CNC PCB milling has emerged as one of the most versatile and efficient methods for producing printed circuit boards (PCBs), offering significant advantages over traditional etching techniques. For anyone involved in PCB manufacturing or those interested in DIY PCB fabrication, understanding the basics of CNC milling can lead to higher precision and a more streamlined production process. In this article, we will delve into the details of CNC PCB milling, exploring its benefits, the equipment used, and how it compares to other PCB fabrication methods.
What is CNC PCB Milling?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece, in this case, a copper-clad PCB. Unlike traditional PCB manufacturing processes that often involve chemical etching, CNC milling offers a more controlled and environmentally friendly method for creating the intricate traces, pads, and vias required on a PCB.
This technique involves a CNC machine, which is programmed with the design of the PCB. The machine then automatically mills out the desired traces and features by removing the unwanted copper from the board’s surface. The precision of CNC milling makes it suitable for both prototype and low-volume PCB production, as it allows manufacturers to achieve high-quality boards quickly without relying on large-scale industrial processes.
The CNC Milling Process for PCBs
The CNC PCB milling process typically involves the following steps:
Design Preparation: The first step is to create the PCB design using specialized software like Eagle, KiCAD, or Altium Designer. The design should include all traces, pads, holes, and other components necessary for the PCB layout. Once the design is complete, it is exported in a format compatible with CNC machines, such as Gerber files or G-code.
Machine Setup: The CNC milling machine must be prepared with the appropriate bit sizes for drilling, cutting, and engraving. For PCB milling, very fine bits are required, usually ranging from 0.1mm to 0.5mm in diameter, to achieve the necessary precision. A copper-clad board is placed securely on the machine’s work table, and the machine is calibrated to ensure accurate depth and alignment.
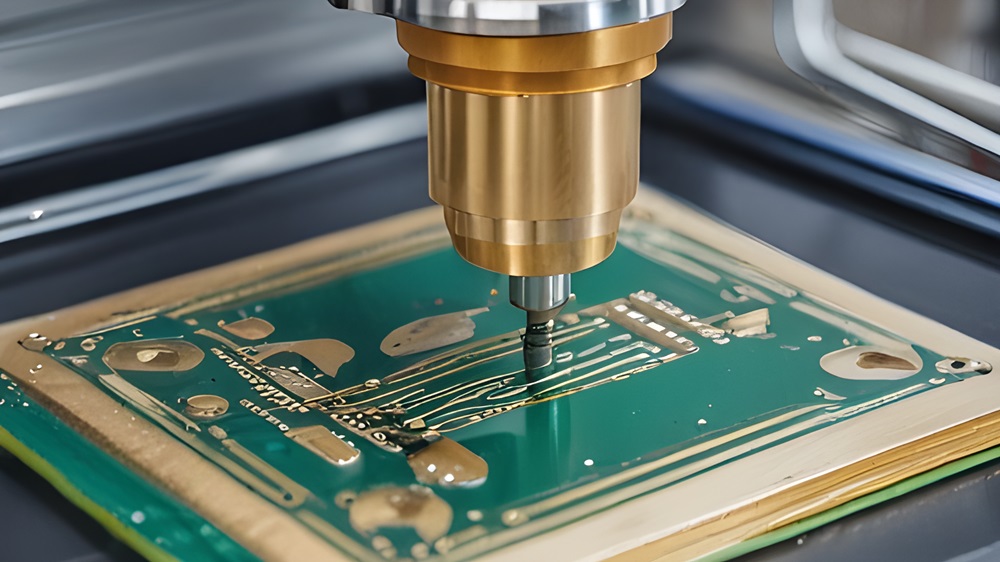
Milling Process: The CNC machine reads the G-code generated from the design software and begins the milling process. The machine uses the milling bits to carve out the necessary patterns on the copper-clad board, removing unwanted copper and leaving behind the desired circuit traces. Additionally, the CNC machine can drill through-holes for vias or component placement.
Post-Milling Steps: After milling, the PCB is cleaned to remove any copper debris. The next steps may include solder mask application, component soldering, and final testing. The milled PCB can either be used directly or undergo further refinement for more complex designs.
