The quality of packaging will directly affect the performance of the chip itself and the design and manufacturing of the PCB connected to it. Therefore, packaging technology is crucial.
An important indicator to measure the advancedness of a chip packaging technology is the ratio of chip area to packaging area. The closer this ratio is to 1, the better.
The main factors to consider when packaging:
• The ratio of chip area to packaging area should be as close to 1:1 as possible to improve packaging efficiency;
• The pins should be as short as possible to reduce delays, and the distance between pins should be as far as possible to ensure no interference and improve performance;
• Based on the requirements of heat dissipation, the thinner the package, the better.
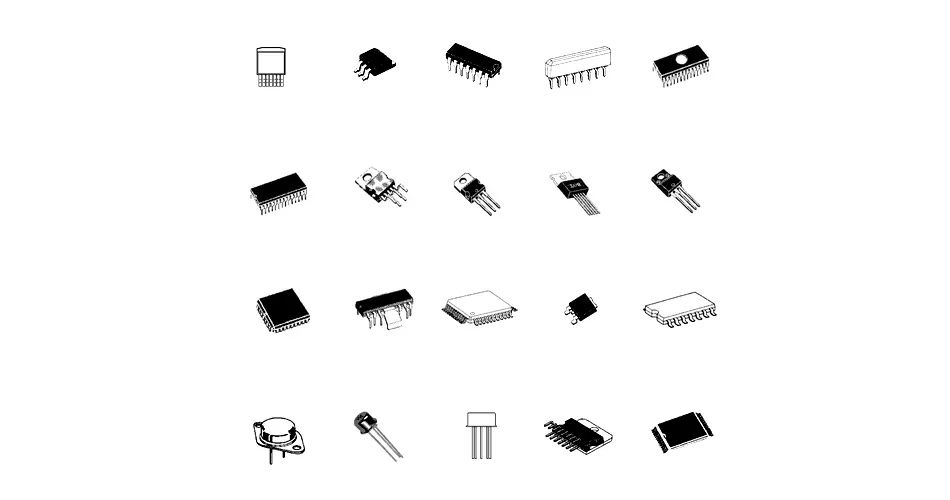
9 Packaging Technologies
The packaging has roughly gone through the following development process: • Structure: TO→DIP→PLCC→QFP→BGA→CSP • Material: metal, ceramic→ceramic, plastic→plastic • Pin shape: long lead straight insertion→short lead or leadless mounting→ball bump • Assembly method: through-hole mounting→surface mounting→direct mounting
9 Common Component Packaging Technologies in PCBA Processing:
SOP/SOIC package:SOP is the abbreviation of Small Outline Package in English, that is, small outline package. SOP packaging technology was successfully developed by Philips in 1968-1969, and then gradually derived:
