In recent years, the market demand for high-layer boards for application communication, base station, aviation, military and other fields is still strong, and with the rapid development of China's telecommunication equipment market, the outlook for the high-layer board market is favourable.
At present, the domestic PCB manufacturers that can mass produce high-level circuit boards mainly come from foreign-invested enterprises or a few domestic enterprises. The production of high-layer circuit boards not only requires high technology and equipment investment, but also requires the accumulation of experience of technicians and production personnel, and at the same time, the introduction of high-level boards customer certification procedures are stringent and cumbersome, so the high-level circuit boards to enter the enterprise threshold is relatively high, and achieve industrialised production cycle is relatively long.
The average number of PCB layers has become an important technical indicator to measure the technical level and product structure of PCB enterprises. This article briefly describes the main processing difficulties encountered in the production of high-level circuit boards, introduces the control of key production processes of high-level circuit boards for your reference.
1.Main Production Difficulties
Compared with conventional circuit boards, high level circuit boards have the characteristics of thicker boards, more layers, denser wires and holes, larger unit size, thinner dielectric layers, etc., and the requirements for inner layer space, interlayer accuracy, impedance control, and reliability are even more stringent.
1.1 Difficulty of Interlayer Alignment
Due to the large number of layers in the high layer circuit board, the customer design side of the PCB layer alignment requirements are becoming more and more stringent, usually interlayer alignment tolerance control ± 75μm, taking into account the design of the high-layer board unit size is larger, the graphic transfer workshop environment temperature and humidity, as well as the inconsistency of the expansion and contraction of different core board layers brought about by the mismatch of the overlap, the interlayer positioning method and other factors, so that the high-layer board of the interlayer alignment control is more difficult.
1.2 Difficulties of inner layer circuit production
High-layer boards use high TG, high-speed, high-frequency, thick copper,thin dielectric layer and other special materials, the inner circuit production and graphic size control puts forward high requirements, such as impedance signal transmission integrity, increasing the difficulty of the inner circuit production.Line width line spacing is small, open short circuit increases, micro-short increase,low pass rate; fine line signal layer is more, the inner AOI leakage rate increases; inner core plate thickness is relatively thin, easy to wrinkle resulting in poor exposure,etching through the machine is easy to roll the plate; high-level boards are mostly system boards, the unit size is larger, in the finished product scrapped at a relatively high cost.
1.3 Pressing production difficulties
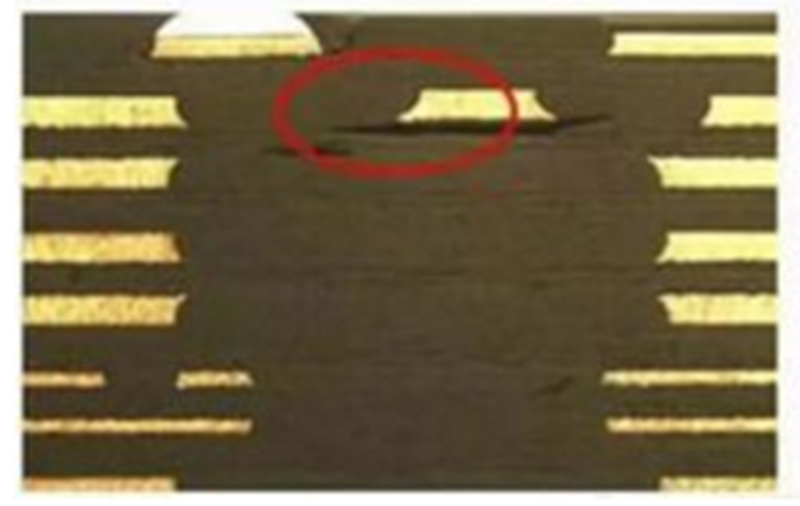
Multiple inner core board and semi-cured sheet superposition,compression production is prone to slip,delamination, resin voids and air bubble residue and other defects.When designing the laminated structure, it is necessary to fully consider the material's heat resistance, voltage resistance,adhesive filler and dielectric thickness,and to set up a reasonable lamination programme for the high-layer boards.If the number of layers is large, the shrinkage control and dimensional coefficient compensation cannot be maintained consistently,the thin insulation layer between layers may easily lead to interlayer reliability test failure.Fig.1 shows the defects of delamination of the exploded board after the heat stress test.
