What is a millimetre wave radar?
Millimetre wave refers to electromagnetic waves with a wavelength between 1-10mm. The wavelength is short and the frequency band is wide. It is relatively easy to realise the narrow beam, and the radar has high resolution and is not easily disturbed. Millimetre wave radar is a high-precision sensor to measure the relative distance, current speed and orientation of the object to be measured, which was used in the military field in the early days. With the development and advancement of radar technology, millimetre wave radar sensors are beginning to be applied in the fields of automotive electronics and drones, intelligent transport and so on.
At present, the frequency bands allocated to automotive millimetre wave radar vary from country to country, but mainly focus on 24GHz and 77GHz, with a few countries (e.g. Japan) adopting the 60GHz frequency band. Due to the many advantages of 77G over 24G, the global automotive millimetre wave radar frequency band will converge to 77GHz (76-81GHz) in the future. Principle of Automotive Millimetre Wave Radar Automotive millimetre wave radar transmits millimetre wave through the antenna, receives the reflected signals from the target, and then quickly and accurately obtains the information of the physical environment around the car body (such as the relative distance between the car and other objects, relative speed, angle, direction of movement, etc.) through the back-end processing, and then performs the target tracking and classification based on the detected information of the objects, and then combines with the dynamic information of the car body for data fusion. Then, based on the detected object information, target tracking and identification classification are carried out, combined with the dynamic information of the vehicle body, data fusion is carried out, and finally, intelligent processing is carried out through the central processing unit (ECU). After reasonable decision-making, it notifies or warns the driver through sound, light, touch, etc., or intervenes in the car in a timely manner to ensure the safety and comfort of the driving process and reduce the probability of accidents.
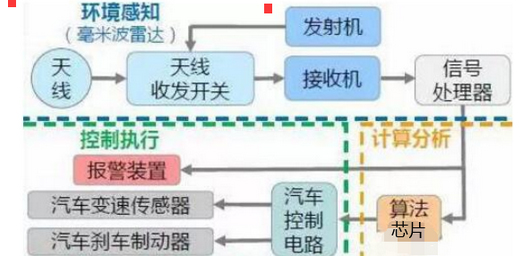
Principle of Millimetre Wave Radar for Vehicles
According to the different ways of radiating electromagnetic waves, millimetre wave radars mainly have two operating systems: pulsed system and continuous wave system. Among them, continuous wave can be divided into FSK (Frequency Shift Keying), PSK (Phase Shift Keying), CW (Constant Frequency Continuous Wave), FMCW (Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave) and so on.
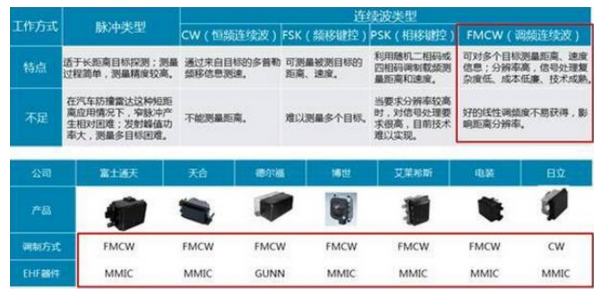
Millimetre wave radar working system
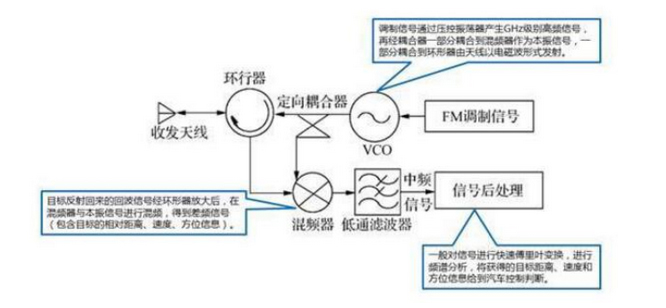
FWCW radar has become the most commonly used automotive millimetre wave radar due to its ability to measure multiple targets, high resolution, low complexity of signal processing, low cost and mature technology.The FMCW radar system mainly consists of a transceiver antenna, a radio frequency front-end, a modulation signal, a signal processing module, etc. The FMCW radar system can detect the distance, bearing, relative speed, etc. of a target by processing the received and transmitted signals. The millimetre wave radar can detect the distance, bearing and relative speed of the target through the processing of the received and transmitted signals.