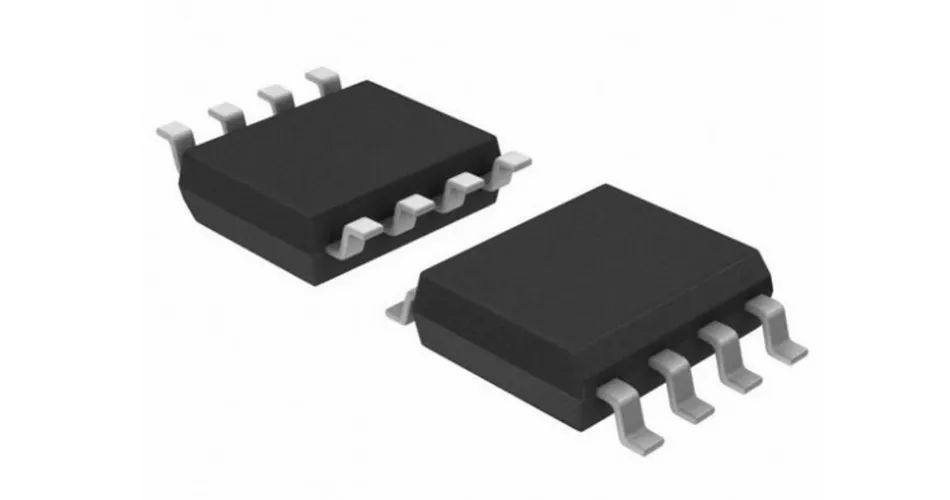
SOP/SOIC package
l SOJ, J-type pin small outline package
l TSOP, thin small outline package
l VSOP, very small outline package
l SSOP, reduced SOP
l TSSOP, thin reduced SOP
l SOT, small outline transistor
l SOIC, small outline integrated circuit
2. DIP package: DIP is the abbreviation of "Double In-line Package" in English, that is, dual in-line package.
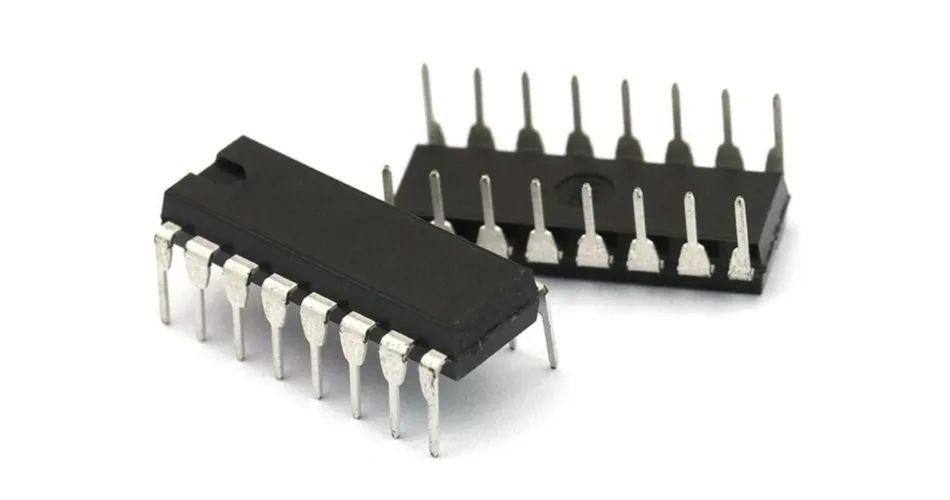
DIP Pacakage
One of the plug-in packages, the pins are led out from both sides of the package, and the packaging materials are plastic and ceramic. DIP is the most popular plug-in package, and its application range includes standard logic IC, memory LSI, microcomputer circuit, etc.
3. PLCC package: PLCC is the abbreviation of "Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier" in English, that is, plastic J lead chip package.
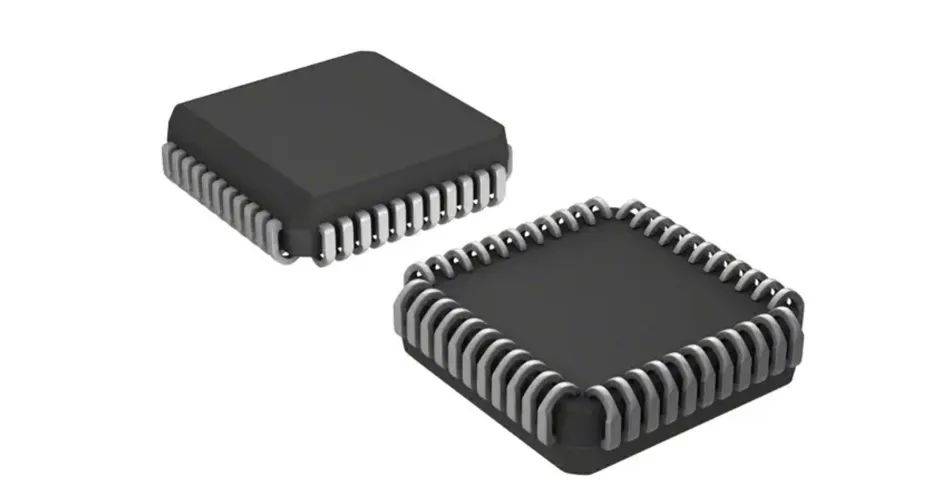
PLCC Package
PLCC packaging method, square shape, 32-pin package, pins all around, much smaller than DIP package. PLCC package is suitable for installation and wiring on PCB using SMT surface mounting technology, with the advantages of small size and high reliability.
4. TQFP package: TQFP is the abbreviation of "Thin Quad Flat Package" in English, that is, thin plastic quad flat package. The quad flat packaging process can effectively utilize space, thereby reducing the requirements for the size of the printed circuit board space.
