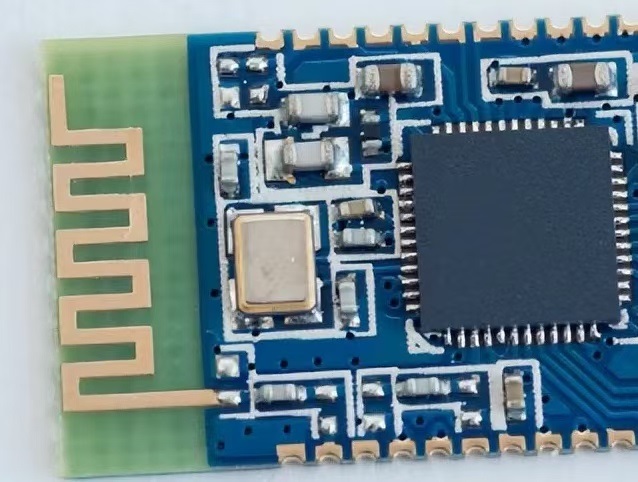
What is PCB side cooper plating?PCB side cooper plating,also known as pcb edge plating, is a copper plating from the top to the bottom surface of the board and along (at least) one peripheral edge. PCB side plating provides a strong connection through the PCB and reduces the possibility of device failure, especially for small PCBs and motherboards. Examples of this plating are common in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth modules.
During the manufacturing process, the edges to be metalized should be milled before the copper plating process. Proper surface treatment of the PCB edge after copper deposition.
PCB edge plating
When to use PCB edge plating?
In what cases is edge plating implemented:
* Need to improve the conductivity of the PCB
* Connections need to be at the edge of the PCB
* The PCB needs to be protected from lateral impact
* The secondary PCB is connected to the main board through the edge
* The edge needs to be soldered to improve assembly
Types of PCB edge plating
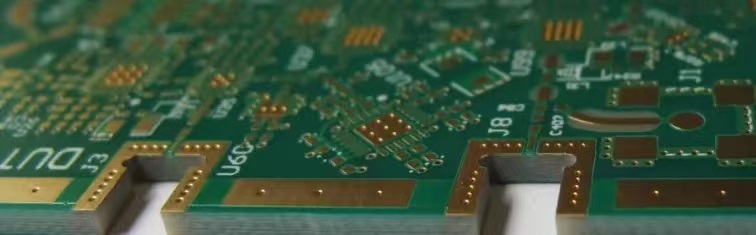
1. Wrap-around edge plating
Wrap-around plating routes the metal edge along the side after drilling. The routing process exposes the PCB board sidewall to the chemically plated base copper so that it can be applied simultaneously when applied to the drilling.
edge plating
In the following case, the base layer creates a conductive surface on which you can electroplate a thicker and more durable copper layer (for better adhesion)
2.Copper board edge
To avoid damaging the copper, we usually require a minimum distance between the copper features and the edge of the PCB. This distance is:
* 0.25 mm on outer layers with breaks
* 0.40 mm on inner layers with breaks
* 0.45 mm on all layers with V-cut notches.
Copper plate edge
Copper to board edge distance should only be used for flat and large copper areas where any minor damage to the copper will not affect the performance of the board. Tracks should not be within the minimum distance to the board edge to avoid damage.
If pads are found within the minimum distance to the board edge, they are trimmed back to restore the minimum copper-free space unless:
* The pad is part of an edge connector (usually with a beveled edge)
* The pad is marked as "to board edge" in a separate mechanical layer
* Trimming exceeds 25% of the pad surface, in which case it is actually abnormal.
3.Board edge PTH
Board edge PTH is a plated hole cut on the edge of the circuit board, also known as a butterfly hole, used to connect two PCBs by direct soldering or through a connector. It is used to connect two circuit boards by direct soldering or through a connector. There must be enough free space on the edge of the PCB to fix the circuit board in the production panel during manufacturing.
