In today's fast-paced technological world, printed circuit board assemblies (PCBAs) serve as the backbone of virtually all electronic devices. These intricate assemblies are the foundation upon which modern gadgets function, and ensuring their longevity is critical. One way to enhance the durability and reliability of PCBAs is through the application of a protective layer known as PCBA coating. This process not only safeguards electronic components from environmental stresses but also boosts the overall performance of the device. In this article, we will explore the importance of PCBA coating, the various types of coatings available, and their benefits.
What is PCBA Coating?
PCBA coating refers to the process of applying a thin layer of protective material over the surface of a printed circuit board assembly. This coating shields the PCBA from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. The protective layer also acts as a barrier against physical damage, improving the reliability and lifespan of the assembly.
There are several types of PCBA coatings, each with unique properties tailored to different applications. Some of the most common coatings include conformal coating, potting, and encapsulation, each providing a different level of protection based on the environment in which the device operates.
Why is PCBA Coating Important?
The primary purpose of PCBA coating is to protect the circuit board from environmental hazards that could compromise its functionality. Many electronic devices are exposed to harsh conditions, including temperature fluctuations, humidity, and chemical exposure. Without a protective coating, the PCB and its components could corrode or become damaged, leading to device failure.
Furthermore, as electronics continue to miniaturize, components are placed closer together on the circuit board, increasing the risk of short circuits. Coatings provide insulation between these components, reducing the likelihood of electrical shorts and improving the overall reliability of the assembly.
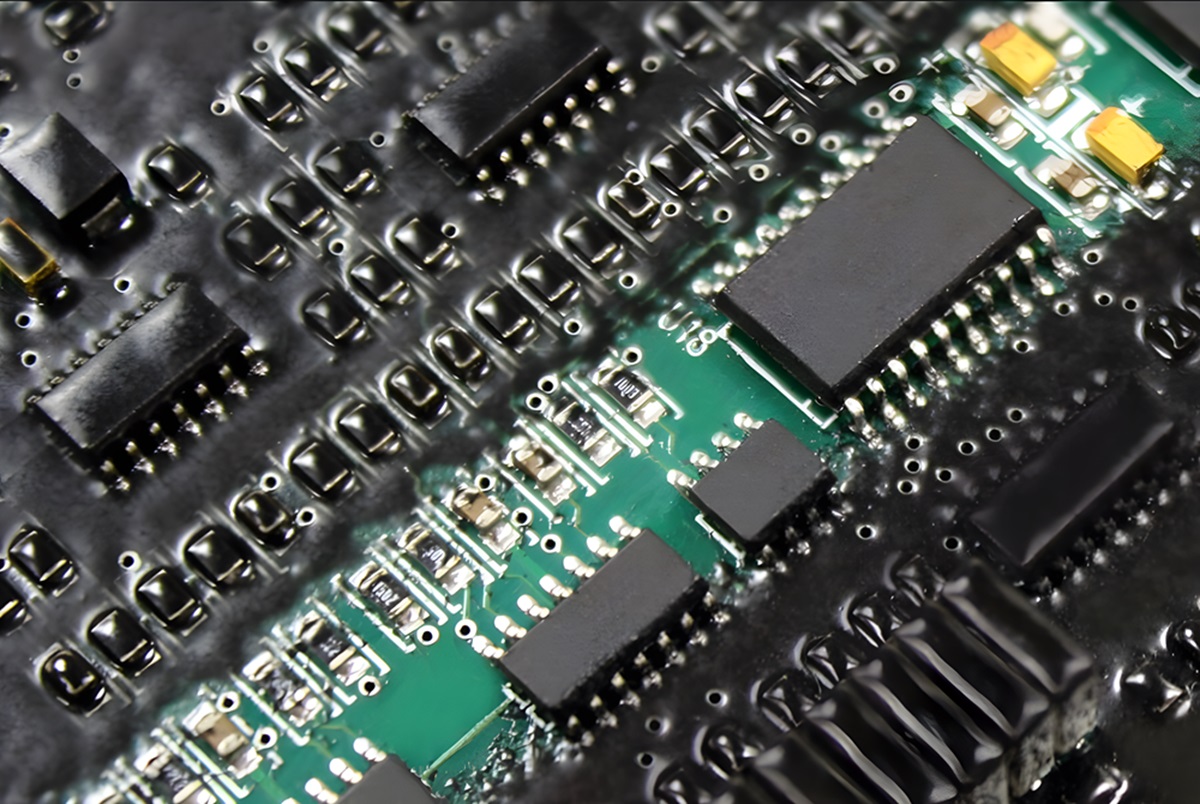
Black conformal coating
Types of PCBA Coatings
There are several common types of coatings used in PCBA manufacturing. Each offers distinct advantages, depending on the specific application and environmental conditions the assembly will face.