Advantages of CNC PCB Milling
Precision: CNC PCB milling provides exceptional precision, making it an ideal method for intricate designs and complex PCB layouts. The ability to control the milling depth and trace width ensures that even fine-pitch components can be reliably produced.
Prototyping Flexibility: One of the most significant advantages of CNC PCB milling is the ability to quickly produce prototypes. Traditional PCB manufacturing often requires lengthy setup times and expensive tooling. CNC milling, however, can create prototypes in a matter of hours, making it highly suitable for rapid prototyping and small-scale production.
No Chemical Usage: CNC milling eliminates the need for harmful chemicals used in traditional etching processes. This makes the process more environmentally friendly and safer for manufacturers.
Cost-Effective for Small Batches: CNC milling can be more cost-effective for small production runs compared to industrial-scale PCB manufacturing, which requires large quantities to be economical. The flexibility of CNC machines makes it possible to produce custom or small-volume PCBs without high upfront costs.
On-Demand Production: With CNC milling, PCBs can be produced on-demand, eliminating the need for large inventories. This also allows for quick adjustments in design without wasting materials or resources.
Equipment Needed for CNC PCB Milling
To start milling PCBs using CNC technology, a few essential pieces of equipment are required:
CNC Milling Machine: The heart of the process, CNC milling machines come in various sizes and capabilities. For PCB milling, a small desktop CNC machine can suffice, especially for DIY or small-scale operations. More advanced machines are available for high-precision work and larger production runs.
Milling Bits: A variety of milling bits are used in PCB milling, including engraving bits, cutting bits, and drill bits. These tools must be capable of working with delicate materials like copper and FR4 (fiberglass).
PCB Design Software: CAD software is essential for creating the PCB layout. As mentioned earlier, popular programs like Eagle, KiCAD, and Altium Designer allow users to design and generate the G-code or Gerber files necessary for CNC milling.
Copper-Clad Boards: These are the raw materials used in CNC milling. Copper-clad boards come in different sizes and thicknesses, and the choice of board depends on the requirements of the PCB design.
Soldering Tools: Once the PCB is milled, components will need to be soldered onto the board. This includes solder paste, soldering irons, and other necessary tools for component placement.
CNC PCB Milling vs. Traditional Etching
While CNC PCB milling has clear advantages, it is important to understand how it compares to the traditional chemical etching method.
Process Complexity: Etching requires a multi-step process involving photoresist, UV exposure, and chemical baths. CNC milling, on the other hand, is a one-step process once the design is complete.
Cost: For large production runs, chemical etching is often more cost-effective due to economies of scale. CNC milling is better suited for low-volume, high-precision work or prototyping.
Time: CNC milling is generally faster for small runs since there is no need to set up complex chemical processes. However, for larger runs, the speed of chemical etching becomes an advantage due to its ability to process many boards at once.
Precision: CNC milling provides excellent precision, especially for complex designs with fine features. Chemical etching can also be precise but may require additional steps, such as applying a protective solder mask.
Environmental Impact: Chemical etching uses hazardous chemicals that require careful disposal and environmental considerations. CNC milling is a cleaner process, producing only copper shavings that are easier to manage.
Applications of CNC PCB Milling
CNC PCB milling is widely used in various fields due to its flexibility and precision. Some of the key applications include:
Prototyping: Engineers and designers often use CNC milling to quickly produce prototypes during the development phase of new products. This allows for rapid iteration and testing.
Custom PCBs: CNC milling is ideal for producing custom PCBs for specialized applications where mass production is unnecessary.
DIY Projects: Hobbyists and makers frequently use desktop CNC machines to create PCBs for DIY electronics projects.
Small Batch Production: Startups and small businesses benefit from the cost-effectiveness of CNC milling for producing limited quantities of PCBs for niche products.
Conclusion
CNC PCB milling offers a practical, precise, and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional PCB manufacturing processes. Whether used for prototyping, custom production, or small batch manufacturing, CNC milling provides an efficient way to produce high-quality PCBs without the need for large-scale industrial processes. As CNC technology continues to improve, it is likely that more industries and individuals will adopt CNC milling as a go-to method for PCB fabrication.
For businesses looking to enhance their PCB production capabilities or hobbyists eager to create their own designs, CNC PCB milling offers a world of possibilities. With the right tools, software, and expertise, anyone can create intricate, reliable PCBs with ease.