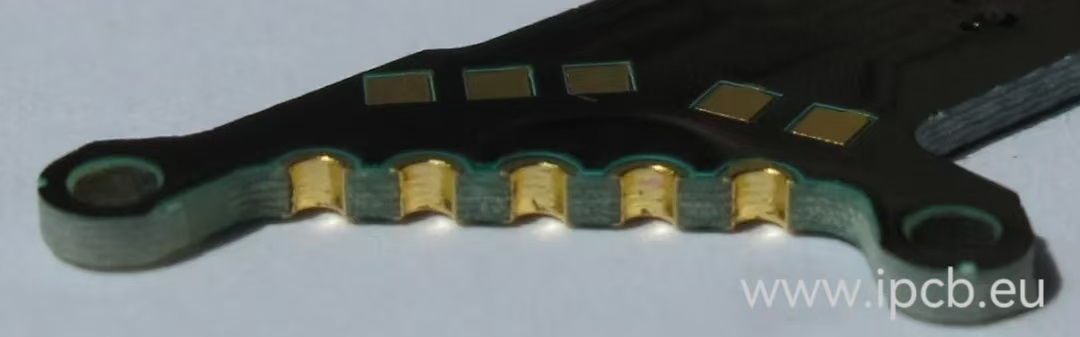
PTH on the edge board
There must be pads on the top and bottom layers to firmly fix the plating on the circuit board. For smaller sizes, a gold finish is preferred.
Here are some points to note:
* There must be enough free space on the edge of the PCB board so that we can fix the PCB in the production panel during manufacturing.
* Pads must be placed on the top and bottom layers (and possible inner layers) to firmly fix the plating on the PCB.
* As a general rule, the hole should be as large as possible to ensure good soldering with the parent PCB, 0.80 mm and above is recommended.
* All surface finishes are OK, but I prefer gold over nickel in the case of smaller sizes.
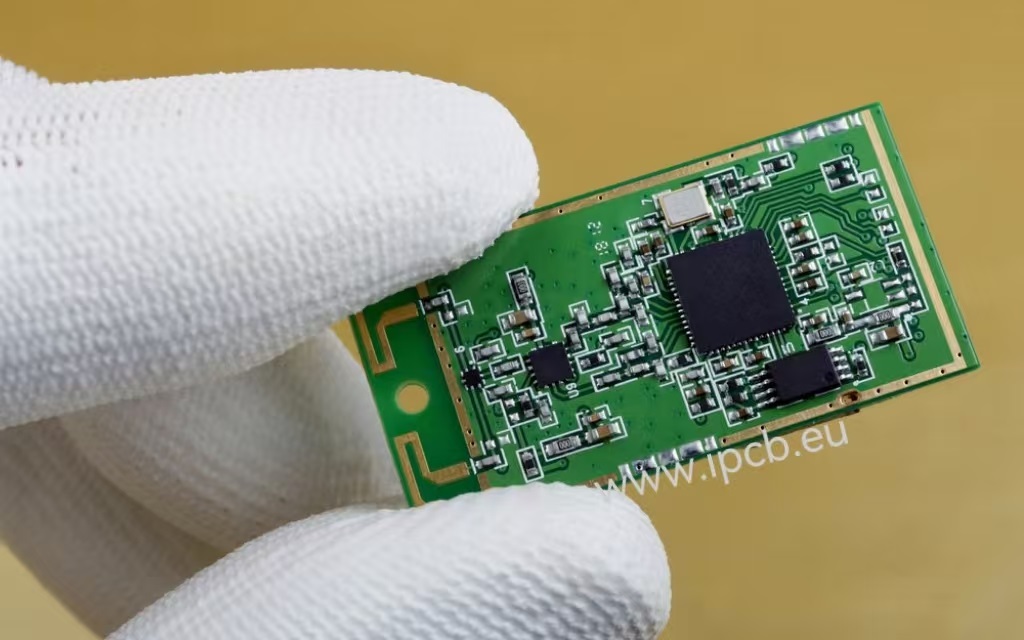
Mini wireless bluetooth module
4.Round edge plating
Round edge plating means that most or part of the PCB or cutout is plated from the top to the bottom surface. It is mainly used to establish a good ground for the purpose of metal housing or shielding. To produce such a circuit board with this kind of plating, the circuit board outline is milled before the through-hole plating process.
