are assembled with the FR4 core boards. The processing method of embedded copper block PCB with high-frequency material local mixing and pressing is firstly to mill the embedded copper groove and local mixing and pressing groove in the mixing and pressing area of the embedded copper block of the inner core board and the semi-cured sheet, and then laminated and heat-melted, the copper block is embedded in the groove, and then pressed together, so as to make the copper block and the FR4 substrate and the High frequency board mix and press together to realise the function of heat dissipation. Embedded copper PCB can be summarised into two main categories from the compression laminate structure: the first category is embedded copper in FR4 (epoxy resin) material three or more layers within the multi-layer board structure; the second category is embedded copper in FR4 core board and high frequency data mixed pressure multi-layer board structure.
Embedded copper block circuit board manufacturing technology
1. Matching of copper block and board (or mixing zone) milling groove size: copper block is placed in the milling groove, copper block is too loose or too tight, which affects the quality and bonding force of the press-filled adhesive.
2. Flatness control of copper block and board (or mixing area): When pressing, the flatness of copper block and FR-4 core board (or mixing area) is difficult to control, and it is necessary to ensure that the flatness of copper block and board is controlled within ±0.075 mm.
3. Residual glue on the copper block is difficult to remove: the resin overflowing from the gap between the copper block and the board during pressing is difficult to remove the residual glue on the copper block, which affects the reliability of the product.
4. Reliability of copper block and board (or mixing zone): There is a certain height difference between the copper block and FR-4 core board (or mixing zone) during pressing, which will easily lead to insufficient filling, voids, cracks, delamination, etc. at the connection between the copper block and board.
Embedded Copper Block Circuit Board Processes
Embedded copper block multi-layer circuit board process flow
Unwrap (copper block, FR4 substrate, semi-cured sheet) → inner layer circuit → inner layer AOI → OPE punching → inner layer core board and semi-cured sheet milling slot → browning → riveting → pressing (placing copper block) → chipping glue (grinding board) → milling blind groove (controlled depth milling machine) → mechanical drilling (including drilling blind holes) → chemical plating of copper → board electroplating → outer layer circuit → graphic plating → external layer etching → external layer AOI → anti-soldering → text → shaping → electrical testing → chemical tin plating → finished product inspection → packaging and stocking Electrical test →chemical tinning →finished product inspection →packaging out of stock
Embedded copper block high-frequency mixed voltage circuit board process flow
Material opening (copper block, FR-4 substrate, HF substrate, semi-cured sheet) → inner layer circuit (including HF board) → inner layer AOI → OPE punching → inner layer core board and semi-cured sheet milling → browning → riveting → compression (placing copper block) → chipping adhesive (grinding board) → mechanical drilling (including drilling of blind holes) → chemical plating of copper → board electroplating → outer layer circuit → graphic plating → external layer etching → external layer AOI → anti-soldering → text → moulding Slot milling →Chemical nickel/gold plating →Moulding →Electrical testing →Finished product inspection →Packaging out of stock
Thermal stress of copper-embedded circuit board
1. Reference standard
IPC-TM-650, 2.6.8 Thermal stress test for plated holes; IPC-6012C Identification and performance specification for rigid printed circuit boards.
2. Test Method
Baking conditions: 121℃~149℃, at least 6H; Heat stress test conditions: 288℃±5℃, 10 s, 3 times. Judgement of the samples after the test: There are no voids, cracks, delamination, etc. in the gap between the copper block and the board.
3. Test Result
After the sample is tested according to the above test method, there are no voids, cracks, delamination and other phenomena in the gap between the copper block and the board, and the heat resistance is good.