Share the millimeter wave radar precision change from 24GHz to 77GHz in the radar band and the advantages of 77G vs 24G.
Comparison of 24GHz and 77GHz bands
1.24GHz Band
The frequency band we are interested in is shown in the figure.The frequency band from 24.0GHz to 24.25GHz is a narrow band (NB) with a bandwidth of 250MHz, which is commonly used in industry, science and medicine. There, the 24GHz band also covers a bandwidth of 5GHz for Ultra Wideband (UWB).
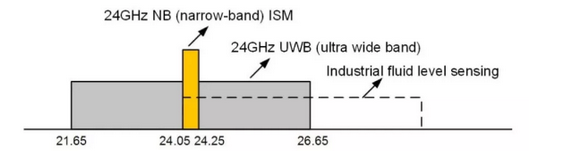
24GHz Band
Among the short-range radars,NB and UWB radars in the 24 GHz band have been applied to conventional transportation sensors. NB radar can be used for simple applications such as inspection and determination of points on the retina that cannot be stimulated by light,but UWB radar is required in most cases covering ultra-short distances because of the need for high frequency defense rate.
However, because of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) and the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to develop the spectrum rules and standards, UWB band will soon be phased out layer by layer.2022 after January 1, UWB band will not be able to use in Europe and the United States and the United States of America, only the narrow-band ISM band can be used in the long term.
The lack of bandwidth in the 24GHz band, coupled with the need for higher performance in recently emerging radar applications,means that the 24GHz band has no gravitational pull on recently emerging radars,especially in the transportation sector where there is now a 50/50 interest in automatic parking and panoramic views.
2.77GHz Band
Turning back to the 77GHz band,where the 76-77GHz band can be used for long range vehicular radar,it also has the advantage of equivalent isotropic isotropic radiated power (EIRP),which can be used to choke long range front-end radar, such as adaptive patrol navigation chokes.
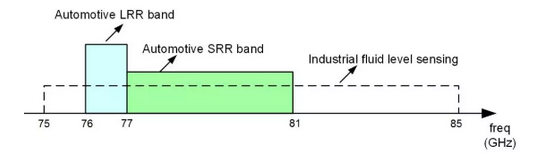
77GHz Band
The band is used in East Asia and Europe for radar systems in traffic infrastructures to perform tasks such as vehicle counting, traffic obstruction, accident detection, speed surveys,and traffic light acquisition by detected vehicles. 77-81 GHz Short Range Radar (SRR) band is a new entry;this band has recently achieved significant attraction in surveillance management and industry fitness for purpose around the world.This band has recently achieved significant traction in monitoring the status of events around the world and in the industry's perceived fitness for use.At the same time,the band can supply a wide E-Scan bandwidth of up to 4 GHz,which is well suited for applications requiring high range defense rate (HRR).
Looking ahead,it is likely that most 24 GHz vehicle radar sensors will move to the 77 GHz band.
Advantages of the 77GHz Band for Transportation and Industrial ApplicationsThe following section introduces the advantages of the 77GHz band for transportation and industrial applications.
Advantage 1:High Distance Defense Rate and Distance Measurement Precision
Compared with the ISM band with only 200MHz bandwidth under the 24GHz band, the SRR band under the 77GHz band can provide up to 4GHz of scanning bandwidth, which significantly increases the distance defense rate and precision. There, the distance defensibility expresses the experience of the radar sensor in being able to isolate two neighboring objects,and the distance precision expresses the very high accuracy when surveying a single object.
Because the distance defense rate and precision are inversely proportional to the electron scanning bandwidth,because of this,compared with the 24GHz radar, the 77GHz radar sensor has a better performance in distance defense rate and precision, which can be found to be increased by a factor of 20 through testing. In fact, the 77GHz radar can successfully achieve a distance defensibility of 4cm (24GHz radar defensibility is 75cm).
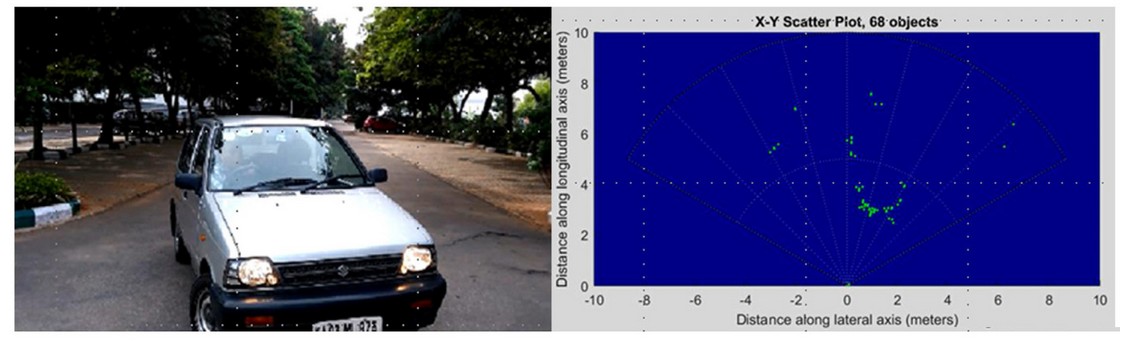
77GHz Radar
High distance defensibility can better isolate the object (e.g., a person standing close to the vehicle) and provide inspection to determine the object's dense distribution point, thus completing the background modeling and object classification, which is very important for the development of advanced manipulation algorithms and semiautomatic manipulation functions.