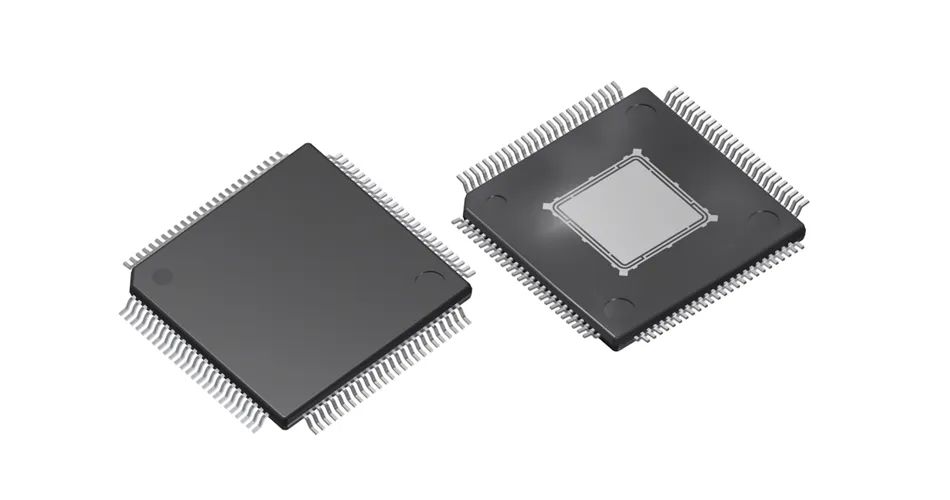
TQFP Package
Due to the reduction in height and volume, this packaging process is very suitable for applications with high space requirements, such as PCMCIA cards and network devices. Almost all ALTERA's CPLD/FPGA have TQFP packaging.
5. PQFP package: PQFP is the abbreviation of "Plastic Quad Flat Package" in English, that is, plastic quad flat package.
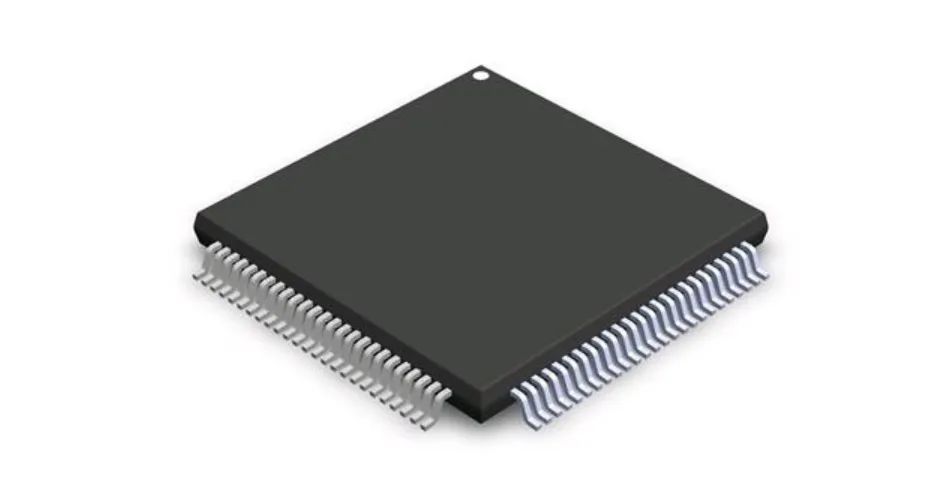
PQFQ Package
The distance between the chip pins of PQFP package is very small, and the pins are very thin. Generally, large-scale or ultra-large-scale integrated circuits use this packaging form, and the number of pins is generally more than 100.
6. TSOP package: TSOP is the abbreviation of "Thin Small Outline Package" in English, that is, a thin and small size package. A typical feature of TSOP memory packaging technology is to make pins around the packaged chip. TSOP is suitable for installing wiring on PCB using SMT (surface mounting) technology.
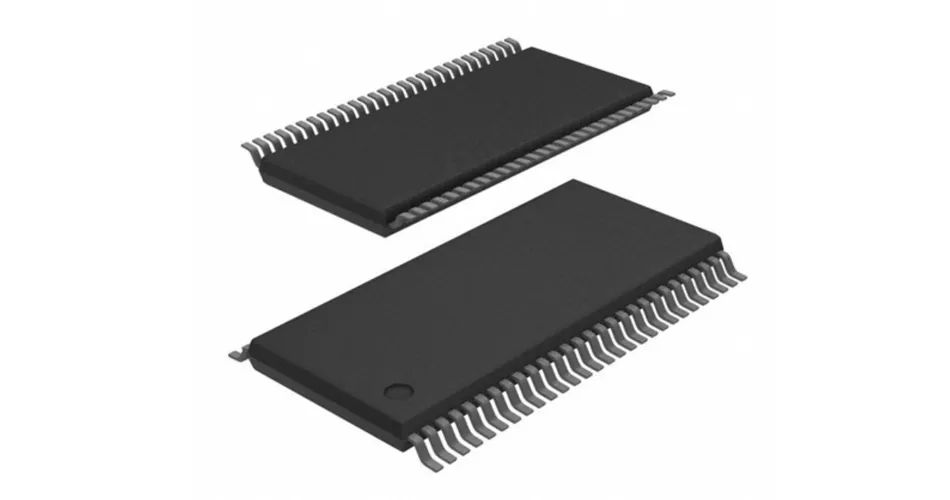

TSOP Package
TSOP package shape, parasitic parameters (when the current changes greatly, it causes output voltage disturbance) are reduced, suitable for high-frequency applications, easy to operate, and reliable.
