SMT Process Introduction
SMT: Surface Mounting Technology
SMD: Surface Mounted Devices
SMT process: The process of assembling components onto PCBs or other substrates is called SMT process.
Automatic Board Feeder: Used at the source of the SMT production line, the PCB boards stored in the rotary box are transmitted to the production line one by one in response to the board movement requirements of the back-up equipment. When the PCBs in the rotary box are all transmitted, the empty rotary box will be downloaded automatically and replaced by the next fully loaded rotary box.
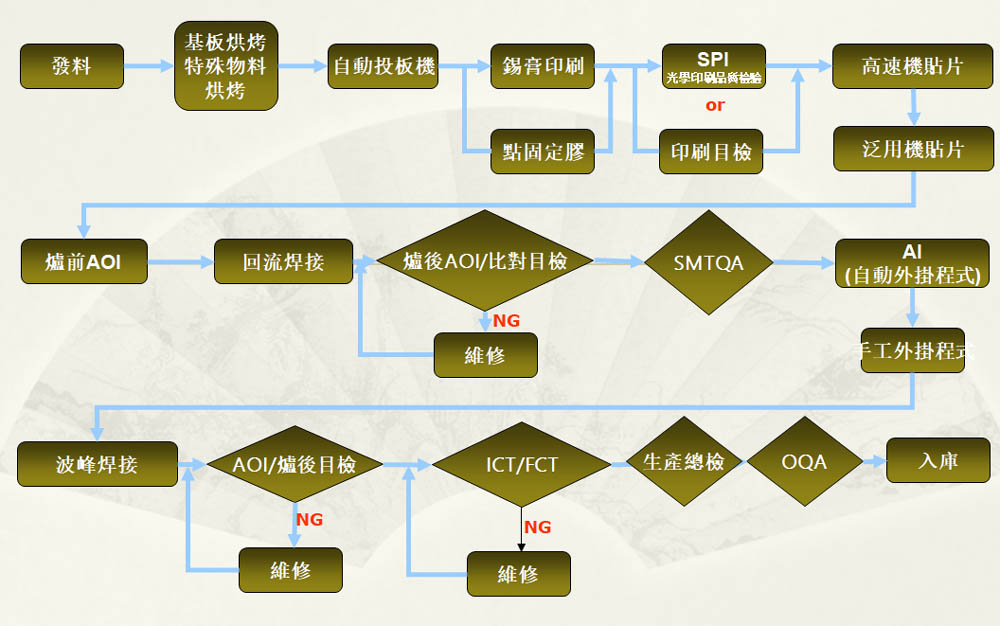
PCB assembly process flow chart
Printing: Printing the solder paste on the circuit board by hand with the aid of a printing machine steel mesh (copper mesh). Printing tools: Printing machine (manual printing table), squeegee, stencil (copper mesh), solder paste, circuit board, etc.
SPI: Measurement of the thickness of the printed solder paste, average value, and record of the highest and lowest point results. Area measurement, volume measurement, XY length and width measurement. Cross-section analysis: height, maximum point, cross-section area, distance measurement. 2D measurement: distance, rectangle, circle, ellipse, length, width, and area measurement. To determine whether the printing requirements are met.
SPI technology: solder paste volume, area, height, flatness, Xbar-R average value control chart, distribution probability bar chart, average value, standard deviation, CPK and other common statistical parameters monitoring.
PCBA Punching and Patching: Patch the components in accordance with the process guide and mount them on the printed circuit board with good solder paste through the programming of the patching machine or manually aligning the pipeline.
PCBA Punching and Patching related work:
(1) According to the roll of material to select the appropriate Feeder, and correctly installed and 100% scanning comparison confirmation.
(2) According to the scheduling of reasonable time to arrange for the preparation of materials, material meter and the preparation of work standards related matters.
(3) 100% first article board confirmation (automatic first article tester)
High-speed SMD machine is suitable for mounting small and large amount of components; such as capacitors,resistors,etc.It can also be used to mount some IC components, but the precision is limited. The speed is the fastest.
The general-purpose SMD machine is suitable for mounting anisotropic or high-precision components; such as QFP, BGA, SOT, SOP, PLCC, Connector, etc. The speed is slower. The speed is slower.
