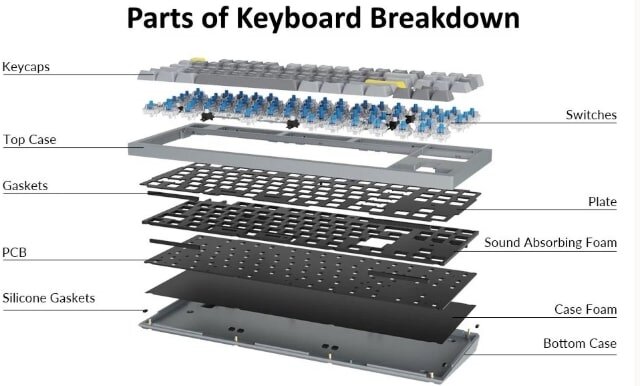
A keyboard PCB is one of the most crucial components of a mechanical keyboard. It connects all the keys, switches, and circuitry, transmitting the signal from each key press to the computer. You could say the keyboard PCB is the brain of the keyboard; without it, the keyboard cannot function properly.
The core components of a keyboard PCB include multi-layered conductive traces, pads for mounting switches, and, in some models, built-in LED lighting circuitry. Each time you press a key, the switch triggers the circuitry on the PCB, detecting the specific key pressed. High-quality keyboard PCBs often also include hot-swap interfaces, compatibility with various layouts, and RGB lighting functionality, greatly facilitating keyboard customization and personalization.
When buying a keyboard, we often hear terms like "RGB switches," "hot-swap," and "PBT keycaps." These terms are usually related to the PCB; for example, RGB switches relate to LEDs, hot-swap relates to the PCB's interface design, and PBT keycaps are a common component on a PCB.
There are several types of keyboard PCBs customized for different applications:
Mechanical Keyboard PCB – For mechanical keyboards, where each key uses an independent physical switch instead of a rubber dome membrane. This allows users to enhance tactile feedback using custom switch types.
Gaming Keyboard PCB – Optimized for gaming, featuring programmable RGB backlighting zones, macro keys, and anti-ghosting switch matrices.
Laptop Keyboard PCB – Compact and thin, designed for integration into compact laptop and laptop cases.
Ergonomic Keyboard PCB – Ergonomically laid out for natural wrist positioning and typing motion, reducing fatigue.
Flexible Keyboard PCB – Manufactured on a thin and flexible substrate, allowing the keyboard to roll/bend, ideal for portable applications.
Wireless Keyboard PCB – Combines wireless connectivity such as Bluetooth, allowing connection to host devices without physical cables.
Number Keyboard PCB – Contains only the numeric keypad section for financial/POS applications that require inputting numerical data.
Multimedia Keyboard PCB – Features dedicated keys for controlling multimedia applications, such as play/pause, volume control, etc. The choice depends on form factor, functionality, interface, and usage environment requirements.
keyboard PCB
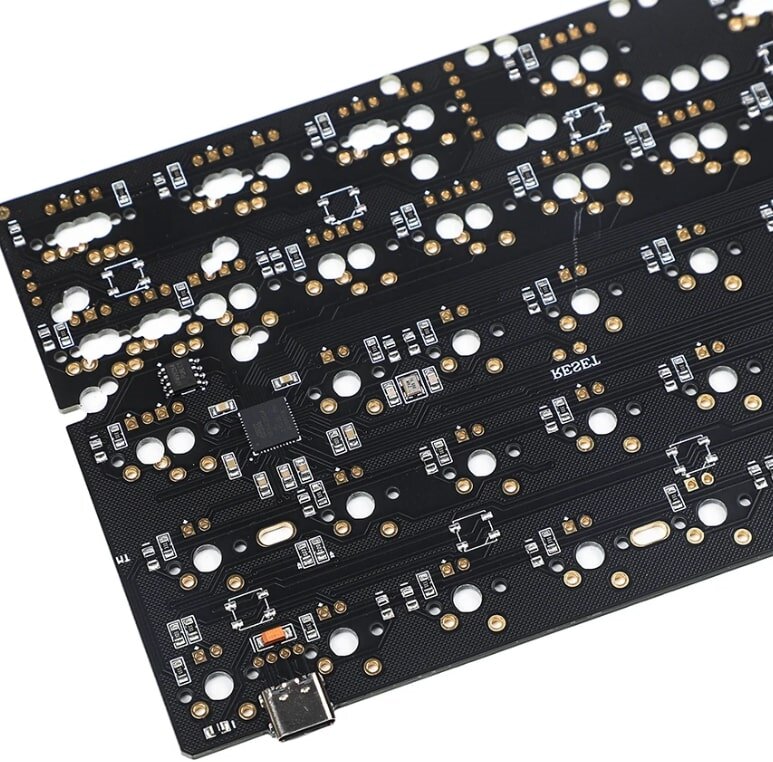
The keyboard's PCB is the core component, playing a crucial role in its performance and stability. When purchasing a keyboard, we need to pay attention to the PCB's design and manufacturing quality, as well as its related technical characteristics, to choose the most suitable keyboard for our needs.
How does a keyboard PCB work? Let's take a look at its working principle.