1. Conformal Coating
Conformal coating is the most widely used form of PCBA protection. It is a thin, lightweight layer of material that conforms to the shape of the PCB and its components. This type of coating is typically applied in liquid form, either by spraying, dipping, or brushing. Once applied, it cures into a protective layer that shields the board from moisture, dust, and chemical exposure.
Common materials used for conformal coatings include acrylic, silicone, epoxy, and polyurethane. Each material offers varying degrees of protection. For instance, acrylic coatings are easy to apply and rework but may not provide sufficient resistance to extreme temperatures or solvents. On the other hand, silicone coatings excel in high-temperature environments and offer excellent flexibility, making them ideal for applications that involve thermal expansion.
2. Potting
Potting involves encasing the entire PCBA in a thick layer of protective material. This technique provides a higher level of protection than conformal coating, as it completely surrounds the board and components, offering enhanced resistance to vibration, shock, and chemical exposure. Potting is commonly used in harsh industrial environments where the PCBA may be subject to mechanical stress or extreme weather conditions.
The potting material is typically a two-part compound, such as epoxy or silicone, that cures into a rigid or flexible form depending on the application’s needs. While potting provides excellent protection, it can make rework or repair of the assembly more difficult, as the coating must be removed before any adjustments can be made.
3. Encapsulation
Encapsulation is similar to potting but typically involves a lighter layer of protective material. Rather than completely encasing the PCBA, encapsulation covers only specific sections or components. This method is ideal for protecting sensitive components without adding too much bulk to the assembly. Encapsulation can be achieved using materials like silicone, epoxy, or urethane, depending on the required level of protection.
Encapsulation offers a balance between protection and flexibility, making it a popular choice for devices that require enhanced durability without significant weight or size increases.
The Benefits of PCBA Coating
PCBA coating offers numerous benefits that enhance both the performance and longevity of electronic devices. Some of the key advantages include:
1. Environmental Protection
One of the most critical functions of PCBA coatings is protecting the assembly from environmental factors. Moisture, dust, and chemicals can damage sensitive electronic components, leading to corrosion, short circuits, or even complete device failure. Coatings act as a barrier, preventing these contaminants from reaching the PCB.
2. Improved Reliability and Performance
By providing insulation between components, coatings reduce the risk of electrical shorts, which can cause malfunctions or failures. This increased reliability is essential for electronics used in critical applications, such as medical devices, aerospace, and automotive systems.
3. Enhanced Durability
PCBA coatings also offer protection against physical damage, such as vibration or impact. In industrial and automotive applications, where devices may be subject to mechanical stress, coatings help prevent damage to the board and its components, extending the device’s lifespan.
4. Thermal Management
Certain types of coatings, such as silicone, can help with thermal management by dissipating heat away from sensitive components. This is particularly important for high-power electronics, where excessive heat can lead to component failure.
5. Cost Savings
While the initial application of PCBA coatings may add to manufacturing costs, the long-term benefits often outweigh this expense. Coatings help reduce the likelihood of device failure, minimizing the need for repairs or replacements. Additionally, the enhanced durability provided by coatings reduces the risk of warranty claims and extends the product’s useful life.
Conclusion
PCBA coatings play a vital role in enhancing the durability, reliability, and performance of electronic assemblies. By providing a protective barrier against environmental hazards and physical damage, these coatings ensure that devices can withstand even the harshest conditions. With various types of coatings available, manufacturers can choose the most suitable solution based on their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance across a wide range of applications.