1. PCBA board welding process
1.1. Introduction of PCBA board welding process: PCBA board welding process requires manual insert, manual welding, trimming and inspection.
1.2. The process of PCBA board soldering: categorize components according to the list - insert - solder - cut foot - check - trim.
2. Process requirements of PCBA board welding
2.1. Processing requirement of components
2.1.1. Before inserting the components, the weldability of the components must be processed, and the pins of the components with poor weldability should be tinned first.
2.1.2. After the component pins are shaped,the spacing between the pins should be consistent with the spacing between the corresponding pad holes of the PCBA board, and all the component pins should not be bent from the root, and generally should be left more than 1.5mm.
2.1.3. The shape of the component pins should be favorable for heat dissipation during welding and mechanical strength after welding.
2.2. Components in the PCBA board insertion process requirements
2.2.1. Components in the PCBA board insertion sequence is the first low and then high, the first small and then large, the first light and then heavy, the first easy and then difficult, the first general components and then special components, and the previous process can not affect the installation of the next process after the installation.
2.2.2. After the components are inserted, their signs should be oriented in a direction that is easy to recognize and read, and they should be read out in the order from left to right as far as possible.
2.2.3. Polarized components, polarity should be installed strictly in accordance with the printed labeling of the PCBA board.
2.2.4. Components on the PCBA board should be evenly distributed, arranged neatly and beautifully, do not allow diagonal rows, three-dimensional cross and overlap arrangement; do not allow one side high, one side low; also do not allow the pin one side long, one side short.
2.3. PCBA board soldering process requirements
2.3.1. Solder joints should be smooth, solder surrounded and wet pads, bright, full, no leakage, no solder, no short-circuit, no cracks, no damage to the pad, no pinholes, no bubbles, no spattering of tin, no pulling the tip of the bridge and so on.
2.3.2 Reliable soldering to ensure conductive performance.
2.3.3. The surface of the solder joints should be smooth and clean, and the excess pins of the components should be cut off. Cutouts are bright, smooth and consistent.
3. PCBA board soldering process and methods
3.1. Preparation
3.1.1 According to the “Component List” to prepare components, PCBA board.
3.1.2. Ensure static electricity protection measures
3.1.2.1. ESD Protection Methods
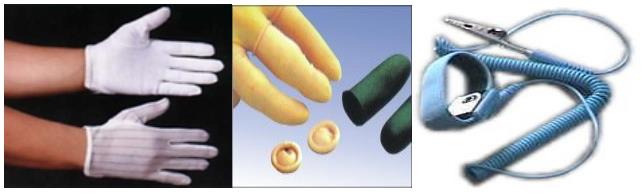
PCBA ESD Protection
----The welder wears an anti-static wrist throughout the welding process and tests for good contact before wearing it.
----The elimination of static electricity from non-conductive belts can be achieved by using ionic fans to generate positive and negative ions to neutralize the static electricity from the static power supply.
3.1.2.2. Commonly used anti-static devices.
3.1.3. Use anti-static adjustable constant-temperature soldering iron, check whether the iron head heating is normal.
3.1.4. Adjust the temperature of the soldering iron head between 280 ~ 360 ℃.
3.2 Soldering
3.2.1. Insertion of electronic components
3.2.1.1. Component pin shaping: Shaping of manually processed components, using tweezers to shape the pins.
3.2.1.2. Order of insertion: manual insertion of components should be carried out according to the basic principles of bottom-to-top, easy-to-difficult, general-to-special.
3.2.2. How to hold the soldering iron and soldering wire

Soldering iron grip soldering wire grip
3.2.3. Manual welding
3.2.3.1. Heating up the soldered parts
Inserted components of the PCBA board turned over, pins facing up, the right hand holding the soldering iron, waiting for the welding, the requirements of the soldering iron tip to keep clean, no welding slag and other oxides.
Constant temperature soldering iron temperature is generally controlled between 280 to 360 ℃.
Part of the original special welding requirements:
Item device
SMD device
DIP device
Soldering iron tip temperature during soldering:
320±10℃
330±5℃
Note: Please use different soldering tips according to the size of CHIP parts:
According to the different sizes of CHIP parts, please use a different soldering iron tip
When welding high-power (TO-220, TO-247, TO-264 and other packages) or soldering joints and large copper foil connected to the above temperature can not be welded, the temperature of the soldering iron can be increased to 360 ℃, when the welding of sensitive parts that are afraid of heat (LEDs, CCDs, sensors, etc.) Temperature control at 260 to 300 ℃.
When soldering the soldering iron head and PCB assembly board at an angle of 45 °, the soldering iron head on top of the pad and component pins and then give the component pins and pad preheat evenly.
3.2.3.2. Transferring the Solder Wire
The solder wire is introduced from the contact surface between the component foot and the soldering iron, and the solder wire should be placed between the component foot and the soldering iron head.
3.2.3.3. Removing the Solder
When the solder is melted (the speed of soldering should be controlled) and the solder is scattered all over the pad, then the solder can be removed from the pad at a 450° angle.
3.2.3.4 Removing the Soldering Iron
After removing the soldering wire, the soldering iron will continue to be placed on the pad for 1~2 seconds. When removing the soldering iron, do not pick it up too quickly or forcefully to avoid spattering of tin beads, tin spots, or pulling the tip of the soldering point, etc. At the same time, we should make sure that the component to be soldered should not be moved or shocked before the soldering tin is solidified, or it will easily result in the loosening of the structure of the soldering point, or false soldering, etc. The whole soldering process generally takes about 3 seconds. The whole soldering process is generally about 3 seconds, and should not exceed 5 seconds at most.
3.2.3.5. Cleaning the soldering surface
If there is too much solder on the soldered part, you can shake off the solder on the iron tip (be careful not to burn your skin or shake it onto the PCBA board), and then use the iron tip to “dab” some solder out. If the solder joints have too little solder and are not round and smooth, you can use the soldering iron tip to “dip” some solder to make up the solder joints.
3.2.3.6 Inspection of solder joints
See if the solder joints are round, bright and firm, and whether there is any phenomenon of continuous soldering with the surrounding components.
Qualified Solder Joints Qualified Solder Joints
3.3. Inspection
3.3.1. Compare with the Component List to see if the components on the PCBA are fully soldered.
3.3.2. Check whether the labeling direction of components with polarity is consistent with the labeling printed on the PCBA board.
3.3.3 Check whether the solder joints are smooth, solder surrounded and wet lead and pad, bright, full, no leakage of solder, no virtual solder, no short circuit, no cracks, no damage to the pad, no pinholes, no bubbles, no spattering of tin, no pulling the tip of the bridge and so on.