The PCB on a keyboard has the same primary function as the circuit boards on other devices. They connect electronic components together to function. Its main function is to transmit signals emitted by the keys.
When building a keyboard, you can add some functions. After checking the PCB, the next step is to clip or screw the stabilizer onto it. After this, you will hot-swap or solder all the switches on the PCB. One thing to remember before soldering the switches is that you can only remove or replace switches; if you try to age them, it takes time and could potentially damage your PCB.
After installing the switches and keycaps, you can check again to ensure all the keys on the PCB are working.
Keyboard PCB Functions and Innovations
Modern keyboard PCBs, beyond basic key recognition, incorporate numerous innovative designs, significantly enhancing the performance, customizability, and user experience of mechanical keyboards. Below are some key features detailed below:
1. Multi-layer Routing
Some high-end keyboard PCBs employ multi-layer routing designs, typically with 2, 4, or even more layers.
Enhanced Circuit Stability: Multi-layer designs separate power, ground, and signal layers, reducing electromagnetic interference and improving key response accuracy.
Function Expansion: Multi-layer PCBs allow for the addition of more function keys, macro keys, or special function areas without increasing board space or signal conflicts.
High-Frequency Application Optimization: For keyboards supporting high-speed input or gaming, multi-layer routing also reduces latency and crosstalk, ensuring accurate response under high-speed operation.
For example, a 75% layout keyboard supporting RGB lighting, multimedia keys, and macro functions might not be able to fully integrate these features without a multi-layer PCB design, or it might result in congested circuitry and increased noise.
2. Custom Firmware Support
Modern PCBs often support user programming, allowing for high customization using firmware such as QMK, VIA, or VIAL.
Key Function Customization: Users can modify the behavior of each key, such as changing Caps Lock to Ctrl or creating custom key combinations.
Macros: Programmable macros in firmware enable one-click input of complex operations, greatly improving office efficiency or gaming experience.
Lighting Effect Control: The mode, brightness, and color of RGB lighting can be freely adjusted via firmware to achieve personalized visual effects.
This design transforms the mechanical keyboard from just an input tool into a vehicle for user creativity and personalization.
3. Switch Compatibility
With the development of hot-swappable technology, more and more PCBs support mechanical switches from different brands and types.
Hot-Swappable Design: Users can easily replace switches without soldering, switching between different tactile or sound styles.
Strong Compatibility: Whether it's a Cherry, Gateron, Kailh, or other manufacturer's switch, as long as its specifications match the PCB's hot-swappable interface, it can be freely replaced. Easy Maintenance: If a key switch fails, simply remove it and replace it with a new one; no need for a complete overhaul, saving time and costs.
This design is especially important for DIY enthusiasts and gamers, allowing for easy adjustment of the keyboard feel to meet different usage needs.
4. Enhanced Signal Stability
High-end PCBs incorporate multiple optimizations in their circuit design to ensure signal stability:
Power and Ground Optimization: Isolation between power and ground layers in multi-layered PCBs reduces current fluctuations and noise interference.
Signal Line Length Matching: Matching the lengths of high-speed signal lines ensures that each key signal arrives at the control chip simultaneously, reducing input latency.
Anti-Crosstalk Design: Appropriate spacing and shielding on the PCB prevent key signals from interfering with each other during high-speed input.
These optimizations allow the keyboard to maintain extremely high accuracy and stability during high-speed input, e-sports competitions, or programming operations, reducing accidental key presses and key loss.
keyboard PCB
The Difference Between Keyboard PCBs and Other PCBs
The keyboard is an important computer peripheral, and its core component—the keyboard PCB (also called the keyboard controller or keyboard circuit board)—is responsible for converting key presses into signals that the computer can recognize. Compared to other types of PCBs, keyboard PCBs have distinct design and structural characteristics.
First, keyboard PCBs typically use a four-layer structure: two signal layers and two power/ground layers. This design ensures a thin and light keyboard while enhancing stability and anti-interference capabilities. Complex PCBs, such as motherboards or graphics cards, often use six or more layers to meet the routing requirements of high-density chips and complex functions.
Second, keyboard PCBs have fewer electronic components. Besides the keyboard controller and LEDs, there are almost no other components, which reduces costs and the risk of failure. In contrast, motherboard or graphics card PCBs need to integrate a large number of chips, interfaces, and functional modules, resulting in a large number of components and a complex layout.
Furthermore, the routing of keyboard PCBs is relatively simple, mainly connecting the controller, LEDs, and power and ground lines. Other PCBs, on the other hand, require complex routing between multiple chips and interfaces, while simultaneously considering signal integrity and high-speed transmission.
Keyboard PCBs differ significantly from other types of PCBs in design, component count, and routing. This is primarily due to factors such as the core functionality of the keyboard, cost control, and simplified design. However, these differences do not diminish the crucial role of the keyboard in computer use or the user's reliance on it.
Overall, the keyboard PCB is an indispensable core component of a mechanical keyboard. It not only transmits key signals to the computer but also affects the feel, typing sound, and overall stability. Whether you are an office user, a gamer, or a DIY keyboard enthusiast, understanding what a keyboard PCB is will help you better choose and use a mechanical keyboard.