7. BGA package: BGA is the abbreviation of "Ball Grid Array Package" in English, that is, ball grid array package. In the 1990s, with the advancement of technology, the integration of chips continued to increase, the number of I/O pins increased sharply, power consumption also increased, and the requirements for integrated circuit packaging became more stringent. In order to meet the needs of development, BGA packaging began to be used in production.
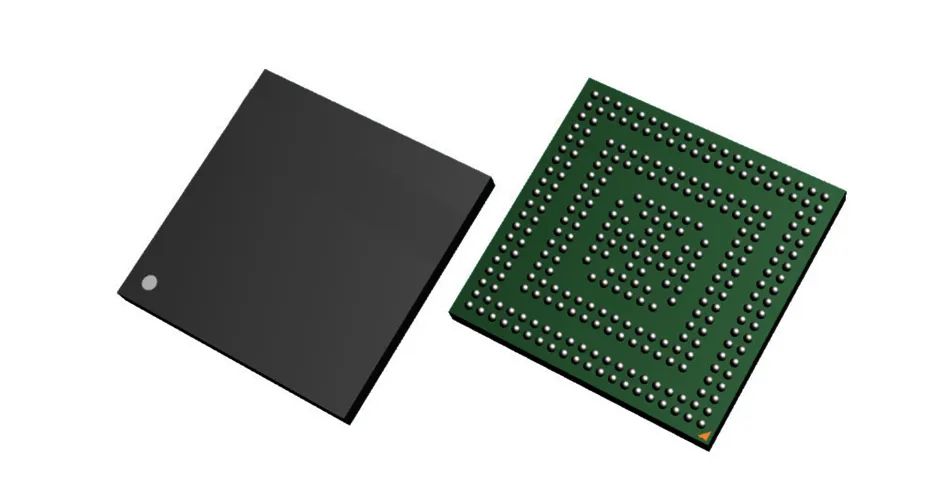
BGA Package
Memory packaged with BGA technology can increase the memory capacity by two to three times without changing the volume. Compared with TSOP, BGA has a smaller volume, better heat dissipation and electrical performance. BGA packaging technology has greatly increased the storage capacity per square inch. The volume of memory products using BGA packaging technology is only one-third of that of TSOP packaging at the same capacity. In addition, compared with the traditional TSOP packaging method, BGA packaging has a faster and more effective heat dissipation path.
The I/O terminals of BGA packaging are distributed under the package in the form of circular or columnar solder joints in an array. The advantage of BGA technology is that although the number of I/O pins has increased, the pin spacing has not decreased but increased, thereby improving the assembly yield rate. Although its power consumption has increased, BGA can be welded using the controlled collapse chip method, which can improve its electrothermal performance. The thickness and weight are reduced compared with previous packaging technologies; parasitic parameters are reduced, signal transmission delay is small, and the frequency of use is greatly increased; coplanar welding can be used for assembly, and the reliability is high.
8. Tiny BGA packaging: When it comes to BGA packaging, we cannot fail to mention Kingmax's patented Tiny BGA technology. TinyBGA is called "Tiny Ball Grid" in English. It is a branch of BGA packaging technology. The ratio of its chip area to packaging area is not less than 1:1.14, which can increase the memory capacity by 2 to 3 times without changing the volume. Compared with TSOP packaging products, it has a smaller volume, better heat dissipation and electrical performance.
