With the continuous development of electronic technology, PCB as one of the core of the components of electronic equipment, the choice of materials is critical, the following will introduce several common PCB materials.
1.Paper substrate
Paper substrate, also known as phenolic PCB paper substrate,composed of pulp wood pulp and other materials, the main component is wood pulp fiber paper, is pressurized by phenolic resin and synthesized a PCB. Therefore, most of the drawbacks of the paper substrate pcb material is not fireproof, only 94V0 belongs to the flame retardant cardboard, can be fireproof. Paper substrate will generally be used to make a single panel,such as in household appliances or switching power supply will be often seen, common brands are Kingboard (KB characters), Changchun (L characters), Doosan (DS characters), Changxing (EC characters), Hitachi (H characters) and so on. Its advantages are low cost, cheap, relatively low density, can be punched processing, common materials are XPC, FR-1, FR-2, FE-3, 94V0 and so on.
2. Aluminum substrate
Aluminum substrate is a special PCB material commonly used in electronic products that require heat dissipation to provide better thermal management and structural support. Aluminum substrate single panel consists of a three-layer structure, respectively, the circuit layer (copper foil), insulation layer,metal base layer. Aluminum substrate has two sides, the white side is used for soldering LED pins, and the other side is aluminum. It is because the other side are aluminum, it is limited to do only a single panel, commonly used in LED lighting products.
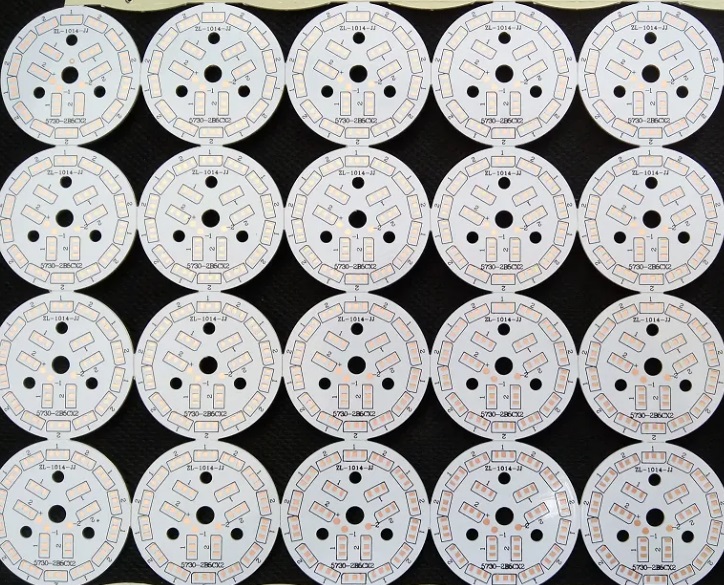
Aluminum substrate
3.FPC flexible board
FPC's full name is Flexible Printed Circuit,also known as Flexible Circuit Board,referred to as flexible board,FPC to polyester film or polyimide as a substrate, through the etching of copper foil to form a line,made of a high degree of reliability, excellent flexibility of the printed circuit. Its advantages are high wiring density,light weight, thin thickness, and good bendability.
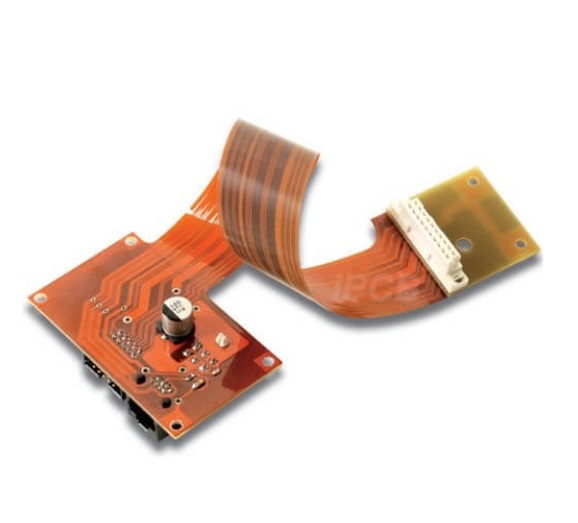

FPC flexible board
4.Epoxy glass fiber board
The most common board,commonly known as epoxy board,glass fiber board,fiber board,FR4,is a class of substrate with epoxy resin as the binder and electronic grade glass fiber cloth as the reinforcing material.Its bonding sheet and inner core thin copper cladding board,is an important substrate for making multilayer printed circuit boards.Higher working temperature, its own performance by the environmental impact of small. In the processing technology,to other resins than the glass fiber cloth substrate has great superiority.These products are mainly used for double-sided PCB, the same than the phenolic paper substrate price is about twice as expensive.
