Antenna for industrial wireless systems (motherboard is high-frequency PCB/RF PCB)
As one of the key components of industrial wireless systems, antennas are specialized devices that convert high-frequency electromagnetic energy in transmission lines into free electromagnetic waves in space or convert free electromagnetic wave energy in space into high-frequency electromagnetic energy in space. Transmission line. So choosing the right antenna is very important for the performance of wireless networks.
According to the radiation direction, antennas can be divided into two categories: omnidirectional antennas and directional antennas.
Omnidirectional antennas propagate in all directions.
Directional antennas propagate highly in very narrow "beams"; The more common ones are parabolic antennas and Yagi antennas. Each type has its unique characteristics and applications
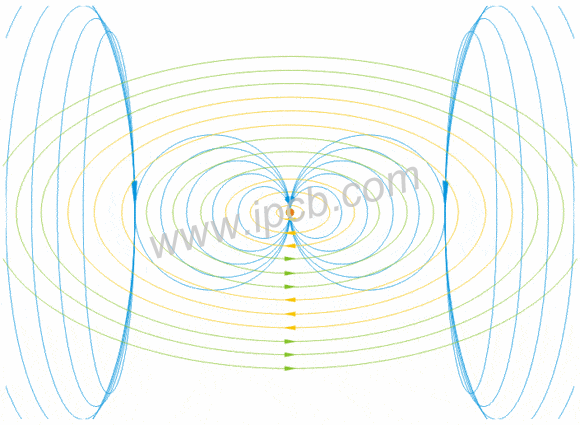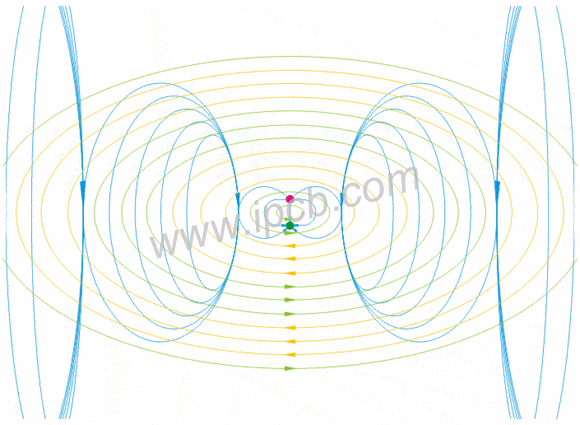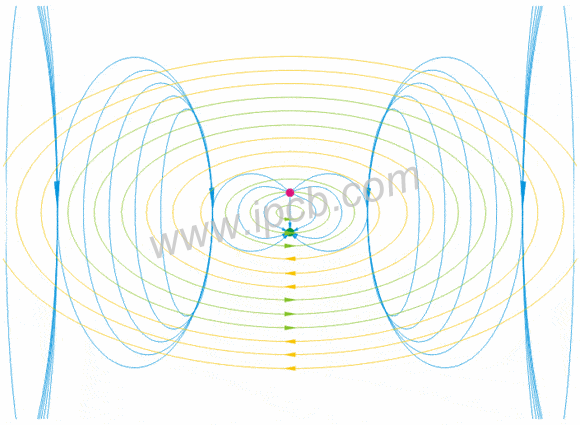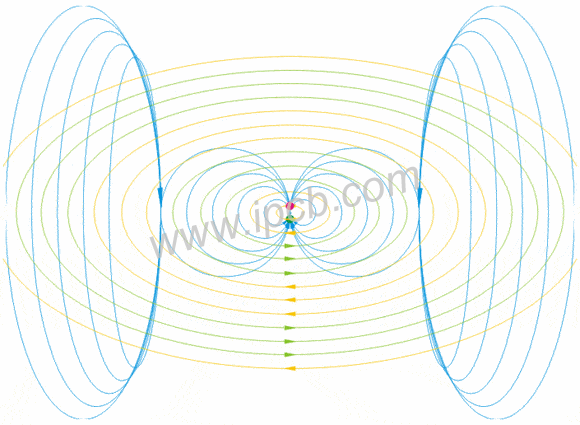
Industrial wireless system antenna
The basic model of wireless communication mainly consists of a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter encodes speech, video, and various data into sinusoidal electromagnetic waves and emits them. The receiver receives and decodes these electromagnetic waves to obtain data. Both the transmitter and receiver require the use of antennas. An Antenna is a device that converts an electric field into electromagnetic waves.
Antennas convert electric fields into magnetic fields, forming electromagnetic waves to transmit signals. Conversely, they convert magnetic fields into electric fields and transmit them to devices through lines, thus forming wireless signal transmission and reception.
Industrial wireless technology can provide secure and reliable wireless connections for industrial applications. According to the requirements, use IWLAN or Bluetooth for real-time communication, use NearFi for close range applications, or use LoRaWAN and Trusted Wireless for long-distance applications.
Correct use of antenna
Antennas are an important component of wireless communication. Appropriate antennas can optimize wireless networks, increase communication range and reliability, while the opposite can lead to a decrease in communication quality. How to choose an antenna correctly? First, it is necessary to understand the antenna parameters: frequency, matching impedance, voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR), gain, and polarization. For industrial wireless communication products, the common antenna parameters in the product manual are operating frequency and gain.
working frequency
Antennas are used to emit and receive electromagnetic waves, like a converter that converts current into electromagnetic waves and then converts electromagnetic waves back into current. The most important parameter is the operating frequency. For example, using a 2.4 GHz antenna for communication with IEEE 802.11a standard devices (operating in the 5G frequency band) may result in very poor signal quality or a decrease in transmission rate, similar to the feeling of shoes not fitting while running.
Another common parameter is gain. The antenna gain represents the degree of energy concentration and conversion efficiency of the antenna on the signal. The gain of adding wireless communication is not to amplify the signal, but to concentrate the energy of the signal. Gain can affect the direction of antenna operation. Generally speaking, the higher the gain, the stronger the directionality of the antenna. Conversely, the radiation distribution in all directions becomes more uniform.