Since Huawei developed the high-speed, high-capacity next-generation communication standard ‘5G’, with the launch of 5G-compatible smartphones, it began to really come into our lives. So let's learn about the difference between 5G high-frequency and millimetre-wave radar, the changing pipeline of PCBs in the 5G industry, and PCB circuit boards for various applications.
1.What is the next generation of 5G communication standards?
5G has the following three main changes:
(1) multiple simultaneous connections;
(2) ultra-high speed and large capacity;
3) low latency.
Compared with 4G, the communication speed is 20 times, the delay is 1/10, and the number of simultaneous connections is 10 times. (4G is 15 times faster than 3G. I thought 4G was fast at the time).
5G is too fast for previous standards. The key is the ability to do high-capacity communications and multiple connections without delay. This will enable remote healthcare, high-definition VR games and movies, massive sensor information and image processing, autonomous driving and smart cities.
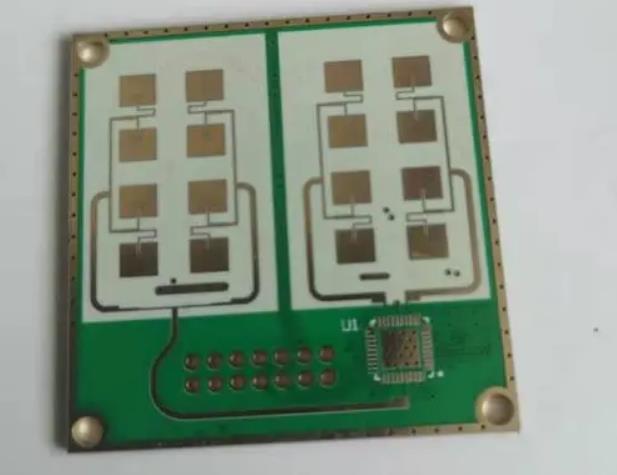
Millimetre wave radar
2.High frequency and the difference between 5G and millimetre wave radar
The frequency band used for 5G communications and the frequency band called millimetre wave are both high frequency. The frequency bands used for 5G are divided into Sub6 and millimetre wave. Sub6 is a frequency band below 6GHz, which can be realised by applying the same communication technology as 4G (LTE, Wi-Fi). However, there is no significant enhancement of ultra-high-speed, high-capacity communications in the Sub6 band.
The characteristics of ultra-high speed and high capacity are attributed to the characteristics of the millimetre wave band.
Generally speaking, millimetre wave is more than 30GHz frequency, but because the 28GHz 5G communication band is close to millimetre wave, so it is indiscriminately called millimetre wave.
3.Alternative Materials for High Frequency Circuit Substrates
In order to meet the millimetre wave range,the dielectric loss of the insulating material must be reduced.Dielectric loss is the loss of energy as heat when an alternating current field is applied to a dielectric, which results in signal degradation.Especially in the millimetre-wave region, signal degradation due to dielectric loss has a significant impact, and the selection of insulation materials for printed circuit boards is therefore very important.
Fluorocarbon resins are representative of resins with low transmission losses and are well known as Teflon and PTFE. It has excellent heat, humidity and chemical resistance, but it is too hard to be processed in the manufacture of printed circuit boards. LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer) is another material with low transmission losses, but it suffers from high thermoplasticity and defects due to high-temperature processing during board manufacturing.
Currently, various companies are developing resin materials with low transmission loss in the millimetre wave region.
For example, Panasonic's MEGTRON6 is used as a substrate for CCL (copper-clad laminate) and has better processability than Teflon in the substrate manufacturing process.
Even for products that support high frequencies, it is not necessary to use the low-transmission-loss materials described above for the entire insulation layer of the printed circuit board. One option is to use only the high frequency circuit layers or only the part of the RF module that emits radio waves as the substrate for the transmission loss.
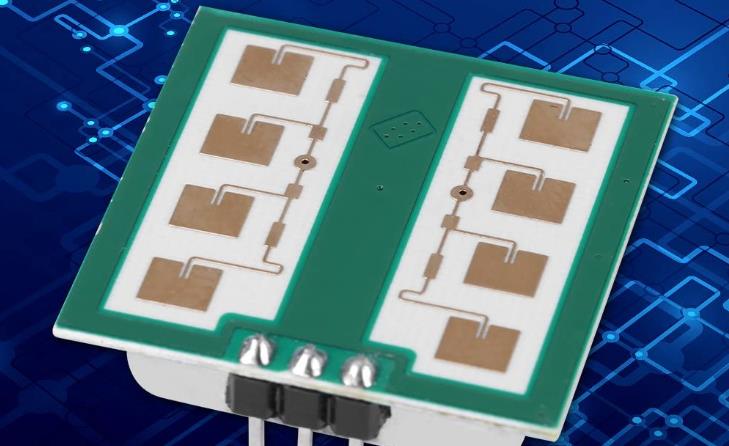
Millimetre wave radar
4.What kind of circuit boards are used for 5G communication?
Circuit boards are used in base stations for transmitting and receiving 5G radio waves, 5G smartphones, various monitoring sensors for smart cities, and radar for autonomous driving. Most of the base station boards are high flux through-hole boards with multiple insulation and pattern layers, RF modules for 5G communication are installed in 5G smartphones and surveillance sensors, and high frequency circuit boards are usually of ultra-high density with any laminate specification. Most radars for autonomous driving have relatively large combined board specifications.
5.Conclusion
For high-frequency applications, as of 2020, there are more parts involved in the research phase, and some areas do not have a clear direction yet. However, with the practical application of 5G communications around the world, we expect many products to be commercialised at a much faster pace. By the time the base station infrastructure is ready, I think all devices are equipped with 5G communication modules, which will provide us with a more convenient life.