FR4 PCB plate is a substrate made of FR-4 material. FR4 is a code for a flame-retardant material grade, meaning that the resin material must be able to self-extinguish after being exposed to fire. FR4 material is the foundation of any PCB circuit board. This material is laminated with a layer of copper foil using heat and adhesive. Copper foil can be laminated on one or both sides of the material. For simpler applications, FR4 material with a TG value of 130-140°C can be selected. For multilayer or thick circuit boards, and products requiring higher heat resistance, FR4 material with a TG value of 170-180°C should be used. With the advent of lead-free soldering processes, indicators such as TD, in addition to TG, also need to be considered. Furthermore, in lead-free soldering applications, a higher TG value does not always mean better performance. In other words, as the range of end applications expands, the range of available FR4 materials will also expand.

fr4 pcb plate
FR-4 is generally divided into:
FR-4 rigid boards, with common thicknesses of 0.8-3.2mm;
FR-4 thin boards, with common thicknesses less than 0.78mm.
Advantages of FR4 PCB plate material
FR4 dominates PCB manufacturing for good reason. Here are its outstanding advantages:
- Cost-effectiveness: Compared to advanced materials like Rogers or PTFE, FR4 offers unparalleled value, helping to control project budgets.
- Reliability: Decades of use have made FR4's behavior predictable, reducing design risks and ensuring consistent performance.
- Versatility: From single-layer boards to complex multilayer designs, FR4 adapts to diverse manufacturing needs.
- Availability: With a global supply chain, FR4 is readily available, minimizing procurement delays.
- Ease of manufacturing: FR4 is compatible with standard processes (drilling, etching, and lamination), simplifying production.
These advantages make FR4 the default choice for most PCB applications, balancing performance with practicality.
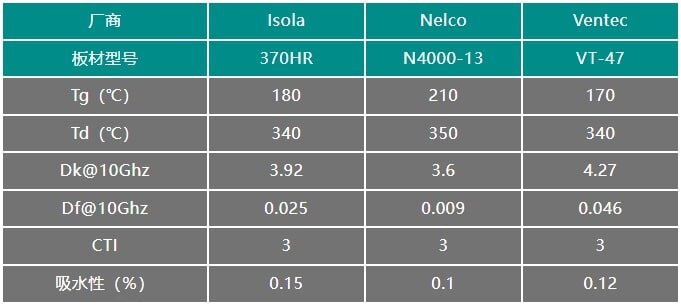
FR-4 Performance Specifications
The performance indicators of FR-4 substrate include: glass transition temperature (Tg), thermal decomposition temperature (Td), dissipation factor (Df), dielectric constant (Dk), comparative tracking index (CTI), coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), water absorption rate, and material adhesion characteristics.
FR4
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) and Thermal Decomposition Temperature (Td)
The Tg value refers to the temperature point at which the material transitions from a relatively rigid "glass" state to a more easily deformable state. As long as the thermal decomposition temperature (Td) is not reached, this thermodynamic change is reversible; when cooled below the Tg value, the material can return to its rigid state. When the temperature exceeds the thermal decomposition temperature, FR-4 will decompose and fail.
The industry typically categorizes FR-4 boards into three grades based on their Tg values:
Low Tg FR-4: Tg value around 135℃;
Medium Tg FR-4: Tg value around 150℃;
High Tg FR-4: Tg value around 170℃.
High Tg boards should be selected if the PCB manufacturing process involves multiple lamination cycles, a high number of layers, high soldering temperatures (≥230℃), high operating temperatures (above 100℃), and high soldering thermal stress (such as wave soldering).
Dissipation Factor (Df) and Dielectric Constant (Dk)
Dielectric constant and dielectric loss angle are two fundamental properties of a dielectric material. These two parameters change with frequency. A higher dissipation factor (Df) results in greater attenuation. The dielectric constant (Dk) primarily affects impedance.
FR-4 can be classified according to its dissipation factor (Df):
Ordinary loss board: Df ≥ 0.02
Medium loss board: 0.01 ≤ Df < 0.02
Low loss board: 0.005 ≤ Df < 0.01
Ultra-low loss board: Df < 0.005
In PCB manufacturing, the selection of FR4 material should be based on specific project requirements. For most conventional applications, such as consumer electronics and automotive electronics, standard FR4 offers a good balance between cost, mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and heat resistance, making it an ideal choice. If the product needs to operate in high-temperature environments, high-Tg FR4 is more suitable for power supplies and industrial equipment due to its higher glass transition temperature and better thermal stability.
In high-frequency or radio frequency applications, standard FR4 often fails to meet performance requirements. In such cases, high-frequency or high-speed materials should be used to achieve lower signal loss and more stable signal transmission, widely used in communications, aerospace, and medical equipment. Additionally, low-flow FR4 is suitable for complex multi-layer PCBs, reducing voids and improving lamination accuracy, ensuring the reliability of high-density interconnect boards. In summary, only by fully understanding the project's requirements in terms of reliability, temperature resistance, and signal performance can the most suitable material be selected, thus ensuring the overall performance and long-term lifespan of the FR4 PCB plate.