In addition, the higher the defense rate, the smaller the minimum distance of the sensing air vision recognition, because of this in parking assistance and other applications requiring high accuracy, 77-81GHz radar has a significant advantage.
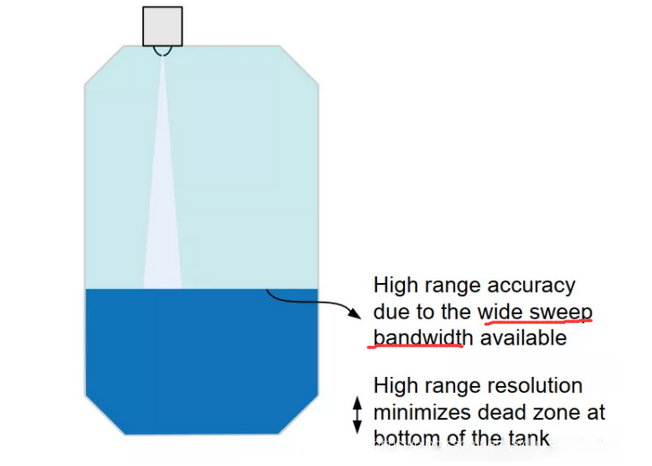
77-81GHz Radar Advantage
English Explanation: 1) High distance measurement precision due to the wide E-Scan bandwidth available; 2) High distance defense rate to minimize dead zones at the bottom of water-filled tanks.
The wide bandwidth of the 77GHZ frequency band has a high defense rate, which can be used in industrial level sensors, enabling the sensor to “survey to the last drop” of liquid level - minimizing the dead zone at the bottom of the water container, as shown in the figure. Also, because of the high whiteout ratio, the minimum survey distance can be improved, as this allows the sensor to survey the level at the top of the water container when the container is full.
Advantage 2: High Speed Defense and Precision
Speed defensibility and precision are inversely proportional to the radio frequency (RF) frequency. Because of this, the higher the frequency, the better the defense and precision. Compared to a 24 GHz sensor, a 77 GHz sensor will.
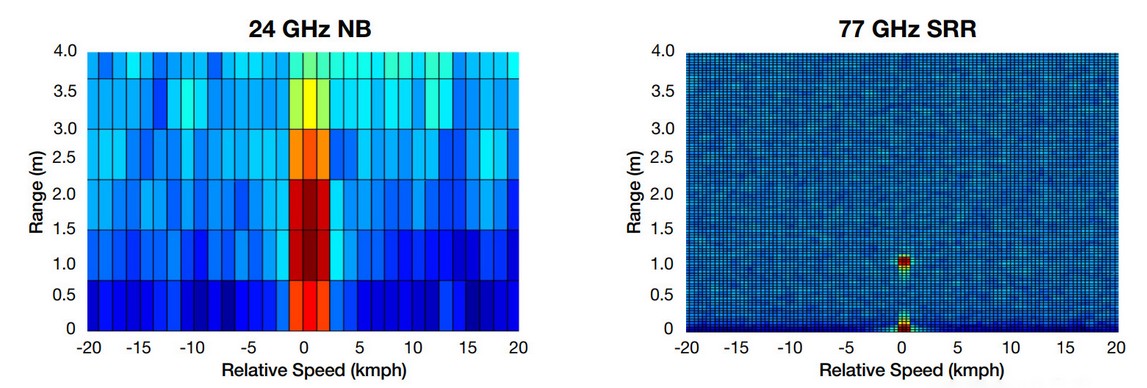
24G vs 77G
For transportation parking assistance applications,velocity defensibility and precision are critical because of the need to drive the vehicle correctly at low speeds while parking.Fig. 4 shows a representative FFT distance-velocity image of a point object at 1m, and depicts the improved defensibility of the 2D image obtained using 77GHz.