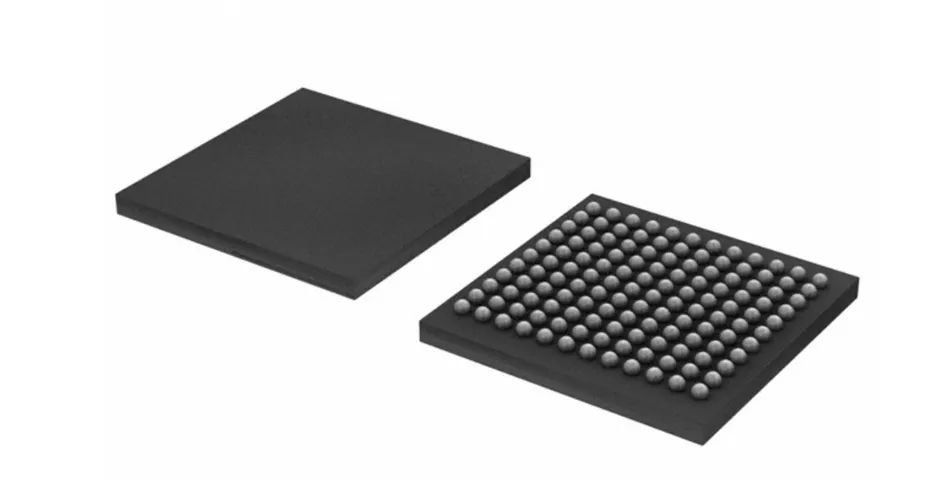
TinyBGA Package
Memory products using Tiny BGA packaging technology have a volume of only 1/3 of TSOP packaging under the same capacity. The pins of TSOP packaged memory are led out from the four sides of the chip, while TinyBGA is led out from the center of the chip. This method effectively shortens the signal transmission distance, and the length of the signal transmission line is only 1/4 of the traditional TSOP technology, so the signal attenuation is also reduced. This not only greatly improves the chip's anti-interference and anti-noise performance, but also improves the electrical performance. Chips packaged with TinyBGA can withstand external frequencies up to 300MHz, while traditional TSOP packaging technology can only withstand external frequencies of up to 150MHz.
The memory of TinyBGA package is also thinner (package height is less than 0.8mm), and the effective heat dissipation path from the metal substrate to the heat sink is only 0.36mm. Therefore, TinyBGA memory has higher thermal conductivity efficiency, is very suitable for long-term running systems, and has excellent stability.
9. QFP package: QFP is the abbreviation of "Quad Flat Package", which is a small square flat package. QFP package is frequently used in early graphics cards, but there are few QFP packaged video memory with a speed of more than 4ns. Due to process and performance issues, it has been gradually replaced by TSOP-II and BGA. QFP package has pins around the particles, which is quite obvious to identify. Four-side pin flat package. One of the surface mount packages, the pins are led out from the four sides in a gull wing (L) shape.
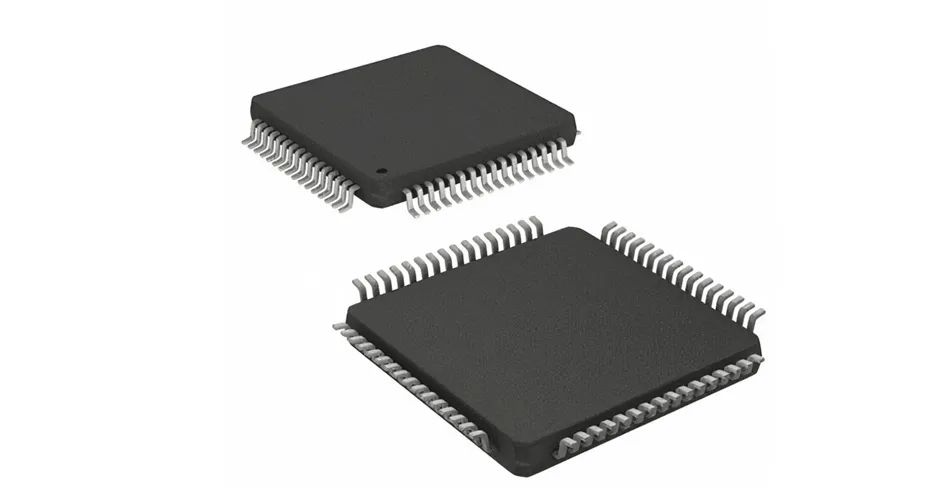
QFP Package
There are three types of substrates: ceramic, metal and plastic. In terms of quantity, plastic packages account for the vast majority. When the material is not specifically indicated, most cases are plastic QFP. Plastic QFP is the most popular multi-pin LSI package, which is not only used for digital logic LSI circuits such as microprocessors and gate arrays, but also for analog LSI circuits such as VTR signal processing and audio signal processing.
The pin center distance has multiple specifications such as 1.0mm, 0.8mm, 0.65mm, 0.5mm, 0.4mm, 0.3mm, etc. The maximum number of pins in the 0.65mm center distance specification is 304.
The above are the 9 common component packaging technologies in PCBA processing shared by iPCB.