1.4 Difficulties in drilling production
The use of high TG, high speed, high frequency, thick copper special plate, increasing the roughness of the drilled holes, drilling burrs and decontamination of the drilling difficulty. The high number of layers, total copper thickness and plate thickness make the drilling easy to break; the high density of BGAs and the narrow hole wall spacing cause CAF failure problems; and the plate thickness easily leads to skewed drilling problems.
2.Critical Production Process Control
2.1 Material Selection
With the development of high performance and multi-functional direction of electronic components, and at the same time bring high-frequency, high-speed development of signal transmission, so the requirements of electronic circuit materials with lower dielectric constant and dielectric loss ratio, as well as low CTE, low water absorption and better high-performance laminating materials to meet the processing and reliability requirements of high-level boards. Commonly used board suppliers are A series, B series, C series, D series, the main characteristics of these four types of inner layer substrate comparison, see Table 1, for the high level of thick copper circuit boards with high resin content of the semi-cured sheet, the interlayer semi-cured sheet of the amount of flow of glue is sufficient to fill the inner layer of the pattern, the insulating dielectric layer is too thick easy to appear in the finished product boards over-thickness, and vice versa, the insulating dielectric layer thin, then it is easy to cause the dielectric delamination, high voltage test failure and other quality problems, so the insulating dielectric layer is too thick, so it is easy to be used for the high level of the boards, so the insulating dielectric layer is too thick. Quality problems, so the choice of insulating dielectric material is very important.
2.2 Compression laminated structure design
The main factors to be considered in the laminated structure design are the heat resistance of the material, voltage resistance, the amount of filler and the thickness of the dielectric layer, etc. The following main principles should be followed.
(1) The semi-cured sheet must be consistent with the core board manufacturer. In order to ensure the reliability of the PCB, all layers of half-cured sheet to avoid the use of a single 1080 or 106 half-cured sheet (except for special customer requirements), the customer does not dielectric thickness requirements, the thickness of the dielectric between the layers must be in accordance with the IPC-A-600G to ensure that ≥ 0.09mm.
(2), when customers require high TG boards, core boards and semi-cured sheets should be made of corresponding high TG materials.
(3), the inner substrate 3OZ or more, select high resin content of the semi-cured sheet, such as 1080R / C65%, 1080HR / C 68%, 106R / C 73%, 106HR / C76%; but as far as possible to avoid the use of all the 106 high adhesive semi-cured sheet structure design, in order to prevent a number of 106 semi-cured sheet stacked, due to the glass fibre yarn is too thin, glass fibre yarn in the large substrate area collapse and affect the dimensional stability and burst board delamination.
(4), if the customer does not have special requirements, the interlayer dielectric layer thickness tolerance is generally controlled by +/-10%, for impedance board, dielectric thickness tolerance according to IPC-4101 C / M tolerance control, if the impedance factors related to the thickness of the substrate, then the plate tolerance must also be according to the IPC-4101 C / M tolerance.
2.3 Control of interlayer accuracy
The accuracy of the inner core board size compensation and production size control, need to be collected through a certain period of time in the production of data and historical data experience, the high layer of the board of the various layers of graphic dimensions of the precise compensation, to ensure the consistency of the various layers of the core board expansion and contraction. Select high-precision and highly reliable inter-layer positioning methods before lamination, such as four-slot positioning (Pin LAM), hot melting and riveting combination. Setting up proper lamination process and routine maintenance of the press is the key to ensure the quality of lamination, controlling the flow of glue and cooling effect of lamination, and reducing the problem of interlayer misalignment. The control of layer alignment needs to be based on a combination of factors such as the inner layer compensation value, press positioning method, press process parameters, and material properties.
2.4 Inner Layer Circuit Process
Since the resolving power of traditional exposure machine is around 50μm, for the production of high layer circuit boards, a laser direct imaging (LDI) machine can be introduced to improve the graphic resolving power to around 20μm. The alignment accuracy of traditional exposure machine is ±25μm, and the interlayer alignment accuracy is more than 50μm; by adopting high precision parity exposure machine, the graphic parity can be increased to about 15μm, and the interlayer alignment accuracy can be controlled within 30μm, which reduces the deviation of parity of the traditional equipment, and improves the interlayer alignment accuracy of the high-layer boards.
