High-frequency circuit boards have a wide range of applications, especially in high-frequency and induction heating technology. They are favored by all walks of life for their high heating efficiency, fast heating speed, and low-consumption and environmentally friendly characteristics. With the excellent performance and broad application prospects of high-frequency circuit boards, induction heating technology will surely be more widely used in all walks of life in the future. Due to its high physical performance requirements, strict precision requirements, and fine technical parameters, high-frequency circuit boards play a vital role in high-end fields such as automotive anti-collision systems, satellite systems, and radio systems. With the high-frequency development trend of electronic equipment, the application of high-frequency circuit boards will continue to expand and deepen.
High-frequency circuit boards are mainly made of materials with high dielectric constants and low high-frequency losses. At present, fluorine-based dielectric substrates, such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, commonly known as Teflon), are widely used in high-frequency fields above 5GHz due to their excellent performance. In addition, FR-4 or PPO substrates are also often selected for products between 1GHz and 10GHz.
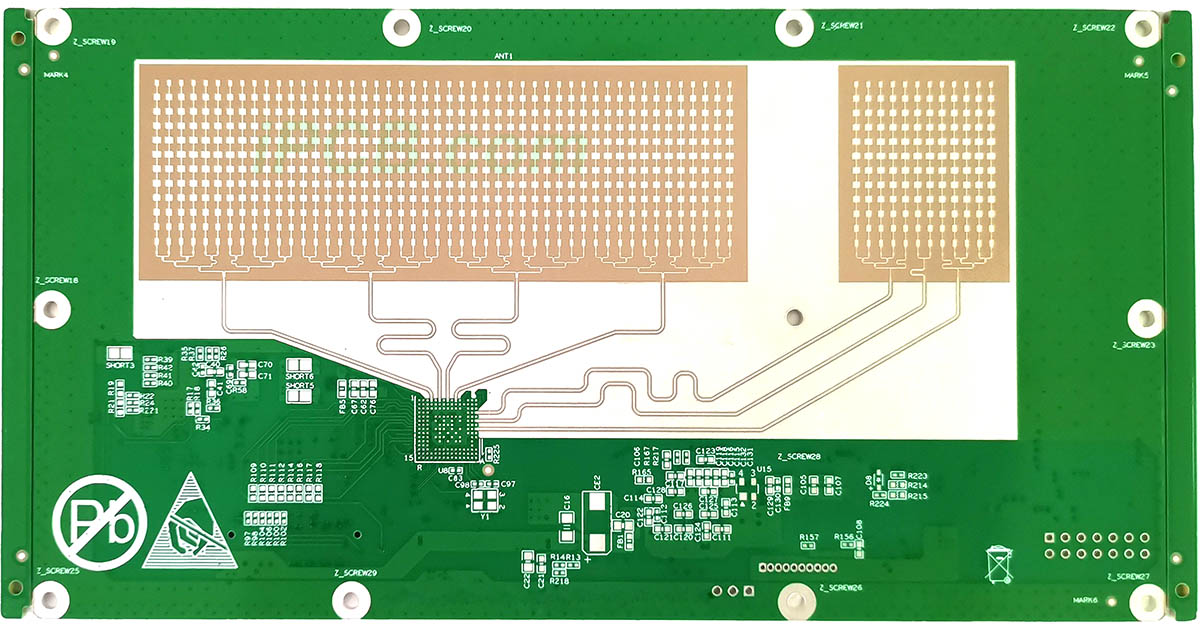
High-frequency circuit board
At present, high-frequency substrate materials are mainly divided into three categories: epoxy resin, PPO resin, and fluorine-based resin. Among them, epoxy resin has the lowest cost, while fluorine-based resin is more expensive. Taking into account the dielectric constant, dielectric loss, water absorption and frequency characteristics, fluorine resin performs best, while epoxy resin performs relatively poorly. Especially when the product application frequency exceeds 10GHz, only fluorine resin printed boards can meet the demand.
Fluorine resin high-frequency substrates are significantly better than other substrates in performance, but they are expensive, lack rigidity, and have a large thermal expansion coefficient. In order to improve the performance of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a large amount of inorganic substances (such as silicon dioxide SiO2) or glass cloth is usually added as reinforcing filler materials to increase the rigidity of the substrate and reduce its thermal expansion. However, due to the molecular inertness of polytetrafluoroethylene resin itself, its bonding with copper foil is poor, so special treatment is required for the bonding surface with copper foil. The treatment methods include chemical etching or plasma etching on the surface of polytetrafluoroethylene to increase the surface roughness; or adding a layer of adhesive film between the copper foil and polytetrafluoroethylene resin to improve the bonding force. However, these methods may have a certain impact on the dielectric performance. Therefore, the development of fluorine-based high-frequency circuit substrates requires close cooperation among raw material suppliers, research institutions, equipment suppliers, PCB manufacturers, and communication product manufacturers to meet the needs of the rapid development of the high-frequency circuit board field.
Basic characteristics requirements of high-frequency circuit boards.
1. The dielectric constant (Dk) should be kept at a low and stable level. Generally speaking, the smaller the value, the more conducive to the rapid transmission of signals. The transmission rate of the signal is inversely proportional to the square root of the dielectric constant of the material. Therefore, a high dielectric constant may cause delays in signal transmission.
