The LTCC process flow includes paste preparation - casting film - downstream - punching - through-hole filling - printing electrodes - printing passive components - single-layer inspection - stacking - hot pressing - slicing batch production - sintering - product inspection and other processes.
LTCC process flow is shown in the figure
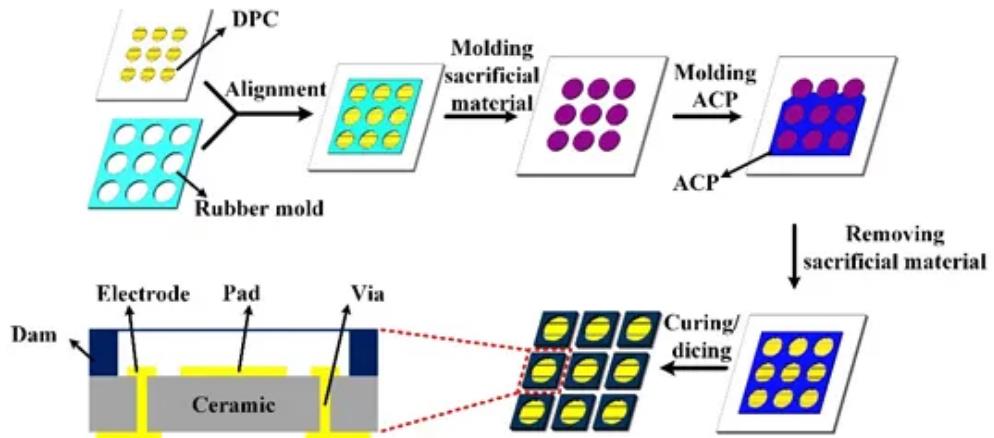
1.LTCC paste preparation:Organic and inorganic parts are mixed according to the appropriate ratio, and paste is formed through pulping.The organic part consists of solvent, dispersant, binder and plasticiser dissolved in solvent,while the inorganic part is microwave dielectric ceramic powder. The organic part is the key to the casting process,controlling the fluidity of the paste and the strength and plasticity of the raw ceramic tape. The size and distribution of the fineness of the inorganic powder has an effect on the uniformity of the paste.
2.LTCC drying to form a dense,thick 2.casting: the paste to remove air bubbles poured on the moving carrier belt is usually a polyvinyl acetate film degree of uniformity and sufficient strength of the raw ceramic tape,the raw ceramic tape will be rolled on the shaft for use.
3.Raw Ceramic Tape Unloading:Most of the raw ceramic tapes are supplied in the form of rolls, when cutting, they should be spread on a clean stainless steel working table, which can be used for cutting by cutting machine, laser or punch press,when slicing,the working table and blade should be heated, which can soften the binders and plasticiser in the raw ceramic tapes, and make the slicing edges smooth. If laser cutting is used, attention should be paid to controlling the power of the laser to avoid causing burns on the tape.
4.LTCC hole punching: hole punching includes punching fixed bit holes and interlayer through holes. Positioning holes are used to stack the single layer alignment, interlayer holes filled with metal conductors to achieve vertical interconnection of the conductors, some are used for heat dissipation. Drilling, punching and laser punching are the usual methods for punching holes, among which punching is faster and more accurate, with the smallest hole diameter up to 0.05mm,which is the commonly used punching method.
5.LTCC through-hole filling:through-hole filling methods include screen printing, negative pressure suction method and conductor filling method. Silk screen printing machine table is a porous ceramic or metal plate, each corner of a positioning column and raw ceramic film on the positioning holes consistent. When working, the underside of the table is vacuumed to negative pressure. Conductor sheet filling method is slightly greater than the thickness of the raw ceramic strip of the conductor sheet into the through-hole to achieve metallisation, the conductor sheet is generated using the casting process. This method can improve the reliability of multi-layer substrates, but the process is not mature enough.
6.Electrode LTCC Printing:Usually adopts screen printing method, but also can be used in computer direct tracing or film deposition method.Silk-screen printing technology is simple and easy to use, can get a higher rate of defence, line width up to 100 μ m,line spacing up to 150 μ m. If you require a smaller line width and line spacing, you can use thin film deposition or thin film lithography process.
7.Single layer LTCC inspection. Thick film printed conductor paste layout pattern, before sintering is not able to carry out electrical force measurement, the need to use non-electrical force measurement method of the layout of the layer to carry out topographic inspection. This includes the integrity of the layout pattern detection, the detection of redundant patterns, the detection of pattern variations.
8.LTCC stacking, hot pressing and slicing: the printed conductor and the formation of interconnecting holes in the raw ceramic sheet, according to the pre-designed number of layers and the order of the sequential alignment of stacking, at a certain temperature of 70-120 - . And pressure under 5-25MPa. compression to form a complete LTCC raw ceramic blank. After sintering the ceramic is not easy to cut, slicing process is the multi-layer ceramic raw ceramic blanks cut into smaller parts or other shapes.
9.LTCC co-firing: Firing is done according to the established sizing and sintering curves. 450 - before the heating rate should be slow, the organic binder will be vaporised or burned off, in 900 - around the ceramic densification and sintering. The key to this process is to ensure the consistency of the firing curve and furnace temperature to ensure the flatness of the product and shrinkage.
10.LTCC product testing: The sintered wafers are subjected to external inspection and electrical performance testing to verify the flatness of the wafers and the connectivity of the wiring.