The most important application of RF circuits is wireless communication, RF circuits mainly include receivers and transmitters.
Transmitter: baseband signal - modulation - amplifier frequency converter (mixer) - amplifier - antenna
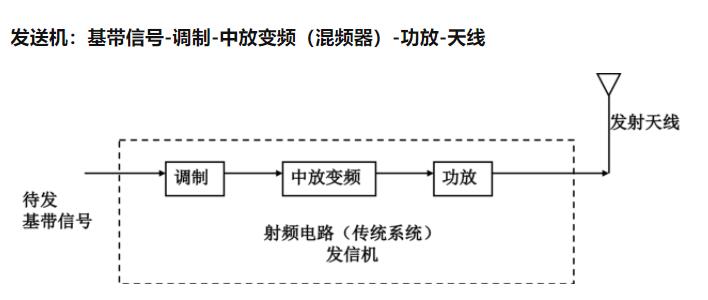
Modulation: This is the process of modulating the baseband signal onto the communication carrier. In some applications, there are other steps such as encryption of the baseband signal.
Amplifier: In this step, basic amplification of the modulated signal is performed to frequency the signal to the actual communication frequency band.
Amplifier: The main purpose is to amplify the signal power to meet the communication (distance) requirements.
Transmitting Antenna: Transmit the signal effectively, in addition to the transmission power (efficiency), and sometimes the direction, as well as the choice of wave propagation channels.
As far as the hardware circuit system of the transmission system is concerned, the most difficult part lies in the intermediate amplifier frequency converter and RF amplifier. The main difficulty lies in the design of the frequency converter system solution. A good system solution design produces less interference and may even reduce the requirement for a local oscillator signal to participate in the frequency conversion. RF amplifiers are mainly concerned with power efficiency and linearity.
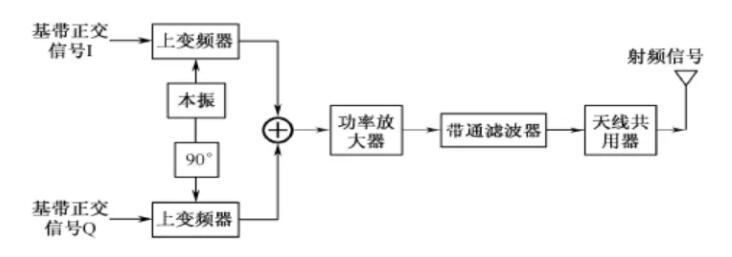
Directly Transformable Quadrature Modulated Transmitter
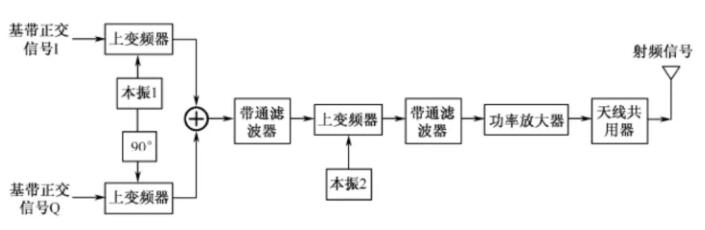
Two-step change of quadrature modulation transmitter
Transmitter: Average transmit power, RF carrier network, RF power control, RF output spectrum, spurious radiation.
Receiver: Antenna - Frequency Selection Amplifier - Intermediate Amplifier - Demodulation - Baseband Signal
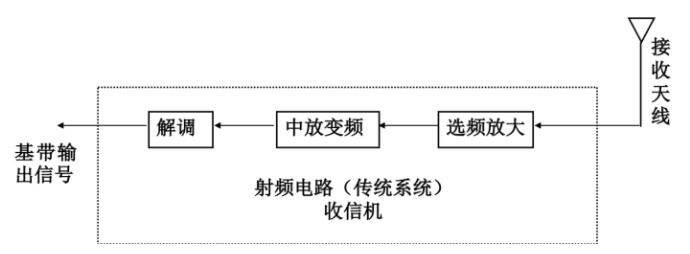
Frequency Selection Amplification: Selects a useful signal from a large number of radio waves and amplifies the weak signal to the level required by the demodulator.
Downconversion: Move the RF signal to the desired frequency band.
Demodulation: Moving the RF signal to the desired frequency band.
Receiving can be thought of as the inverse of transmitting. The most difficult part of a receiving system is the front end. The space is full of all kinds of electromagnetic signals, and useful signals are among them. It is difficult to receive useful signals efficiently and at the same time suppress useless signals as much as possible. Receiver to complete the main function is to select the useful signals received from the antenna, under the frequency converter amplified to the baseband by the demodulator demodulation, to achieve the conversion of band signals to baseband signals.
Common receiver structures include: super-aberrant structure, direct down converter structure (zero IF structure), low IF structure, etc.
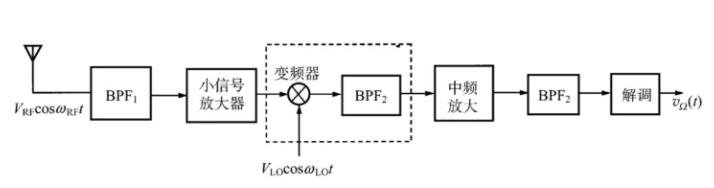
RF front-end module: RF low noise amplification, frequency band selection.
Frequency converter function: Reduce the received RF frequency to a fixed IF frequency without distortion. Features of frequency converter: Frequency reduction, spectrum structure remains unchanged. Reasons for frequency reduction: 1. To solve the selectivity, the RF band is very difficult to select the channel (the requirement of the filter Q value is very high), the antique products reduce the frequency to select the channel. 2. 2. In order to make the receiver reach a stable high gain. Total gain = RF gain + mixing gain + IF gain, so that the gain is spread out in each frequency band, easy to be stable; IF gain frequency is low and fixed, easy to gain and stable. 3. It is relatively easy to demodulate or modulate on the lower fixed IF frequency.
IF module: selective channel, main gain stage.
Disadvantage: Inverter introduces numerous combinations of frequency interference (mirror frequency interference).
Advantages and disadvantages of high IF and low IF: High IF: Mirror frequency is far away from the useful signal, easy to filter, good for anti-interference. Low MF: Under the same Q condition, MF filter is narrow band, which is good for selecting channel and stable high gain.