2. The dielectric loss (Df) should be as small as possible, which is a key factor in ensuring the quality of signal transmission. The smaller the dielectric loss, the less signal loss will be.
3. The thermal expansion coefficient should be kept consistent with that of the copper foil as much as possible, because the inconsistency between the two will cause the separation of the copper foil during hot and cold changes.
4. The water absorption should be kept at a low level, because high water absorption will affect the dielectric constant and dielectric loss when the material is damp, which will have an adverse effect on signal transmission.
5. In addition, other properties such as heat resistance, chemical resistance, impact strength and peel strength should also reach a good level to ensure that high-frequency circuit boards can work stably under complex environmental conditions.
FR-4 circuit boards vs high-frequency circuit boards
1. Ordinary FR-4 circuit boards use glass fiber materials. High-frequency circuit boardsare made of alkali-free glass cloth. High-frequency circuit boards are generally pressed from FR-4 glass fiber boards, which are pressed from a whole sheet of epoxy resin glass cloth. From the color point of view, the whole board has uniform and bright color. Due to the increase in density, high-frequency circuit boards are heavier than low-frequency boards.
2. FR-4 circuit boards, as low-frequency circuit boards, are mostly pressed from some low-end materials, such as paper substrates, composite substrates, epoxy boards (also known as 3240 epoxy boards or phenolic boards) and FR-4 glass fiber boards (splicing boards). Among them, the overall density of paper substrates and composite substrates is low, and the color of the back is consistent, but a closer look will reveal that there is basically no glass fiber cloth texture inside these substrates. The epoxy board and the FR-4 fiberglass splicing board are different in appearance. The back of the epoxy board has different shades of color. If you gently scrape it with your hands or other tools at the fracture, you can easily see the off-white powder. As for the FR-4 splicing board, since it is pressed from the scraps of FR-4 fiberglass cloth, large stripes can be clearly seen on the back of the board.
The performance of high-frequency circuit boards seriously affects the working stability of high-frequency circuits. High-frequency circuits have the characteristics of skin effect, and high-frequency circuit boards with low dielectric constants will cause leakage of high-frequency components, thereby causing problems such as signal attenuation and frequency deviation drift. In severe cases, it may even cause vibration stop. This series of problems ultimately leads to a significant reduction in the overall electrical performance indicators.
The production requirements and precautions of high-frequency circuit boards. As one of the most difficult circuit boards, high-frequency circuit boards must strictly follow the production requirements to ensure quality.
High-frequency circuit board drilling
1. The drilling feed speed should be controlled to 180/S, and a new drill bit should be used, and aluminum sheets should be placed on the upper and lower pads. It is best to perform single PNL drilling to ensure that the hole is not exposed to moisture.
2. When applying the hole-leveling agent, for the PTH hole sample, although concentrated sulfuric acid can be used, we do not recommend this practice for safety reasons, and the processing time should be 30 minutes.
3. The production process of grinding, copper deposition, and circuits should be the same as that of normal double-sided boards. It is particularly important to note that high-frequency circuit boards do not require desmearing during the production process.
High-frequency circuit board solder mask production: If the high-frequency circuit board requires green oil primer, grinding the board before solder mask is prohibited, and a red seal is stamped in MI to distinguish it. Secondly, if green oil needs to be printed on the substrate, it should be printed twice (to prevent green oil bubbling), and the board should not be ground from etching to tin removal, and can only be air-dried. The first primer should be printed normally with a 43T screen, and the board should be baked in sections. The temperature and time are 50 degrees for 50 minutes, 75 degrees for 50 minutes, 95 degrees for 50 minutes, 120 degrees for 50 minutes, 135 degrees for 50 minutes, and 150 degrees for 50 minutes. After exposure and development, the board can be ground, and then the second production is carried out according to the normal process. It should be noted in the MI that the first primer needs to be aligned with the circuit film. In addition, if part of the substrate needs to be printed with green oil and part does not, a special "priming film" needs to be made, and only the part of the substrate that needs to be printed with green oil is retained. After the primer is baked, the second normal production can be carried out. It is particularly important to note that for substrates like 018092, if there is no need to print green oil on it, only one green oil needs to be printed to avoid the green oil not being able to be developed cleanly after the first primer.
High-frequency circuit board tin spraying process: In the tin spraying process, the board needs to be baked before tin spraying, the temperature is 150 degrees, and the time is 30 minutes to ensure the tin spraying effect.
High-frequency circuit board line tolerance control: In terms of line tolerance, if there are no special requirements, the line width tolerance should be controlled within ±0.05mm; if there are special requirements, it will be made according to customer requirements.
iPCB focuses on high-end circuit board production. iPCB provides customers with reliable high-frequency circuit boards, microwave RF boards, HDI boards, multi-layer mixed-pressure boards, F4B antenna boards and other 5G communication substrates. It cooperates with aerospace, medical equipment, communication base stations, research institutes and other technology companies to provide PCB circuit board prototypes and circuit board batch production with stable quality. We look forward to working with you.