Since the plating needs to be fixed within the production panel during processing, 100% edge plating is not feasible, and there must be some problems in placing the routing tab. For round edge plating, choosing chemical nickel gold is the ideal surface treatment.
How to design PCB edge plating?
1. PCB edge plating guidelines
Use overlapping copper to define the copper plating area in the design/layout file. This additional copper deposition can be a copper pad, surface or trace
To ensure the producibility of the side panel, the metallization area must be defined in the CAD layout using overlapping copper (copper surface, pad or track).
* Minimum overlap: 500μm.
* On the connection layer, the minimum. 300?m connection copper line must be defined.
* On the non-connection layer, the copper should have a minimum gap of 800μm from the outer contour.
2. Metallization plating process
Only four steps need to be performed in the following order in this process: drilling -> milling metal groove -> removing dirt -> chemical copper plating
The outer contour that needs to be metallized must be milled before the through-hole plating process, because the metallization of the edge is carried out in this manufacturing step. After copper deposition, the expected surface finish is finally applied to the edge.
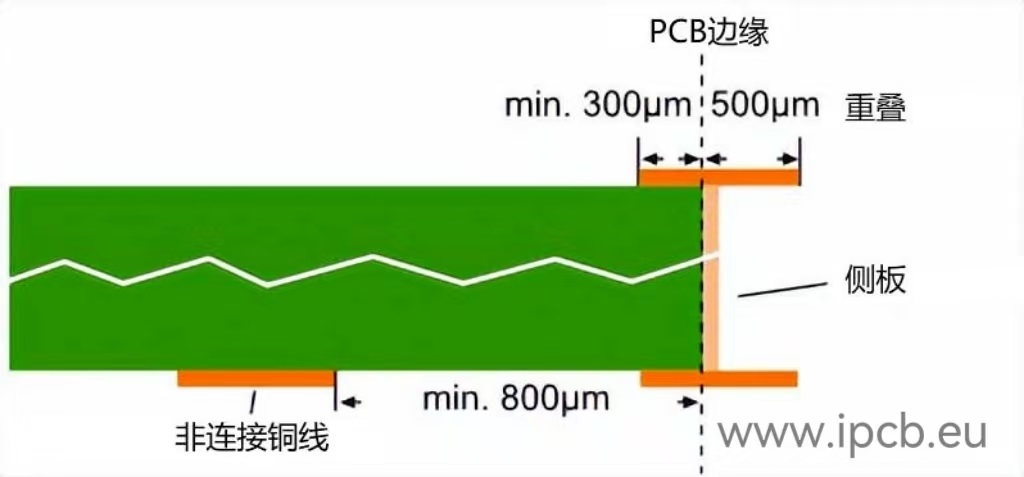
PCB Edge Plating Guidelines
3. Manufacturing Issues
1) Copper Peeling - On Large Substrates
Plating on surfaces can cause copper plating to peel off due to lack of adhesion. This problem needs to be addressed by first roughening the surface with a combination of chemical and other proprietary methods. Next, direct metallization with higher copper bonding strength is used to prepare the plating surface.
2) Burrs - Edge Plating
In some electroplating processes, burrs are generated during final processing. A modified proprietary process is required to allow the burrs to be polished to the edge of the feature.
4. Fab Notes
* The gold pad antenna position is too large, affecting welding or signal transmission.
* The inner edge pad is connected to the wire on the board, which may cause a short circuit.
* The stamp hole is designed at the edge grinding groove and must be processed in the second drilling process.
* It is impossible to achieve continuous metallization of the outer edge by processing the individual PCBs as panels. Metallization cannot be applied where the small panel bridge is located. The sliding electroplated metallization layer can be covered with a solder mask.