In order to improve the line etching capability, it is necessary to give appropriate compensation for the width of the line and the soldering disc (or soldering ring) in the engineering design, and it is also necessary to make more detailed design consideration for the amount of compensation for special patterns, such as the return type line, independent line, and so on. Confirm the inner layer line width, line spacing, isolation ring size, independent line, hole to line distance design compensation is reasonable, otherwise change the engineering design. There are impedance, inductive design requirements to pay attention to the independent line, impedance line design compensation is sufficient, etching control parameters, the first piece of confirmation before mass production. In order to reduce the etching side corrosion, need to etching solution of each group of water composition control in the optimal range. Traditional etching line equipment etching capacity is insufficient, the equipment can be technically modified or imported into the high-precision etching line equipment to improve etching uniformity and reduce the problem of etching burrs, etching is not clean and so on.
2.5 Pressing technology
At present, the interlayer positioning methods before pressing mainly include: four-slot positioning (Pin LAM), hot melt, rivets, hot melt and rivets combined with different product structure using different positioning methods. For high layer boards, we adopt four-slot positioning method (Pin LAM), or use fusing + riveting method, OPE punching machine punches out the positioning holes, and the punching accuracy is controlled at ±25 μm. X-RAY checking of layer deviation is required for the first board to be adjusted in fusing, and the batch can only be made if the layer deviation is qualified,and each board is required to be checked whether it is fused into the unit during the batch production in order to prevent subsequent delamination, and the high performance matching press is adopted for the press equipment to satisfy the requirements of high layer circuit boards, and to meet the requirements of different product structures. The laminating equipment adopts high-performance matching presses to satisfy the precision and reliability of inter-layer alignment of high-layer boards.
According to the laminated structure of the high-layer boards and the materials used, we will study the suitable laminating programme and set the optimal heating rate and curve. On the conventional laminating programme for multi-layer circuit boards,we will appropriately reduce the heating rate of the laminating boards and prolong the high-temperature curing time, so as to enable the resin to fully flow and cure, and at the same time to avoid slipping of the boards and misalignment of the layers in the process of laminating.The boards with different TG values cannot be lined up in the same furnace; the boards with common parameters cannot be mixed with the boards with special parameters; the reasonableness of the deflation coefficient is guaranteed; the properties of different boards and semi-cured sheets are not the same, so it is necessary to press the boards and semi-cured sheets with the corresponding parameters; the special materials that have never been used before need to be verified for the technological parameters.
2.6 Drilling process
Due to the superposition of layers,the plate and copper layer are super thick,which causes serious wear to the drill bit and easily breaks the drill cutter, so the number of holes, the falling speed and the rotational speed are appropriately adjusted downwards. Precise measurement of board expansion and contraction to provide accurate coefficients; number of layers ≥ 14 layers, hole diameter ≤ 0.2mm or hole to line distance ≤ 0.175mm, using hole precision ≤ 0.025mm drilling machine production;diameter φ4.0mm or more holes using step-by-step drilling, thickness to diameter ratio of 12:1 by using step-by-step drilling, positive and negative drilling method of production; control of drilling phi and hole thickness, high-level boards,as far as possible,using a brand new drill cutter or grinding 1 drill cutter drilling holes, hole number and rotation speed appropriately adjusted downward. The hole thickness is controlled to be within 25um. In order to improve the drilling burr problem of high-level thick copper plate, after batch verification, the use of high-density pads, the number of stacked boards is one, and the number of drill sharpening times is controlled to be within 3 times, which can effectively improve the drilling burr, as shown in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3.
For high-frequency, high-speed, massive data transmission with the high level circuit board, back drilling technology is to improve the signal integrity and effective methods. Back drilling is mainly used to control the length of residual stubs, the consistency of the hole position between two drilled holes, and the copper wire inside the holes, etc. Not all drilling machines have the capability of drilling the holes in the same way. Not all drilling machines have back-drilling capability. It is necessary to upgrade drilling machines (with back-drilling capability) or purchase drilling machines with back-drilling capability. Back drilling techniques from industry literature and mature mass production applications include: traditional depth control back drilling methods, back drilling of the inner layer as a signal feedback layer, and back drilling of the depth of the board proportionally to the thickness of the board, which will not be repeated here.
3.Reliability Test
High layer circuit boards are generally system boards, which are thicker and heavier than conventional multi-layer boards, with larger unit sizes, and correspondingly larger heat capacities, which require more heat when soldering and experience longer soldering times at higher temperatures. At 217°C (the melting point of tin-silver-copper solder) it takes 50 seconds to 90 seconds, and at the same time, the cooling speed of the high-layer board is relatively slow, so the time for the reflow test is prolonged, and combined with the IPC-6012C, IPC-TM-650 standard and the industry's requirements, the main reliability test for high-layer boards.