FPC, short for Flexible Printed Circuit (FPC), represents a key advancement in the electronics industry. Unlike rigid pcbs, flexible pcb prototypes can bend, twist, and fold, allowing them to fit into spaces where traditional circuit boards cannot. This adaptability makes them a crucial component of many modern electronic devices, from smartphones to complex medical devices. However, manufacturing flexible pcb prototypes presents unique challenges, requiring precision and innovation.
The FPC industry first emerged in Japan around 2002. The FPC industry outside of Japan began to emerge in 2003, expanding rapidly in 2005 before declining in 2006. The industry hit rock bottom in mid-2007 before recovering in 2008.
In 2005, the FPC industry's low barriers to entry and high profits attracted a large number of companies.
What are the characteristics of flexible pcb prototypes?
FPCs are thin, lightweight, flexible, and easily bendable, which are their advantages and unique features. Therefore, it's particularly suitable for products with limited space where a single rigid pcb can't meet all design requirements.
Some products may stack multiple pcbs to maximize internal space, requiring flexible FPCs for connection.
Some may use flexible circuit boards to connect distant pcbs for signal transmission to save board material. Others may require certain pcbs to cross at right angles or at varying angles.
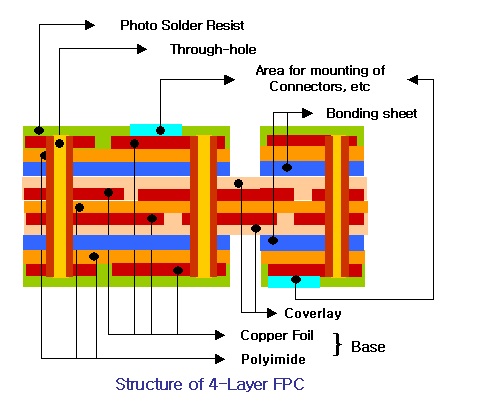
FPC Basics
1. Substrate: There are two types of substrates: adhesive-coated and adhesive-free. The details are as follows:
• Adhesive-coated substrates: A layer of adhesive (such as acrylic adhesive) is added between the substrate (such as copper foil, PET, etc.) and the adhesive layer, achieving a connection through the adhesive.
• Adhesive-free substrates: Different material layers (such as copper foil, polyimide) are directly laminated through a hot press process, without the need for additional adhesive.
• Adhesive-coated substrates
o Lower cost, but the long-term operating temperature is only approximately 105°C
o The adhesive layer is prone to aging and may produce toxic gases at high temperatures
o Relatively rigid when bent;
•Adhesive-free substrates
o Long-term operating temperatures can reach 150°C
o Good flexibility and high dimensional stability
o The adhesive-free structure makes it more environmentally friendly and safer.

2. Cover Film
It consists of three main components: release paper, adhesive, and PI. Ultimately, only the adhesive and PI remain on the product. The release paper is removed during the production process and is no longer used (it protects the adhesive from foreign matter).
3. Reinforcement
This is a material specifically used for FPCs. It is applied to specific areas of the product to increase support strength and compensate for the "soft" nature of FPCs. Currently, the following reinforcement materials are commonly used:
1) FR4 reinforcement: Its main components are glass fiber cloth and epoxy resin adhesive, the same FR4 material used in pcbs;
2) Steel reinforcement: Its main components are steel and offer greater hardness and support strength;
3) PI reinforcement: Similar to the cover film, it consists of PI and adhesive release paper, but the PI layer is thicker and can be produced in thicknesses ranging from 2 mils to 9 mils. 4. Other Auxiliary Materials
1) Pure Adhesive: This adhesive film is a thermosetting acrylic adhesive consisting of a protective paper/release film and a layer of adhesive. It is primarily used for bonding laminates, rigid-flex boards, and FR-4/steel reinforcement boards.
2) Electromagnetic Protection Film: Adhesive applied to the board surface for shielding.
3) Pure Copper Foil: Composed solely of copper foil, it is primarily used in the production of hollow boards.
Advantages of Flexible Printed Circuit Boards
Flexible printed circuit boards (FPCs) are printed circuits made from a flexible insulating substrate and offer many advantages over rigid pcbs:
1. They can be bent, rolled, and folded freely, allowing for arbitrary arrangement according to spatial layout requirements and free movement and expansion in three dimensions, enabling integrated component assembly and wiring connections.
2. FPCs can significantly reduce the size and weight of electronic products, meeting the needs of the trend toward higher density, miniaturization, and higher reliability. Therefore, FPCs have found widespread application in aerospace, military, mobile communications, laptops, computer peripherals, PDAs, digital cameras, and other fields and products.
3. FPCs also offer advantages such as good heat dissipation and solderability, easy assembly, and low overall cost. The rigid-flex design also compensates for the limited component load capacity of flexible substrates.
Disadvantages of Flexible Circuit Boards
1. High initial cost: Because flexible pcbs are designed and manufactured for specialized applications, the initial costs of circuit design, wiring, and photolithography are high. Unless there is a specific need for flexible pcbs, they are generally not recommended for small-scale applications.
2. Modifications and repairs to flexible pcbs are difficult: Once a flexible pcb is manufactured, any changes must be made from the original base design or the pre-programmed photolithography program, making them difficult to modify. The surface is covered with a protective film that must be removed before repair and restored afterward, making it a relatively difficult task.
3. Size limitations: Before flexible pcbs became common, they were typically manufactured using a batch process. This limited the size of production equipment and prevented them from being very long or wide.
4. Fragile pcbs can be easily damaged by improper handling: Fragile circuits can be easily damaged by improper handling by assembly personnel, and soldering and rework require trained personnel.
Flexible pcb prototyping is a specialty handled by the best pcb manufacturers and assemblers, demonstrating the complexity and innovation of the electronics manufacturing world. As the demand for multifunctional and flexible electronic products continues to grow, the role of flexible pcbs is becoming increasingly important.