5.Composite substrate
Composite substrate commonly known as powder board, CEM-1 plate in some parts of the country is also called 22F, which mainly refers to the CEM-1 and CEM-3 composite base copper-clad plate. With wood pulp fiber paper or cotton pulp fiber paper as the core reinforcing material, with glass fiber cloth as the surface reinforcing material, both of which are impregnated with flame-retardant epoxy resin made of copper-clad laminates, known as CEM-1, with glass fiber paper as the core reinforcing material, with glass fiber cloth as the surface reinforcing material, both of which are impregnated with flame-retardant epoxy resin, the copper-clad laminates made of copper-clad laminates, known as CEM-3, the two types of copper-clad laminates are the most common composite.These two types of copper-clad laminates are currently the most common composite copper-clad laminates, this type of sheet is cheaper than FR4 type of sheet. Composite substrates are special PCB materials with multilayer structure and excellent thermal and electrical properties, thus enhancing the overall performance and reliability of the PCB.
6.Frequency Board
High-frequency board in the electromagnetic frequency of 1GHz above the higher frequency board will see, common high-frequency high-speed circuit boards have hydrocarbon resin, PTFE, LCP liquid crystal polymer, PPE / PPO, etc.. High-frequency boards are more difficult both for designers and manufacturers, so it is also more expensive, rarely used in consumer electronics.
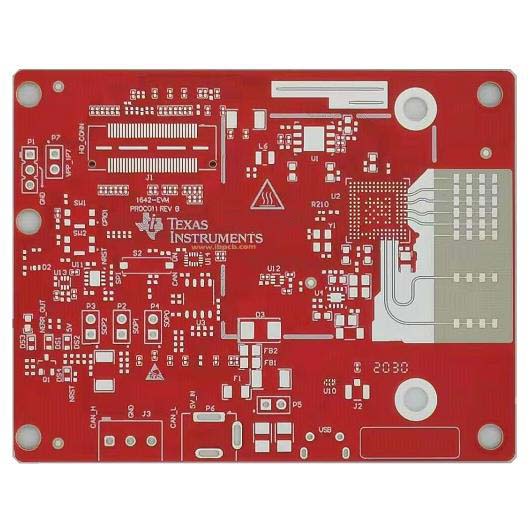
High-Frequency Board
6.1 Hydrocarbon Resin
Hydrocarbon resins are polyolefin homopolymers or copolymers, including butadiene styrene copolymer, butadiene homopolymer, styrene, homopolymer, styrene/divinylbenzene copolymer, styrene-butadiene-divinylbenzene copolymer, and so on. The main advantages include excellent dielectric properties, higher heat resistance, and better chemical resistance.
6.2 PTFE flexible film
PTFE resin melt temperature and melt viscosity are relatively high. Common commercial forms are resin dispersion, resin suspension and resin powder. Common processing methods are molding/turning method, impregnation/molding method, extrusion/molding method and so on. Due to the disadvantages of PTFE such as high coefficient of linear expansion and low thermal conductivity, enhancement modification is required. The modified membrane product form usually has PTFE+ceramic, PTFE+glass fiber cloth, PTFE+ceramic+glass fiber cloth, and so on.
6.3 LCP Liquid Crystal Polymer Liquid Crystal Polymer (Liquid Crystal Polymer), referred to as LCP, is a new type of high-performance specialty engineering plastics developed in the early 1980s. According to the different formation conditions, liquid crystal can be divided into heat-melted thermotropic liquid crystal Thermotropic LCP and solvent-dissolved solvatochromic liquid crystal Lyotropic LCP. in the heat-melted or dissolved by the solvent, this material will lose the solid macroscopic size and shape, hardness, rigidity, and other properties, and the appearance of the liquid material to obtain the liquidity, but at the same time maintains the crystalline material of the Orientation orderliness, so that the physical form of the formation of the various anisotropy, but also both liquid liquid fluidity and crystalline molecular ordering characteristics of the transition state, this intermediate form becomes liquid crystal state.
6.4PPE/PPO polyphenylene ether is a high-strength engineering plastics developed in the 1960s of this century, the chemical name is poly 2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether, abbreviated as PPO (Polyphenylene Oxide) or PPE ( Polypheylene ether), also known as polyphenylene oxide or polyphenylene ether. The two methyl groups close the active points of the two neighboring positions of the phenol group, resulting in increased rigidity, stability, heat resistance and chemical resistance. The ether bond increases flexibility but makes heat resistance poorer. Two methyl for the hydrophobic non-polar group, reduce the water absorption and polarity of the PPO macromolecule, close the two active points of the phenol group, so that there is no hydrolyzable groups in the molecular structure of the PPO, good water resistance, moisture absorption, dimensional stability and good electrical insulation.
To summarize, there are many kinds of PCB materials, each of which has its unique characteristics and application scenarios. When choosing the PCB material, you need to make comprehensive consideration according to the specific application needs, cost budget and performance requirements. Only by choosing the right PCB material can you effectively improve the performance, reliability and service life of the circuit board to meet the needs of different electronic devices.