Semi-flex PCBs have become widely used in the market and are now indispensable in the electronics industry. These PCBs adapt to various applications such as wearable devices, artificial organs, medical devices, RFID modules, and more. Semi-flex PCBs offer a robust design with the flexibility needed for moving or bending product components.
Semi-flex PCBs are characterized by their ability to bend or flex to a certain extent while maintaining structural integrity. They are commonly used to save space in the final product and to avoid using connectors between two circuit boards. The manufacturing of semi-flexible printed circuit boards combines traditional PCB manufacturing processes (such as photolithography, etching, and drilling) with specialized techniques for handling flexible substrates. The result is a PCB that can bend or flex to a limited degree while maintaining electrical performance and durability.
Specifications of Semi-flex PCBs
Substrate: The substrate used in semi-flexible printed circuit boards is FR4.
Flexible Area: Flexibility is achieved by milling the flexible area in the FR4 along the Z-axis or through sequential layering. Thinner FR4 regions offer static flexibility but can only bend less than 10 times.
Line Width and Spacing: There are limitations on the minimum line width and spacing in the flexible area to ensure the strength and reliability of the trace.
Layers: There is no limitation on the total number of layers for FR4 semi-flexible printed circuit boards, but the flexible portion can only accommodate a maximum of two layers.
Surface Treatment: FR4 semi-flexible printed circuit boards are compatible with all common surface treatments.
Solder Mask: The solder mask in the flexible area needs to be a flexible solder mask or polyimide coverlay. Other parts of the board can have a standard liquid solder mask.
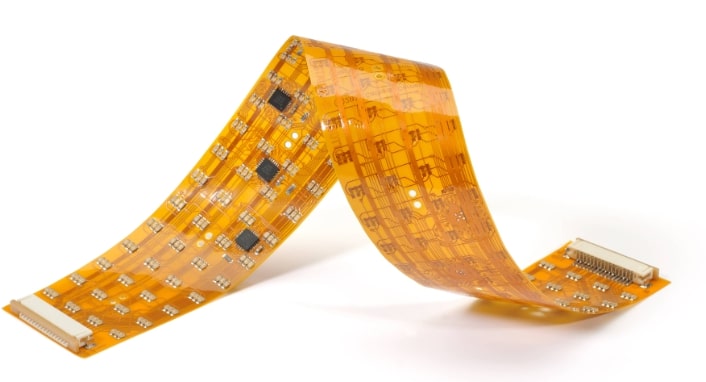
Manufacturing Process of Semi-flex PCBs
Lamination and Bonding: The flexible PCB is combined with the rigid PCB using lamination processes. The choice of adhesive and process control is critical to the quality of the semi-flexible PCB.
Patterning: This includes steps such as photolithography and etching to form circuit patterns on the board. Special care must be taken during the patterning of the flexible areas to ensure precision and durability.
Assembly and Testing: Components are soldered to the circuit board, and functional testing is performed to ensure all electrical connections and mechanical structures meet design requirements.
Advantages of Semi-flex PCBs
High Space Utilization: Semi-flex PCBs allow for complex circuit designs in confined spaces. The flexible portion can bypass obstacles, saving space and enhancing design flexibility.
Improved Reliability: By using rigid PCB sections for mechanical stability in critical areas and flexible parts where bending or movement is needed, the risk of breakage or poor connections due to over-bending is minimized.
Simplified Assembly Process: Semi-flex PCBs can integrate multiple components within the design, reducing the need for connectors and solder points, thus simplifying the assembly process and enhancing the reliability and stability of the product.
High Vibration Resistance: The flexible portion can absorb vibrations that occur during the operation of equipment, reducing connection issues caused by vibration and improving product durability.
Application Areas of Semi-flex PCBs
Medical Imaging Instruments: Semi-flex PCBs are widely used in medical devices such as endoscopes and imaging instruments. Endoscopes, for example, require a flexible design for easy insertion into the body to perform diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Automotive Applications: Semi-flex PCBs are used in automotive applications that experience high temperatures and vibrations. They are particularly suited for components like digital control units (DCU) and electronic control modules (ECM), which require PCB that can withstand temperatures up to 150°C without damage.
Wearable Devices: As wearable technology becomes more popular, semi-flexible and rigid-flex PCBs are found in devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers. Semi-flex PCBs are particularly used in fitness trackers due to their ability to bend with body movement.
Smartphones and Laptops: Semi-flex PCBs are often used in applications where the PCB needs to flex but not constantly bend. For instance, they are commonly used in high-end flexible smartphone displays and in the rigid back sections of devices like laptops.

Future Developments of Semi-flex PCBs
Advancements in Material Technology: As new flexible materials are developed, the performance and durability of Semi-flex PCBs will continue to improve. The use of ultra-thin and high-temperature-resistant materials will extend their use in extreme environments.
Improved Manufacturing Processes: The introduction of advanced manufacturing techniques will enhance the production efficiency and quality of Semi-flex PCBs. For example, advancements in laser cutting and high-precision printing technologies will improve patterning accuracy in flexible areas.
Integration and Smart Technology: As the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart devices evolve, Semi-flex PCBs will be utilized in a broader range of applications. Future designs will focus on higher integration and intelligence to meet the changing market demands.
Sustainability: Environmental protection and sustainability will become important considerations in the design and manufacture of Semi-flex PCBs. Developing eco-friendly materials and improving production processes to reduce environmental impact will be key areas of focus.
Conclusion
Semi-flex PCBs, which combine the benefits of rigid and Semi-flex PCBs, are playing an increasingly important role across various industries. As technology advances and demand for innovative applications grows, Semi-flex PCBs will continue to drive the development of electronic products, offering greater possibilities for future designs.