* When purchasing edge-sealed boards, it is necessary to confirm with the PCB supplier the possibility of manufacturing the PCB using the electroplating process and the extent to which the manufacturer can edge-seal the PCB. Gerber files or factory drawings are required. They should indicate in the mechanical layer where they need to slide electroplating and the surface finish they need. Benefits of PCB edge plating
ENIG Plating on PCB
1. Enhanced current conduction
Improving current carrying capacity improves the reliability and quality of the circuit board. In addition, the correct level of conduction is ideal for components to operate as required, and it also protects vulnerable edge connections.
2. Signal integrity
Edge plating enhances signal integrity by preventing interference from entering the internal electrical pulse transmission.
3. Heat distribution
Because the plated edges are metal, they create additional cooling surface area for dissipating heat into the surrounding air. The metal surface improves the reliability of the circuit board, especially when the components are heat-sensitive.
4. Better EMC/EMI performance
Metalized edges allow stray currents to escape, preventing the generation of sporadic electric and magnetic fields.
5. Improve electromagnetic compatibility
Edge plating enhances the electromagnetic compatibility of multi-layer boards.
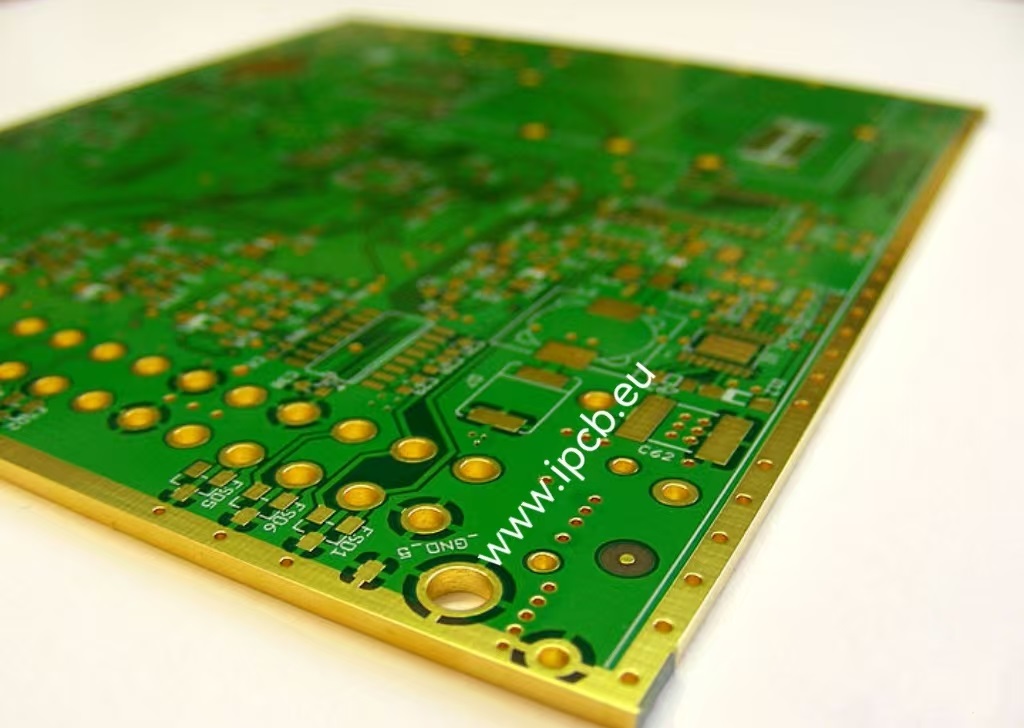
PCB side plating
6. Prevent static damage
When handling circuit boards, static electricity can hit sensitive components, and the metal surface helps absorb static electricity.
7. Application of PCB side plating
* Improve EMC performance by shielding the internal area of multilayers (such as high-frequency circuit boards)
* The cooling function of the edge as an additional cooling surface can use active heat dissipation
* Shell connection
* Board-to-board connection (see plated half-hole)
This is the article about PCB side copper plating shared by iPCB. I hope you like it.