>
Automotive Millimetre Wave Radar
Current Development of Millimetre Wave Radar
At present, there are two main types of millimetre wave radar: 24GHz and 77GHz. The 24GHz radar has a short measuring range (5-30m) and is mainly used at the rear of vehicles; the 77GHz radar has a longer measuring range (30-70m) and is mainly used at the front and side of vehicles. Millimetre wave radar mainly includes three parts: radar RF front-end, signal processing system and back-end algorithm. In the existing products, the patent licence fee of the radar back-end algorithm accounts for about 50% of the cost, the RF front-end accounts for about 40% of the cost, and the signal processing system accounts for about 10% of the cost.
1.The RF front-end obtains the IF signal by transmitting and receiving millimetre waves, and extracts information such as distance and speed from it. Therefore, the RF front-end directly determines the performance of the radar system. At present, the RF front-end of millimetre wave radar is mainly a planar integrated circuit, with two forms of hybrid microwave integrated circuit (HMIC) and monolithic microwave integrated circuit (MMIC). Among them, the MMIC form of RF front-end has low cost, high yield, and is suitable for mass production. In the production process, generally use epitaxial MESFET, HEMT, HBT and other device technology. GaAs-based HEMT process is the most mature, excellent noise performance.
2.The signal processing system is also an important part of the radar. By embedding different signal processing algorithms, it extracts the IF signal collected from the RF front-end and obtains specific types of target information. The signal processing system generally uses DSP as the core to implement complex digital signal processing algorithms to meet the real-time requirements of the radar.
3.The back-end algorithm accounts for the highest proportion of the cost of the entire millimetre wave radar.Domestic researchers have proposed a large number of algorithms for millimetre wave radar from various perspectives, such as frequency domain, time domain, time-frequency analysis, etc., and the accuracy rate of offline experiments is also very high.However,domestic radar products are mainly analysed by fast Fourier transform and its improved algorithms based on the frequency domain. There are some limitations in measurement accuracy and applicability, and the foreign algorithms are strictly protected by patents and are expensive.

Automotive Millimetre Wave Radar
Automotive millimetre wave radar applications
1.Millimetre wave radar can realise various functions of automatic driving.The sensors used in ADAS are mainly cameras, millimetre-wave radar, laser, ultrasonic, infrared, etc. Millimetre-wave radar has a long transmission distance, small attenuation and loss of atmospheric attenuation within the transmission window,and strong penetration.It can meet the requirement of all weather weather adaptability of vehicles. The characteristics of millimetre wave itself determines the millimetre wave radar sensor device size is small, light weight and other characteristics.Compensate for the camera, laser, ultrasonic, infrared and other sensors in automotive applications do not have the use of the scene.
By installing a millimetre-wave radar in a vehicle,it is possible to measure the distance,angle and relative speed from the radar to the object under test.Millimetre wave radar can be used to achieve self-adjusting cruise control (AdaptiveCruiseControl), forward collision warning (ForwardCollisionWarning), blind spot detection (BlindSpotDetection), parking assistance (Parkingaid), lanechangeassistant,Lanechange assistants (Lanechangeassistant), and other functions. Parkingaid, Lanechangeassistant, Automatic Cruise Control (ACC) and other Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) features.The more common automotive millimetre wave radars operate at frequencies around 24GHz and 77GH. The 24GHz radar system mainly realises short-range detection (SRR),while the 77GHz system mainly realises remote detection (LRR).
2.Millimetre wave radar has a wide market space. Due to the continuous improvement of national automobile safety standards, the active safety technology Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) has shown a rapid development trend in recent years. Automotive millimetre wave radar has been recognised as a mainstream choice by automotive electronics manufacturers due to its all-weather capability, and has huge market demand. In 2014, the global automotive millimetre wave radar market shipped 19 million units. According to market research organisations, the global automotive millimetre wave radar market will reach nearly 70 million units by 2020, with a CAGR of about 24% from 2015 to 2020.
As automotive millimetre wave radar transmits and receives signals at 24GHz and 77GHz, millimetre wave radar circuit boards include clocks, signal modulation, amplifiers, filters, antennas and other parts, which have higher requirements on circuit boards and manufacturing processes. Therefore, millimetre wave radar circuit boards will bring higher value. High-frequency PCBs often require PTFE-filled ceramic and glass materials to meet design requirements above 77GHz.
Above is to take you to understand what is the millimetre wave radar, according to the characteristics of millimetre wave radar, millimetre wave radar is easy to meet the automotive needs. To understand the circuit board of automotive millimetre wave radar, please click: Automotive millimetre wave radar 1, Automotive millimetre wave radar 2.