The characteristics of medium-speed mounters are in between those of high-speed mounters and general-purpose mounters.
Pre-furnace AOI: online through the graphical identification method. That is, the AOI system stored in the standard digital image and the actual detection of the image for comparison, so as to obtain the results of the inspection, focusing on the detection of components of the wrong material, fewer pieces, the monument, offset, reverse, tin, tin, and other bad.
Reflow Soldering: The PCB board with components pasted on it goes through hot air reflow soldering to melt the solder paste at high temperature so that the components can be firmly soldered on the pads, the most important control point is the control of the furnace temperature curve, and it is necessary to measure whether the curve is normal or not at regular intervals.
Solder paste melting point: 183℃ for lead, 217℃ for Rohs.
Reflow is divided into four stages:
1.Pre-heating (so that the PCB and components pre-heating, to reach equilibrium, and at the same time remove water and solvents in the solder paste to prevent the solder paste from collapsing and solder splattering)
2.Constant temperature (Soak) to ensure that the reflow temperature before the material can be completely dry, but also plays a role in the activation of the flux to remove components, solder pads, solder powder in the metal oxides
3.Reflow area (Reflow) solder paste in the solder alloy powder began to melt, again in a mobile state, instead of liquid flux wetting pads and components
4.Cooling area (Cooling) solder with the lowering of temperature and solidification, so that the components and solder paste to form a good electrical contact
Post-furnace AOI: AOI similar to the front of the furnace online through the graphical identification method. That is, the AOI system will be stored in the standard digital image and the actual detection of the image for comparison, so as to obtain the results of the inspection.
SMT QA: The batch materials are correct, the appearance and labelling meet the requirements, the soldering quality meets the requirements, and the raw product quality of SMT is subject to sampling inspection (full inspection of repair products).
AI insert: It is the mechanical equipment to insert some regular electronic components into the printed circuit board conductive through holes automatically (automatic plug-in machine) in a standard way, mainly used for automatic insertion of resistor, capacitor, diode, triode, jumper and other similar types of components.
Manual insert work: The process of transferring the PCB mainly through the rotation of the chain and manually inserting the parts (after moulding) into the corresponding position of the PCB according to the requirements of the process file or programme (through-hole components category).
Wave soldering is the molten liquid solder, with the help of the pump, in the solder tank liquid surface to form a specific shape of the solder wave, inserted components of the PCB placed with the conveyor chain, after a particular angle and a certain depth of immersion through the solder wave peak and achieve the soldering process.
Flux flow: Determined according to the flux contact PCB circuit board bottom surface.
Preheating temperature: set according to the actual situation of the preheating zone of the wave soldering machine (90-150 ℃).
Transfer speed: Set according to different wave soldering machines and PCB to be soldered (0.8-1.9M/MIN).
Soldering temperature: must be the actual wave soldering temperature of 260±5℃.
Wave Height: Beyond the bottom of the PCB, at 2/3 of the PCB thickness.
Hand-inserted segment AOI: through the graphical identification method. That is, the AOI system will be stored in the standard digital image and the actual detection of the image to compare, so as to obtain the results of the inspection, hand-inserted section of the AOI is mainly used to measure the bottom of the board false soldering, tin, not out of the foot, less tin, fewer pieces, the wrong pieces and other bad!
ICT (online electrical test): ICT Test is mainly * test probe contact PCB layout out of the test point to detect the PCBA line open circuit, short circuit, all parts of the soldering situation, can be divided into open circuit test, short circuit test, resistance test, capacitance test, diode test, three-pole tube test, field effect tube test, IC pin test (testjet ` connect check) and other general and special test. connect check) and other general and special components, such as leakage, misinstallation, parameter deviation, soldering joints, circuit board open and short circuit faults.
Functional testing, also known as behavioral testing, tests a product's characteristics and operable behaviours to determine that they meet design requirements, based on product characteristics, operational descriptions and user scenarios.
Functional testing techniques: test environment, test conditions, OK/NG standards, manipulation and judgement of the anti-defective. Yield, false positives, blind spots.
Final Inspection & Scanning: Through visual inspection to confirm that the PCBA is free of defects of an external nature (dirty, damaged, missing pieces, skewed and other defects) and then through scanning and comparison to confirm that the model, batch, number of directions, labelling, etc. are correct.