In addition to this, recent studies have further improved pedestrian inspection measurements and advanced object classification algorithms by utilizing millimeter wave radar with higher deflection rates and micro-Doppler signals. The increase in speed measurement precision will help industrial applications, as well as improving things like traffic inspection measurements in the current semi-automated vehicle environment.
Advantage 3: Smaller size of 77G compared to 24G
One of the main advantages of higher RF frequencies is that the sensor size can be smaller.For the same receiver antenna field of view and gain,the 77GHz receiver antenna array can be reduced in size by a factor of about 3 in the X and Y dimensions (see figure). This reduction in size is very useful in transportation, primarily in applications around the perimeter of the vehicle (covering doors and trunks where proximity sensors are required) and inside the vehicle.
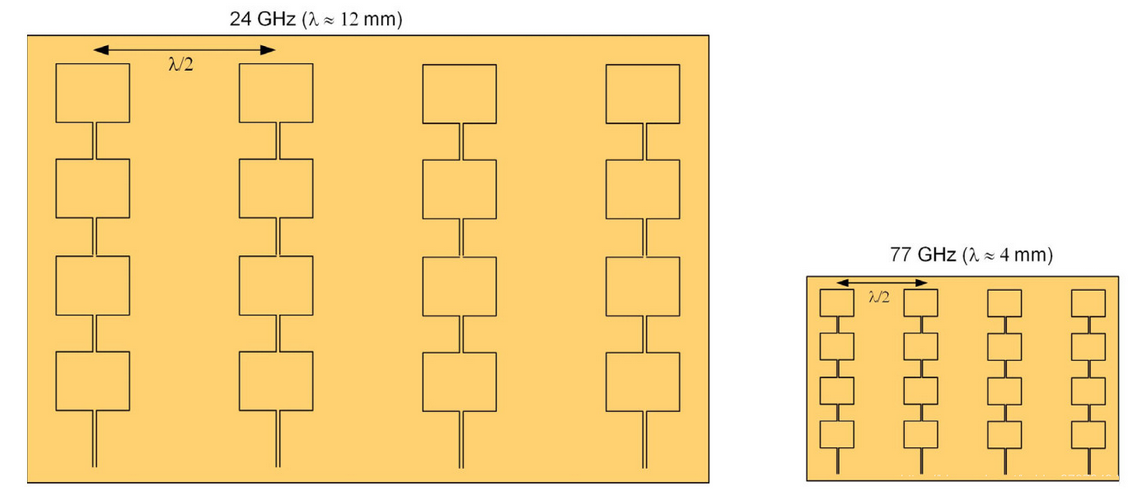
24G vs 77G
In industrial fluid parallel line sensing,a higher RF frequency provides a narrower beam for the same size receiving antenna and sensor. As shown in the figure, a narrower beam reduces unwanted reflections from the sides of the water box and interference from other tripwires inside the box,resulting in a more accurate survey end result. In addition,for the same wide beam, the higher the RF frequency, the smaller the size of the sensor and the easier it is to install.
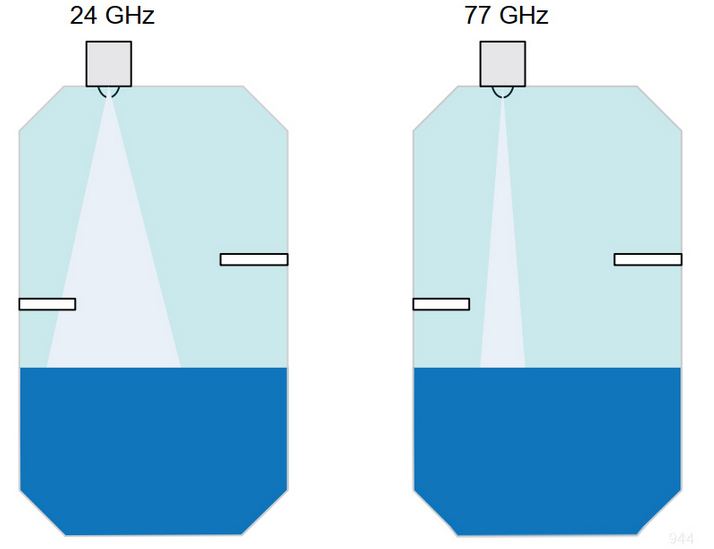
24G vs 77G
Generalization of 77G and 24G
The 24GHz has the advantage of being in the unauthorized ISM band and worldwide frequency tuning support,but only 200MHz of bandwidth is available,whereas the 77GHz has a usable bandwidth of 4GHz, which has stopped its progress.
TI's highly integrated and easy-to-use 77GHz millimeter wave radar facilities enable the development of compact, high-performance radar sensors for a variety of transportation and industrial applications.